User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Document history
- Introduction
- Product concept
- Application Interface
- Antenna interface
- Electrical, reliability and radio characteristics
- Mechanics
- Reference Approval
- Design example
- List of parts and accessories

MC55/56 Hardware Interface Description
Confidential / Preliminary
s
MC55/56_hd_v03.00 Page 101 of 104 16.08.2005
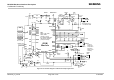
8 Design example
Figure 45 shows a sample application that incorporates an MC55/56 module and an external
µController. This solution is typical of devices designed for audio and GSM capability, such
as mobile phones, PDAs, Tablet PCs etc.
The audio part is made of internal transducers (earpiece and microphone) and integrates an
additional interface for connecting an external headset. This interface detects the presence
of a plugged headset and verifies whether the headset key (push-to-talk key) is pressed.
The charging circuit is designed to ensure trickle charging that takes effect when the battery
is deeply discharged. Used components: 100
Ω series resistance, Z diode 4V3, 1SS355
diode. If the charger supplies a voltage from 5.5V to 8V this arrangement will deliver an
overall current of approx. 15mA (5.5V) to 37mA (8V) for trickle charging and
for the
application. If the application circuit draws a greater current another LDO (Low Dropout
Regulator) can be added to allow for an additional parallel power supply dedicated to the
application. This LDO can be connected between the positive charger input and the 3V
power supply source.
Caution: Trickle charging is done when the voltage of the Li-Ion battery is below 3.2V.
High level of the VDD line indicates that the MC55/56 module is active.
While MC55/56 is in POWER DOWN mode the application interface is switched off and must
not be fed from any other source. Therefore, the application must be designed to avoid any
current flow into any digital pins of the application interface.
The RING0 line notifies, primarily, incoming calls. Therefore, if connected with an interrupt of
the application µController, the RING0 line can be effectively used to wake up the application
µController from power saving.
The test points (referred to as “TPx”) can be used for downloading firmware to the MC55/56
module.
TP0: GND
TP1: Data transfer from MC55/56
TP2: Data transfer to MC55/56
TP3: Starts up MC55/56 (high active)
The EMC measures are best practice recommendations. In fact, an adequate EMC strategy
for an individual application is very much determined by the overall layout and, especially,
the position of components. For example, mounting the internal acoustic transducers directly
on the PCB eliminates the need to use the ferrite beads shown in the sample schematic.
Disclaimer
No warranty, either stated or implied, is provided on the sample schematic diagram shown in
Figure 45 and the information detailed in this section. As functionality and compliance with
national regulations depend to a great amount on the used electronic components and the
individual application layout manufacturers are required to ensure adequate design and
operating safeguards for their products using MC55/56 modules.