User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Document History
- Introduction
- Product concept
- Application Interface
- Antenna interface
- Electrical, reliability and radio characteristics
- Mechanics
- Reference Approval
- List of parts and accessories
MC46 Hardware Interface Description
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
MC46_HD_V03.05 Page 91 of 99 13.11.2003
6.2 Mounting MC46 onto the application platform
There are many ways to properly install MC46 in the host device. An efficient approach is to
mount the MC46 PCB to a frame, plate, rack or chassis.
Fasteners can be M1.6 or M1.8 screws plus suitable washers, circuit board spacers, or
customized screws, clamps, or brackets. Screws must be inserted with the screw head on
the bottom of the MC46 PCB. This is necessary to avoid contacting the shielding covers on
top.
In addition, the board-to-board connection can also be utilized to achieve better support.
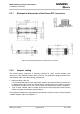
A number of ground planes are provided on the bottom of the MC46 module, all of them
illustrated in Figure 40. For proper grounding it is strongly recommended to use these
ground planes in addition to the five GND pins of the board-to-board connector. To avoid
short circuits ensure that the remaining sections of the MC46 PCB do not come into contact
with the host device since there are a number of test points. The largest ground pad in the
middle of the board can also be used to attach cooling elements, e.g. a heat sink or
thermally conductive tape. Refer to Chapter 6.4 for an overview on a variety of cooling
elements.
Particular attention should be paid to the test point TP 402. Placed beneath the large ground
pad it has been added for manufacturing only. When the pad is used for grounding the unit
or connecting a heat sink, extra care must be taken not to contact this test point. Figure 40
shows the positions of all test points.
To prevent mechanical damage, be careful not to force, bend or twist the module. Be sure it
is positioned flat against the host device.
All the information you need to install an antenna is summarized in Chapter 4. Note that the
antenna pad on the bottom of the MC46 PCB must not be influenced by any other PCBs,
components or by the housing of the host device. It needs to be surrounded by a restricted
space as described in Chapter 4.1.