Pilot's Guide
190-00663-02 Rev. B
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Hawker Beechcraft C90A/GT/GTi
329
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
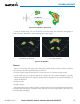
6.2 AIRBORNE COLOR WEATHER RADAR
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
TheGarminGWX68AirborneColorWeatherRadarisafour-colordigitalpulsedradarwith6.5kilowatts
ofoutputpower.Itcombinesexcellentrangeandadjustablescanningproleswithahigh-denitiontarget
display.Thepulsewidthisfourmicroseconds(µs)onallrangesexceptthe2.5nmrange.TheGWX68usesa
oneµspulsewidthatthisrangetoreducethetargetssmearingtogetheronthedisplayforbettertargetdenition
at close range.
TheKingAir300/B300Seriesusesa12-inchphasedarrayantennathatisfullystabilizedtoaccommodate30º
of pitch and roll.
Tofocusradarscanningonspecicareas,SectorScanningofferspilot-adjustablehorizontalscananglesof
20º,40º,60º,or90º.Averticalscanningfunctionhelpstoanalyzestormtops,gradients,andcellbuildup
activity at various altitudes.
Radarfeaturesinclude:
•ExtendedSensitivityTimeConstant(STC)logicthatautomaticallycorrelatesdistanceofthereturnechowith
intensity, so cells do not suddenly appear to get larger as they get closer.
•WATCH™(WeatherATtenuatedColorHighlight)helpsidentifypossibleshadowingeffectsofshort-range
cellactivity,identifyingareaswhereradarreturnsignalsareweakenedorattenuatedbyintenseprecipitation
(orlargeareasoflesserprecipitation)andmaynotfullyreecttheweatherbehindastorm.
•WeatherAlertthatlooksaheadforintensecellactivityinthe80-320nmrange,eveniftheserangesarenot
being monitored.
PRINCIPLES OF PULSED AIRBORNE WEATHER RADAR
ThetermRADARisanacronymforRAdioDetectingAndRanging.Pulsedradarlocatestargetsbytransmitting
amicrowavepulsebeamthat,uponencounteringatarget,isreectedbacktotheradarreceiverasareturn
echo.Themicrowavepulsesarefocusedandradiatedbytheantenna,withthemostintenseenergyinthe
centerofthebeamanddecreasingintensityneartheedge.Thesameantennaisusedforbothtransmittingand
receiving.TheG1000processesthereturnedsignalanddisplaysitontheMFD.
Radardetectionisatwo-wayprocessthatrequires12.36µsforthetransmittedmicrowavepulsestotravelout
andbackforeachnauticalmileoftargetrange.Ittakes123.6µsforatransmittedpulsetomaketheroundtrip
if a target is ten nautical miles away.
Airborneweatherradarshouldbeusedtoavoidsevereweather, notfor penetratingsevereweather.The
decision to fly into an area of radar targets depends on target intensity, spacing between the targets, aircraft
capabilities, and pilot experience. Pulse type weather radar detects only precipitation, not clouds or turbulence.
Thedisplaymayindicateclearareasbetweenintensereturns,butthisdoesnotnecessarilymeanitissafetoy
betweenthem.OnlyDopplerradarcandetectturbulence.
Airborneweatherradarhasothercapabilitiesbeyondweatherdetection.Italsohastheabilitytodetectand
providedistancetocities,mountains,coastlines,rivers,lakes,andoceans.