User Guide
190-00592-01 Rev. A
Garmin G1000 Pilot’s Guide for the Diamond DA40/40F
6-27
HAZARD AVOIDANCE
6.2 TERRAIN PROXIMITY
CAUTION: Do not use Terrain Proximity information for primary terrain avoidance. Terrain Proximity is
intended only to enhance situational awareness. It is the pilot’s responsibility to provide terrain avoidance
at all times.
NOTE: Terrain Proximity data is not displayed when the aircraft latitude is greater than 75
°
North or 60
°
South.
G1000 Terrain Proximity is a non-TSO-C151b-certified terrain awareness system. It increases situational
awareness and aids in reducing controlled flight into terrain (CFIT).
Do not confuse Terrain Proximity with Terrain Awareness and Warning System (TAWS). TAWS is more
sophisticated and robust, and is TSO-C151b-certified. Terrain Proximity does not provide warning annunciations
or voice alerts. It only provides color indications on map displays when terrain and obstacles are within a certain
altitude threshold from the aircraft. Although the terrain and obstacle color map displays are the same, TAWS
uses more sophisticated algorithms to assess aircraft distance from terrain and obstacles.
Terrain Proximity requires the following components to operate properly:
• Valid 3D GPS position
• Valid terrain/obstacle database
The G1000 GPS receiver provides the horizontal position and altitude. GPS altitude is derived from satellite
position. GPS altitude is then converted to a mean sea level (MSL) based altitude (GPS-MSL altitude) and is used
to determine terrain and obstacle proximity. GPS-MSL altitude accuracy is affected by satellite geometry but is not
subject to variations in pressure and temperature that normally affect pressure altitude sensors. GPS-MSL altitude
does not require local altimeter settings to determine MSL altitude. It is a reliable MSL altitude source.
Terrain and obstacle databases are referenced to MSL. Using the GPS position and altitude, the Terrain Proximity
feature portrays a 2D picture of the surrounding terrain and obstacles relative to the position and altitude of the
aircraft. GPS position and GPS-MSL altitude are used to calculate and predict the aircraft’s flight path in relation
to the surrounding terrain and obstacles. In this way, the pilot can view predicted dangerous terrain and obstacle
conditions.
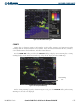
Terrain elevation is shown relative to the aircraft altitude in Figure 6-39. Obstacle symbols and colors are given
in Table 6-3. Terrain and obstacles that are above the aircraft or less than 100 feet below the aircraft altitude are
shown in red. Those between 100 feet and 1000 feet below the aircraft altitude are shown in yellow. Terrain
lower than 1000 feet below the aircraft altitude is shown in black. Obstacle data is displayed in gray when the
difference in aircraft altitude and obstacle height is greater than 1000 feet.