User's Manual
40
6.2 Web Cache
Cache is the so-called Proxy Network Service System. All of the webpages that users
access via the Internet are handled by cache, enabling clients to hide their IP addresses,
reducing the traffic and managing accesses. It has the basic firewall functions and can
accelerate the transmission of webpages and FTP.
Squid is one the commonly used cache services, with configuration file located at
/usr/local/etc/squid/squid.conf. It allows a number of parameters to be configured. For
your reference, the parameters listed in the Service Interface here are merely those
frequently used, while the rest are automatically configured by the system for you. If you
want to edit these parameters yourself, please edit the file located at
/usr/local/etc/squid/squid.conf and then have the management Interface read the
parameters all over again. (However, you are advised not to edit parameters yourself.)
6.2.1 Steps of Cache Configuration
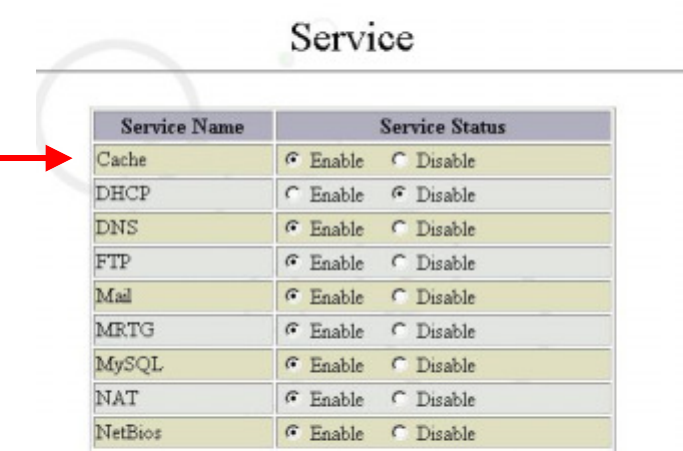
1. Enable Cache
Click “Service” in the “System Management Tools” screen. Then select “Enable”
cache and click “Submit”.
As shown in the figure below:
2. Default Value of Cache Configuration
Then click “Cache” in the “Service” screen. The default parameter screen of Cache
will appear as shown in the figure below:










