Datasheet
PROTECTING PHOTOVOLTAIC (PV) SYSTEMS AGAINST
LIGHTNING
Photovoltaic systems are generally located external to a building and
can be subjected to the direct or indirect effects of lightning.
Whilst the installation of photovoltaic panels on the roof does not, in
itself, increase the risk of direct lightning, the only practical way to
protect against the effects of a direct lightning strike would be the use
of a lightning protection system (LPS).
The indirect effects of lightning can however, be mitigated by the
appropriate use of Surge Protection Devices (SPD). These indirect
effects occur when lightning strikes in proximity to the structure and where
magnetic induction creates an overvoltage in the conductors – a
danger to both people and equipment. In particular, the DC cables of
a PV system would be exposed to the high conducted and radiated
disturbances caused as a result of the lightning currents. In addition,
overvoltages in PV systems are not only of atmospheric origin. It is
also necessary to consider overvoltages due to switching on electrical
networks connected to them. These overvoltages can also damage both
the inverter and the PV panels, and this explains the need to protect the
inverter on both DC and AC sides.
Installation characteristics
[U
OC STC
] PV voltage: corresponds to the SPD maximum operating
voltage and must be greater or equal to the maximum no-load voltage
of the PV system - depending on the configuration: earth free or mid
central earthing.
It is suggested that the maximum no-load voltage of the PV system is
calculated on the basis 1.2 x N x U
OC(module)
, where U
OC(module)
is the
no-load voltage of the single PV module in standard conditions and
N is the number of modules connected in series in each array of the
PV system (TS 50539-12).
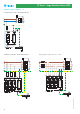
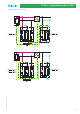
Earth free system
An earth free system installation, typical of smaller systems, is
characterized by the DC side floating, without connection to the
ground. U
OC STC
refers to the voltage between positive and negative
poles. Class II photovoltaic panels are normally used in earth free
system. However, if Class I panels are used, their metallic frames have
to be earthed for safety reasons.
Figure 8: Earth free system installation
Mid central earthing
This system is used in larger installations, with high voltages: the
ground connection to the mid point reduces by half the maximum
voltage with respect to the ground. In this case U
OC STC
is the
voltage between the pole connected to the SPD and the ground.
Figure 9: Mid central earthing installation
21
7P Series - Surge Protection Device (SPD)
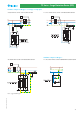
Photovoltaic system on a building without a lightning protection
system (LPS)
As an example, Figure 10 represents a simplified photovoltaic system
placed on a building without lightning rod. In such a system, the
protection against lightning must be considered at the following points
of installation:
- DC input of the inverter
- AC output of the inverter
- Low voltage supply network
At the DC input to the inverter SPDs specific for photovoltaic systems
must be installed, according to the PV system voltage. At the inverter
AC output, type 2 surge arresters must be installed suitable for the type
of system. At the point of connection to the LV supply network, install
type 2 surge arresters suitable to the type of system (TT, TN). In more
complex systems, it might be necessary to introduce additional SPDs.
For example; if the PV panels are more that 10m from the inverter: fit
one set of SPD as close as possible to the panels and one close to the
inverter. At the point to delivery of energy, must be connected an SPD
Type 1 or combined (1+2).
Figure 10: example of a photovoltaic system located on a building
without LPS, protected on the DC side by an SPD with U
OC STC
= 420 V,
and on the AC side by a 7P.22, specific for TT systems.
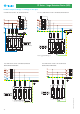
Photovoltaic system on a building with a lightning protection
system (LPS)
Where an LPS exists it is good practice to install the photovoltaic
panels in the area protected by the lightning rod.
In addition it is necessary to realize a good equipotential bonding
system, which must be positioned as close as possible to the entry point
of LV supply into the structure. The LPS, the SPD and all metal parts have
to be connected to this equipotential system.
SPD protection on the DC side is the same as for systems without LPS,
consequently an arrester for PV systems of a suitable voltage (U
OC STC
)
should be used.
An appropriate Type 2 SPD should protect the AC side of the inverter,
assuming a Type 1 SPD is already installed upstream.
However, if the inverter is sited in the field, for example; below the
structure that supports the panels, then we recommend installing a Type
1 SPD to the AC side, instead of Type 2. Note that under EN 62305
installation of a Type 1 SPD is mandatory at the point of delivery of
electricity, if the building has LPS (with or without solar panels).
XII-2012, www.findernet.com