Operating instructions
SEPTEMBER 2005 MAGNUM 1X7 LTO AUTOLOADER
14-3
WHAT YOU SEND TO THE AUTOLOADER
14.2.1 USING READ BUFFER TO COPY THE AUTOLOADER
M
ICROCODE TO THE INITIATOR
The autoloader EEPROM has a capacity of 100000h (1,048,576 bytes). This
memory is organized into eight sections of 20000h (131,072) bytes each, as
follows:
The first two sections (Buffer IDs 00h and 01h) of the memory (bytes 000000h
through 03FFFFh) contain the Boot Block code. This portion of the code is a
subset of the autoloader microcode that allows the functional code to be
updated even if the functional code currently stored in the autoloader has
been so damaged as to make it inoperable.
The functional code resides in the remainder of the memory (040000h
through 0FFFFFh) and is divided into six equal sections, as shown in
Figure 14-1:
Use one or more READ BUFFER commands to copy a section of the functional
microcode to the initiator. Set the Mode field to 1 (Vendor Unique) and the
desired Buffer ID (02h through 07h). If you use multiple READ BUFFER
commands to transfer a section of the functional code, use the Offset field and
the Parameter List Length to specify the offset into the section and the amount
of data to be transferred by the command.
14.2.2 USING READ BUFFER TO COPY DIAGNOSTIC DATA TO
THE INITIATOR
Use one or more READ BUFFER commands to transfer the autoloader’s
diagnostic data (also known as Dump Data) to the initiator. The Mode field
must be 010b (Data), the Buffer ID must always be 80h, and the Offset field
must always be 000000h. The Parameter List Length should be the lesser of
0FFE0h (the maximum size of the diagnostic data) and the largest data transfer
the host can perform.
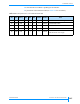
Table 14-1 Byte locations of function code sections in the EEPROM
Buffer ID Byte location in EEPROM
02h 040000h through 05FFFFh
03h bytes 060000h through 7FFFFh
04h bytes 08000h through 9FFFFh
05h byte 0A000h through BFFFFh
06h bytes 0C0000h through DFFFFh
07h bytes 0E0000h through 0FFFFFh