Installation guide
Network Infrastructure for EtherNet/IP™
6-78
Infrastructure Application Scenarios
6.4.3.2 Interlock Connections
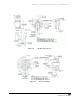
An interlock connection is used if there is implicit message traffic traversing the backbone network. As
shown in Figure 6-12, the traffic being passed is real-time implicit, supervisory, programming,
monitoring, and so forth. There is real-time data being passed. There is no CIP gateway in use. The
backbone is connected directly to the plant-floor network infrastructure. There will be implicit messaging
within the local network zone and some will be passed across the backbone network to another zone.
Protection (firewall, ACL, VLAN, etc.) may be needed to prevent unwanted multicast traffic from
adversely affecting the backbone environment or the plant floor. The recommended connection point is a
Layer 3 switch or router.
Interlocking Across Corporate Backbones
Interlocking across corporate backbone systems should be only considered by expert users. There
are baseline requirements for the backbone that must be met, such as multicast routing protocols,
spanning VLANs, redundancy protocol interaction, etc. that must be extensively tested, and timing
characteristics must be confirmed before deployment. The impact on control system throughput
(determinism, control data latency) must be extensively tested and evaluated for a successful
deployment.
Figure 6-12 Example of an Interlocked Integrated Network.
Corporate
Backbone
Plant
Floor
Enterprise
Network
Layer3 switch
or router
Industrial
switch
Industrial
switch
PLC
I/O
I/O
I/O
Plant
Floor
Enterprise
Network
Layer3
switch
or router
Industrial
switch
Industrial
s
wit
c
h
PLC
I/O
I/O I/O