Installation guide
Network Infrastructure for EtherNet/IP™
Planning the Infrastructure
3-28
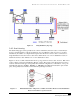
Figure 3-6 Ring Redundancy Topology.
3.8.3 Dual Homing
The dual homing approach is typically used to achieve redundancy between routers or network layer
(Layer 3) switches that have router-level functions. (See 4.11 Multilayer Ethernet Switches for more
information.) In addition to a simple hub-and-spoke network where a remote router is connected to a
single distribution router, the remote router can be dual-homed to two or more distribution routers. A
dual-homed remote router will have two or more distribution routers.
Figure 3-7 shows a common dual-homed remote topology with one remote router; however, 100 or more
routers could be connected to Distribution Routers 1 and 2. The remote router will use the best route to
reach its destination. This approach typically allows flexible configurations, combinations of two ports
with different data rates (10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 1000 Mbps) and different media (fiber optic, twisted
pair), and typically faster switchover times than the spanning tree method.
Figure 3-7 If Distribution Router 1 Experiences a Failure, the Remote Router Can Use Distribution
Router 2 to Reach the Corporate Network.