Installation guide
Network Infrastructure for EtherNet/IP™
Planning the Infrastructure
3-27
The Rapid Spanning Tree (RSTP) specification (originally IEEE Std 802.1W, now included in IEEE
Std 802.1D) is an enhancement over the original Spanning Tree specification. It allows for faster recovery
times (a few seconds) than Spanning Tree. In Spanning Tree applications, recovery times typically range
from 30 to 60 seconds. Large and complex topologies may result in minutes of recovery time.
3.8.1.2 Link Aggregation
The Link Aggregation method (IEEE Std 802.3AD
15
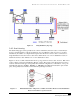
) is used to provide redundant communication paths
between two devices when two or more links connect the devices as shown in Figure 3-5. When one link
is broken, the others carry the traffic.
Link Aggregation uses all the links all the time, typically in situations where high traffic volume (such as
uplinks from lower-level networks to higher-level enterprise networks) requires the added bandwidth of
multiple communication paths. For example, four fast Ethernet links (100 Mbps) produce a bandwidth of
a single 400-Mbps link. In a case where one of the links is cut, traffic continues but at a slower 300-Mbps
equivalent bandwidth.
Figure 3-5 When One of Four Fast Ethernet Links between the Two Devices is Broken,
Message Traffic Capacity Decreases but Continues.
3.8.2 Ring Redundancy
Ring redundancy schemes are proprietary in nature and are available from multiple vendors. These
redundancy schemes are not interoperable between different vendors’ infrastructure products.
Redundancy configurations require multiple switches to be connected in a ring manner as shown in
Figure 3-6. These systems allow typical communications recovery times in the 100s of milliseconds
range.
15
IEEE 802.1AD, IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks – Virtual Bridged Local Area Networks.
http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802/802.1.html
Infrastructure
Component
Infrastructure
Component