Installation guide
Network Infrastructure for EtherNet/IP™
Planning the Infrastructure
3-26
3.8.1 IEEE Standard Network Redundancy Options
The Spanning Tree and Trunking/Aggregation methods are standard, multi-vendor approaches to
achieving network redundancy.
3.8.1.1 Spanning Tree Protocol Method
The
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a Layer 2 (data link layer) protocol designed to run on bridges
and switches. The specification for STP is IEEE Std 802.1D.
14
The main purpose of STP is to ensure that
there are redundant paths while avoiding a loop situation that causes network messages to endlessly cycle
around the loop and repeat, causing the network to saturate and communications to effectively stop.
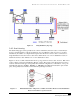
As shown in Figure 3-4, switches with STP can detect one or more cable cuts and automatically
determine the next best path for the data to travel. This capability requires switches that support the
Spanning Tree algorithm, and transmit and receive Spanning Tree configuration messages. Vendors
should be consulted to determine how many bridges/switches can be supported, and to determine the
length of the time lapse from when a break is detected to when the network is reconfigured and normal
communications resume.
Figure 3-4 Using the Spanning Tree Protocol Method, Switches Detect a Cut Cable and Automatically
Determine the Next Best Path for the Data to Travel.
14
IEEE 802.1D, IEEE Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks – LAN/MAN Bridging and Management – Media
Access Control (MAC) Bridges. http://standards.ieee.org/getieee802/802.1.html