Installation guide
Network Infrastructure for EtherNet/IP™
Planning the Infrastructure
3-25
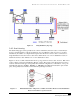
Figure 3-3 VLAN-tagged Frames are Identified when the MAC Finds the LAN Type Value in the
Normal Length/Type Field Location.
The VLAN header contains a Tag Control field that defines the transmission priority (0 to 7, where 7 is
the highest) and a
VLAN ID that identifies the particular VLAN over which the frame is to be sent. These
provide the means to expedite time-critical network traffic. Ethernet switches or routers use the VLAN
header information to direct the message to the correct port and transmit the frames according to their
priority.
VLAN tagging requires that all infrastructure devices involved with a VLAN group be equipped
with the VLAN option.
3.7.2 VLAN Benefits
The application of VLANs allows the flexibility of using interconnecting devices while reducing
unnecessary network traffic and delay time. In addition to managing network traffic, VLANs provide
added system scalability and security, and they simplify network management by making device adds,
moves, or changes easier to administer. The configuration of a VLAN requires managed infrastructure
components.
3.8 Topologies to Provide Ethernet Network Redundancy
Infrastructure components come with a variety of system redundancy options, from redundant power
supplies, to cable and communication path redundancy. Cable and communication path redundancy is
often required in larger scale installations or in cases where an infrastructure component or cable failure
may cause significant scrap of manufactured product or result in damage to a machine or process.
There are both standardized and proprietary methods of achieving redundancy in Ethernet networks that
involve variations on standard Ethernet topologies. Standardized methods have the benefits of allowing
the mix of multi-vendor products or the ability to easily change vendors without re-engineering the
system. Like PLCs, proprietary redundancy methods may offer special features or performance
advantages in certain applications, but the approach cannot be mixed with multiple vendors’ components.
In addition, special attention needs to be paid to how, and if, the proprietary method can be used in
conjunction with standardized redundancy approaches.
If a user mixes proprietary and nonproprietary methods within an overall system,
communication loops
can be formed, creating spurious traffic that can overload and effectively shutdown the network. Different
vendors’ equipment should be evaluated based on the type of redundancy offered, the switchover time,
and if there is message storage capacity to reduce “lost messages” during switchover time.