User's Manual Part 2
RBS 2109 User’s Guide
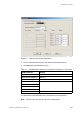
In this example, network interface, RBS 1,
RBS 2 and RBS 3 refer to the figure above.
RBS 1:
Carrier advised code at the network interface is
“C” (-15 dB) and the cable attenuation is 5 dB.
1. See the table Long haul parameters for different
carrier advised codes at the network interface to
find the correct LBO parameter for LBO A.
2. Set LBO A to “Long h., -15 dB”.
3. Set LBO B to “Long h., 0 dB”.
4. Set LBO C and D (not connected) to
“Short h., 0 - 133 feet”.
RBS 2:
The cable attenuation between RBS 1 and RBS 2 is 3 dB.
1. Calculate the total cable attenuation between RBS 2
and the network interface:
5 + 3 = 8 dB
2. See the table Long haul parameters for different
carrier advised codes at the network interface
to find the correct LBO parameter for LBO A.
3. Set LBO A to “Long h., -7.5 dB”.
4. Set LBO B to “Long h., 0 dB”.
5. Set LBO C and D (not connected) to
“Short h., 0 - 133 feet”.
RBS 3:
The cable attenuation between RBS 2 and RBS 3 is 9 dB.
1. Calculate the total cable attenuation for RBS 3
and the network interface:
5 + 3 + 9 = 17 dB
2. See the table Long haul parameters for different
carrier advised codes at the network interface
to find the correct LBO parameter for LBO A.
3. Set LBO A to “Long h., 0 dB”.
4. Set LBO B, C and D (not connected) to
“Short h., 0 - 133 feet”
Example 7 Calculating LBO Parameters Manually for Long Haul
Defining LBO Parameters as Long Haul Automatically
This section describes how to define LBO to long haul when the maximum
input signal level at the Far End is known, but not the cable attenuation. The
cable attenuation can be measured by the RBS according to the instructions
below. See figure below.
127EN/LZT 720 0090 Uen R1A 2004-09-17