User`s manual
Introduction
Page 1-6
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP or A.G.P.)
Typically, 3D graphics rendering requires a tremendous amount of memory, and
demands ever increasing throughput speed as well. As 3D products for the
personal computer become more and more popular, these demands will only
increase. This will cause a rise in costs for both end users and manufacturers.
Lowering these costs as well as improving performance is the primary motivation
behind AGP. By providing a massive increase in the bandwidth available between
the video card and the processor, it will assist in relieving some of these pressures
for quite sometime.
The board provides the AGP 2.0 interface. The AGP Interface Specification
revision 2.0 enhances the functionality of the original AGP Interface Specifica-
tion (revision 1.0) by allowing 4X data transfers (4 data samples per clock) and
1.5 volt (power supply) operation. The AGP 2.0 interface, along with SDRAM
memory technology, allows graphics controllers to access main memory at over
1GB/s (1.5 volt AGP Card supports only).
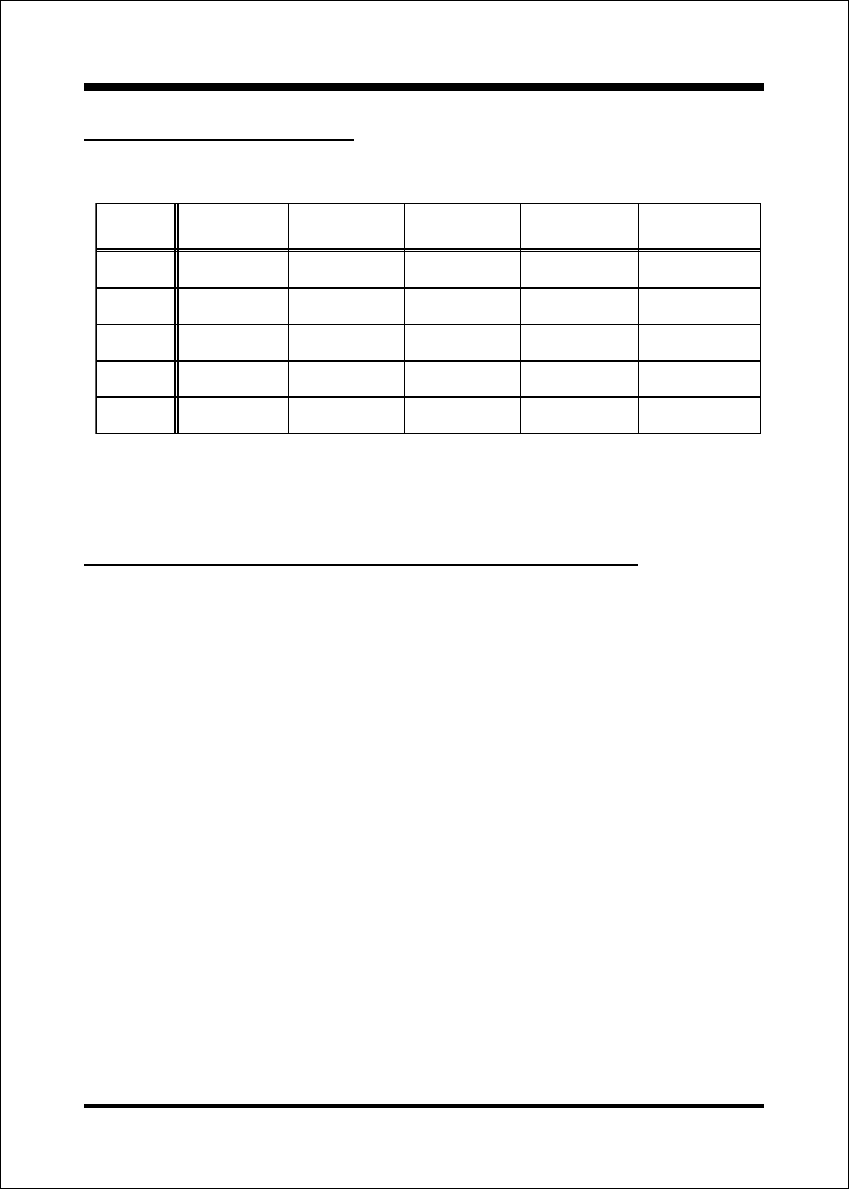
Bandwidth Overview
Table 1 provides a summary of the bandwidth requirements for the Intel
®
850E chipset.
Table 1: Intel
®
850E platform Bandwidth Summary
ecafretnI
deepSkcolC
)zHM(
rePselpmaS
kcolC
etaRataD
)s/selpmas-ageM(
htdiWataD
)setyB(
htdiwdnaB
)s/BM(
suBUPC
331/0014 335/0048 4624/0023
MARDR
335/0042 6601/0084 4624/0023
0.2PGA
6.664 6624 6601
kniLbuH
6.664 6621662
2.2ICP
3.3313.334 331










