Specifications
Computer Architecture and Maintenance (G-Scheme-2014)
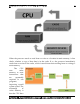
• The same block of data which are stored on the main memory resides on the
cache. Thus the instructions takes less time to execute.
• The CPU and the cache are connected with a local bus which is of high capacity
and speed due to which the data transfer is quick.
• Cache memory is intelligent memory.
• It holds current working set of code and data.
• It reduces wait state or no wait states (LI cache) in system.
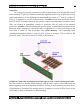
* The initial level of storage on a processor are the registers. The registers are where the
actually processing input and output takes place.
* L1 cache – Then the level 1 cache comes next. It is logically the closest high speed
memory to the CPU core / registers. It usually runs at the full speed (meaning the same
as the CPU core clockspeed). L1 often comes in size of 8kB, 16kB, 32kB, 64kB or 128kB.
But, it is very high speed even though the amount is relatively small.
* L2 cache – The next level of cache is L2, or level 2. Nowadays L2 is larger than L1 and
it often comes in 256kB, 512kB and 1,024MB amounts. L2 often runs at 1/4, 1/2 or full
speed in relation to the CPU core clockspeed.
* L3 cache – Level 3 cache is something of a luxury item. Often only high end
workstations and servers need L3 cache. Currently for consumers only the Pentium 4
Extreme Edition even features L3 cache. L3 has been both “on-die”, meaning part of the
CPU or “external” meaning mounted near the CPU on the motherboard. It comes in
many sizes and speeds.
Q.Describe different types of Cache Memories with respect to processor
Ans. There are Three Types
1.Level-1
2.Level-2
3.Level-3
Internal Level 1 Cache
All modern processors starting with the 486 family include an integrated L1
cache and controller. The integrated L1 cache size varies from processor to processor,
starting at 8 KB for the original 486DX and now up to 128 KB or more in the latest
processors.
Prepared By – Prof. Manoj.kavedia (9860174297 – 9324258878 ) (www.kavediasir.yolasite.com)
67