User's Manual Part 4
T
ECHNICAL
D
OCUMENTATION
P
ROTECTING
P
EOPLE AND
A
SSETS
®
D
ATE
:
27
M
ARCH
2017
|
V
ERSION
:
1.8
83
R
ANGER
®
-
X5
R
ADAR
S
YSTEM
(M
OBILE
)
F
UNCTIONAL
O
VERVIEW AND
T
HEORY OF
O
PERATION
EEC
®
|
C
OMPANY
P
ROPRIETARY
encoders and convert them to an absolute angle. The Aquarian performs this when a restart of the
controller causes the loss of the zero set point on an axis and there is a request for servo power. In
azimuth, the motor is driven clockwise until the homing sensor is detected and the quadrature
decoder hardware is reset to zero. In elevation, the motor is driven until it reaches the lower electrical
limit. Once the lower electrical limit is detected, the motor will drive in the opposite direction until it
detects the homing sensor. At that point, the quadrature encoder hardware is reset to zero.
4.6.
Communication Interface
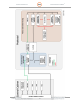
The radar uses an Ethernet network (see Figure 68) to provide command and control of the radar
set and to receive status flags and BITE information. Three Ethernet switches provide connection
points for all the I/O and controlled devices in the Control Cabinet, the Pedestal Enclosure, and RF
Enclosure.
Ethernet communications between the Pedestal and the Control Cabinet are provided over a fiber-
optic connection by the use of Ethernet Switches with Fiber-Optic Media Converters in the Control
Cabinet and Pedestal Enclosure. Communications within the Pedestal is possible by the use of the
Ethernet connection through the Slip-ring Module. Communications between the Radar and the
local host computer are provided through the rear panel of the Control Cabinet. Additional ports on
the front and rear of the Control Cabinet provide access to the radar network for expandability and
testing.
Received data from the IQ2-IFD, on the Pedestal, is transmitted via a fiber-optic cable through the
Fiber-Optic Rotary Joint to the downlink input and the IQ2-DSP. Uplink information is transmitted
from the IQ2-DSP over the Ethernet network to the IQ2-IFD.