Reference Manual
9−2
E1387
PRESTEAMER
CHIPS
FRESH STEAM
PCV-2
TMP PULP
PCV-3
REFINER
CYCLONE
STEAM TO
STACK
PCV-1
PCV-4
PROCESS
STEAM
STEAM TO
RECOVERY
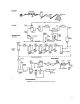
Figure 9-1. Thermomechanical Pulping Process
refiner. The refiner may then be fed with fresh
steam via PCV-4, during startup, to increase the
pressure to 60-75 psig or 300°F.
The refiner discharges the pulp and steam to the
cyclone, which separates the steam from the pulp.
The PCV-1 and PCV-2 valves control the pressure
in the refiner. During production, this steam is sent
to heat recovery, while during startup it goes to the
steam stack for disposal. The TMP pulp
(approximately 35% solids) is discharged through
valve PCV-3 from the first stage refiner to the
second stage, and from there, to further treatment
in the screening and cleaning stages.
Valve Selection:
The control of clean steam from PCV-4 can be
easily accomplished by the Fisher Vee-Ball
segmented ball valve. Where fibers can build up
and result in potential plugging problems, namely
PCV-1 and PCV-2, the Vee-Ball has proven
successful with its V-notch ball, as this shears
through any pulp fibers. However, any use of the
Vee-Ball attenuator must be evaluated with care.
The Fisher Control-Disk can also be used in this
service.
The TMP discharge, or blow valve, PCV-3
contains pulp at 35% consistency, and
steam/condensate. Because of the high pressure
drop of the system, this valve must withstand
erosion. One solution is the Vee-Ball with stellited
internals and trim, including the ball seal. The
water control valve should be a Vee-Ball to ensure
optimal control.
Valve Selection
Tag Application Recommended Alternate
PCV-1,
PCV-1
Steam
(process)
Vee-Ball
segmented ball
Control-Disk
PCV-3 Refiner Blow
Vee-Ball segmented
ball w/ stellited trim
PCV-4 Steam (fresh)
Vee-Ball
segmented ball
Control-Disk
---
Water (control)
Vee-Ball
segmented ball
Control-Disk
Chemithermomechanical Pulp
Process:
Wood chips can be pretreated with sodium
carbonate, sodium hydroxide, sodium sulfide, or
other chemicals prior to refining with equipment
similar to a mechanical mill. The conditions of the
chemical treatment are much less vigorous than in
a chemical pulping process since the goal is to
make the fibers easier to refine rather than
removing the lignin as in a fully chemical process
(described later in this section). Pulp made using
these hybrid processes are known as
chemithermomechanical pulp (CTMP).