Instruction Manual
Instruction Manual
D103434X012
Blocks
November 2014
131
Input Selection
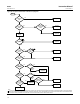
The ISEL function block reads the values and statuses of as many as eight inputs (IN_1 [11], IN_2 [12], IN_3 [13], IN_4
[14], IN_5 [25], IN_6 [26], IN_7 [27], IN_8 [28]). To use any of the six selection algorithms to select the output,
OP_SELECT [22] must be 0. To specify which algorithm to use, configure the selector type parameter (SELECT_TYPE
[19]) as follows:
D Maximum—selects the input with the highest value from the inputs that are not bad and not disabled.
D Minimum—selects the input with the lowest value from the inputs that are not bad and not disabled.
D Average—calculates the average value of the inputs that are not bad and not disabled and provides it as the output.
For example, if the number used to average (AVG_USE [33]) is 4 and the number of connected inputs is 6, then the
highest and lowest values would be dropped prior to calculating the average. If AVG_USE [33] is 2 and the number
of connected inputs is 7, then the two highest and lowest values would be dropped prior to calculating the average
and the average would be based on the middle three inputs.
D Middle—If the number of good usable inputs is odd, then it selects the middle value. If the number of good usable
inputs is even, then it averages the middle two values and selects status as worst of two. If both inputs' limit status
are not the same then it sets limit status of Not Limited.
D First Good—selects the first input that is not bad and not disabled, starting with IN_1 [11].
D Hot Spare—initially uses the input selected as first good. If the selected input goes bad, the first good selection is
repeated. If the selected input remains good, it stays selected. If the originally selected input returns to good status
the selection does not change. Selection changes only if the currently selected input goes bad.
Disabling Inputs
Use the parameters DISABLE_1 [15], DISABLE_2 [16], DISABLE_3 [17], DISABLE_4 [18], DISABLE_5 [29], DISABLE_6
[30], DISABLE_7 [31] and DISABLE_8 [32] to disable the corresponding inputs. An input that is disabled will not be used
by any of the selection algorithms.
The status of the disable parameter must be “Good,” “Good_Cascade,” or “Uncertain” with a STATUS_OPTS [10] of
“Use Uncertain as Good” in order to be evaluated. If the status of the disable parameter is Bad, its last usable value is
maintained and acted upon. If the device restarts, losing the last usable value, the last usable value is set to disabled.
IN_1 through IN_8 and DISABLE_1 through DISABLE_8 are non‐volatile type parameters so if they are Linked they will
automatically have Bad status until connections are re‐established. If they are not Linked, they will be restored with the
previous value from NVM across device restarts.
Direct Selection of Inputs
The parameter OP_SELECT [22] can be used to select a particular input. If OP_SELECT [22] is non‐zero, the selection
algorithm is bypassed and the value of OP_SELECT [22] is interpreted as the input number to select. If the OP_SELECT
[22] value is greater than the number of inputs, then the highest input is selected. The status of OP_SELECT [22] must
be “Good,” “Good_Cascade,” or “Uncertain” with a STATUS_OPTS [10] of “Use Uncertain as Good” in order to be
evaluated. If the status of OP_SELECT [22] is Bad, then the OUT [7] status is Bad.
Identification of Selected Inputs
For a SELECT_TYPE [19] of Maximum, Minimum, Middle, First Good, and Hot Spare, SELECTED [21] indicates the
number of the selected input. When Middle is computed from more than one input, SELECTED [21] is set to 0.