Specifications
60
General Heating and Cooling Run Control — For
normal comfort conditioning there are three basic modes.
These are:
• HEAT — Air is warmed by electric or gas heat. There are
actually two modes under heat which are Low Heat (Mode
6—HVAC_HEAT)andHighHeat(Mode7—
HVAC_HTHI).
• VENT — No cooling or heating is activated and just out-
side air is introduced into the conditioned space to control
Indoor Air Quality. This is the vent mode (Mode 2 —
HVAC_VENT).
• COOL — In this mode either free cooling and or mechani-
cal cooling will be used to condition the space. There are
also two versions of this mode which are High Cool (Mode
3 — HVAC_COOL) and Low Cool (Mode 4 —
HVAC_LOCL). Also free cooling (Mode 5 —
HVAC_UEFC) can be used in cooling.
Once the system is running and nothing is preventing the
selection of one of the three run modes, a routine will be run to
select the modes and control routines. There are three basic
routines that will be called based on unit configuration data and
the status of the input switches and temperatures. These three
routines are HVACSTAT, HVACSPT2, and HVAC_VAV.
• HVACSTAT — This routine is used for heating and cooling
with a conventional 2-stage thermostat and 2 stages heating
and cooling. The routine can be used with units with more
than two stages of mechanical cooling, but stages will be
combined to yield only two stages. If multiple stages are
desired, then HVACSPT2 should be used.
• HVACSPT2 — This routine is used for demand drive heat-
ing and cooling using high and low demand levels and will
allow for more than 2 stages of cooling even if controlled
with a 2-stage thermostat.
• HVAC_VAV — This routine is used for VAV system cool-
ing and supply air temperature control.
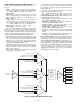
The logic used to select which of these three routines should
be used is shown in Fig. 22. Once the routine is selected then
the appropriate economizer, compressor and heating staging
routines will be used.
Selection of the three routines is dependent on the status of
the inputs and the configuration of the unit.
The configuration variable that influences the selection
of the routines is Unit Control Type (CTL.T) in the
CONFIGURATION-UNIT submenu. This variable allows for
the selection of the following options:
• SPT 2 STAGE — Two-stage control using a T55, T56, or T58
sensor. Calls the HVACSPT2 routine.
• SPT MULTI — Multiple stage control using a T55, T56, or
T58 sensor. Calls the HVACSPT2 routine.
• TSTAT 2 STAGE — Two-stage control using a conven-
tional thermostat. Calls the HVACSTAT routine.
• TSTAT MULTI — Multiple stage control using a 2-stage
thermostat. Calls the HVACSTAT routine.
• VAV RAT — VAV operation with return air temperature
heating and transition control. Calls the HVAC_VAV
routine.
• VAV SPT — VAV operation with space temperature heating
and transition control. Calls the HVAC_VAV routine.
HVACSTAT ROUTINE — This is a conventional heating and
cooling routine where the Y1 and Y2 thermostat inputs are used
to turn on stage 1 and stage 2 of cooling. It will be used when
SPT 2 STAGE and TSTAT 2 STAGE are selected. If the econo-
mizer is usable then the control will use the HVACSPT2 routine
and the high and low cooling demand and leaving air set points
to position the economizer. If mechanical cooling is used, the
control will sequence the compressors on based on the
compressor loading sequence. See the section on compressor
sequencing. For heating, the 2 stages of gas or electric heat are
controlled by the W1 and W2 signals.
2 Stage Heat
Staged Heat
IAQ
Economizer
Compressors
Control
Routines
Morning Warmup
Low Heat
Hight Heat
Staged Heat
Vent
Vent/Tempering
Free Cooling
Low Cool
High Cool
Economizer
Cooling
HVACSTAT
HVACSPT2
Heating
Tempering
HVAC_VAV
Configuration
Values
Select
Mode
Routine
Configuration Data
Setpoint Data (HI.SA, LO.SA, OC.SP
UC.SP, OH.SP UH.SP, CL.OF)
Calculated Variables (MAT, ECACTIVE)
Temperature Inputs (SPT, OAT,
RAT, EDT, ORH, IRH)
Configuration Data
Setpoint Data (HI.SA, LO.SA, OC.SP
UC.SP, OH.SP UH.SP, GAP)
Calculated Variables (MAT, ECACTIVE)
Temperature Inputs (SPT, OAT,
RAT, EDT, ORH, IRH)
Configuration Data
Setpoint Data (HI.SA, LO.SA)
Calculated Variables (MAT, ECACTIVE)
Temperature Inputs (OAT,
RAT, EDT, ORH, IRH)
Switch Inputs (Y1, Y2, W1, W2, G
Fig. 22 — Routine Run Mode Selection Logic