- Siemens Cordless Telephone User Manual
Vector control
4.2 Vector control with encoder
Drive Functions
118 Function Manual, (FH1), 07/2007 Edition, 6SL3097-2AB00-0BP4
I0
W
I0
W
FRQWUROOHG
6WDUW =HURWUDQVLWLRQ
FRQWUROOHG
I
0VHWU
0VHWU
I
S S
SS
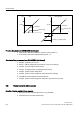
Figure 4-3 Zero crossover for permanent-magnet synchronous motors
Function diagrams (see SINAMICS S List Manual)
● 6730 Interface with Motor Module for induction motor (p0300 = 1)
● 6731 Interface to the Motor Module (PEM, p0300 = 2)
Overview of key parameters (see SINAMICS S List Manual)
● p0305[0...n] Rated motor current
● r0331[0...n] Motor magnetizing current/short-circuit current (actual)
● p1610[0...n] Torque setpoint static (SLVC)
● p1611[0...n] Supplementary accelerating torque (SLVC)
● p1750[0...n] Motor model configuration
● p1755[0...n] Motor model changeover speed sensorless operation
● p1756 Motor model changeover speed hysteresis
● p1758[0...n] Motor model changeover delay time, open/closed-loop control
4.2 Vector control with encoder
Benefits of vector control with an encoder:
● The speed can be controlled right down to 0 Hz (standstill)
● Constant torque in the rated speed range