Web Management Guide-R01
Table Of Contents
- How to Use This Guide
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Getting Started
- Web Configuration
- Using the Web Interface
- Basic Management Tasks
- Displaying System Information
- Displaying Hardware/Software Versions
- Configuring Support for Jumbo Frames
- Displaying Bridge Extension Capabilities
- Managing System Files
- Setting the System Clock
- Configuring the Console Port
- Configuring Telnet Settings
- Displaying CPU Utilization
- Configuring CPU Guard
- Displaying Memory Utilization
- Resetting the System
- Interface Configuration
- VLAN Configuration
- Address Table Settings
- Spanning Tree Algorithm
- Congestion Control
- Class of Service
- Quality of Service
- VoIP Traffic Configuration
- Security Measures
- AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting)
- Configuring User Accounts
- Web Authentication
- Network Access (MAC Address Authentication)
- Configuring HTTPS
- Configuring the Secure Shell
- Access Control Lists
- Filtering IP Addresses for Management Access
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring 802.1X Port Authentication
- DoS Protection
- DHCP Snooping
- DHCPv6 Snooping
- ND Snooping
- IPv4 Source Guard
- IPv6 Source Guard
- ARP Inspection
- Application Filter
- Basic Administration Protocols
- Configuring Event Logging
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Simple Network Management Protocol
- Configuring Global Settings for SNMP
- Setting Community Access Strings
- Setting the Local Engine ID
- Specifying a Remote Engine ID
- Setting SNMPv3 Views
- Configuring SNMPv3 Groups
- Configuring Local SNMPv3 Users
- Configuring Remote SNMPv3 Users
- Specifying Trap Managers
- Creating SNMP Notification Logs
- Showing SNMP Statistics
- Remote Monitoring
- Switch Clustering
- Setting a Time Range
- Ethernet Ring Protection Switching
- OAM Configuration
- UDLD Configuration
- LBD Configuration
- Multicast Filtering
- Overview
- Layer 2 IGMP (Snooping and Query for IPv4)
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and Query Parameters
- Specifying Static Interfaces for a Multicast Router
- Assigning Interfaces to Multicast Services
- Setting IGMP Snooping Status per Interface
- Filtering IGMP Packets on an Interface
- Displaying Multicast Groups Discovered by IGMP Snooping
- Displaying IGMP Snooping Statistics
- Filtering and Throttling IGMP Groups
- MLD Snooping (Snooping and Query for IPv6)
- Configuring MLD Snooping and Query Parameters
- Setting Immediate Leave Status for MLD Snooping per Interface
- Specifying Static Interfaces for an IPv6 Multicast Router
- Assigning Interfaces to IPv6 Multicast Services
- Filtering MLD Query Packets on an Interface
- Showing MLD Snooping Groups and Source List
- Displaying MLD Snooping Statistics
- Filtering and Throttling MLD Groups
- Multicast VLAN Registration for IPv4
- IP Tools
- IP Configuration
- General IP Routing
- IP Services
- Appendices
Chapter 13
| Basic Administration Protocols
Simple Network Management Protocol
– 449 –
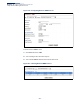
Figure 287: Showing SNMP Notification Logs
Showing
SNMP Statistics
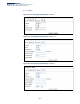
Use the Administration > SNMP (Show Statistics) page to show counters for SNMP
input and output protocol data units.
Parameters
The following counters are displayed:
◆ SNMP packets input – The total number of messages delivered to the SNMP
entity from the transport service.
◆ Bad SNMP version errors – The total number of SNMP messages which were
delivered to the SNMP entity and were for an unsupported SNMP version.
◆ Unknown community name – The total number of SNMP messages delivered
to the SNMP entity which used a SNMP community name not known to said
entity.
◆ Illegal operation for community name supplied – The total number of SNMP
messages delivered to the SNMP entity which represented an SNMP operation
which was not allowed by the SNMP community named in the message.
◆ Encoding errors – The total number of ASN.1 or BER errors encountered by the
SNMP entity when decoding received SNMP messages.
◆ Number of requested variables – The total number of MIB objects which have
been retrieved successfully by the SNMP protocol entity as the result of
receiving valid SNMP Get-Request and Get-Next PDUs.
◆ Number of altered variables – The total number of MIB objects which have
been altered successfully by the SNMP protocol entity as the result of receiving
valid SNMP Set-Request PDUs.
◆ Get-request PDUs – The total number of SNMP Get-Request PDUs which have
been accepted and processed, or generated, by the SNMP protocol entity.
◆ Get-next PDUs – The total number of SNMP Get-Next PDUs which have been
accepted and processed, or generated, by the SNMP protocol entity.
◆ Set-request PDUs – The total number of SNMP Set-Request PDUs which have
been accepted and processed, or generated, by the SNMP protocol entity.