Web Management Guide-R07
Table Of Contents
- How to Use This Guide
- Contents
- Figures
- Tables
- Getting Started
- Introduction
- Key Features
- Description of Software Features
- Configuration Backup and Restore
- Authentication
- Access Control Lists
- Port Configuration
- Rate Limiting
- Port Mirroring
- Port Trunking
- Storm Control
- Static MAC Addresses
- IP Address Filtering
- IEEE 802.1D Bridge
- Store-and-Forward Switching
- Spanning Tree Algorithm
- Virtual LANs
- IEEE 802.1Q Tunneling (QinQ)
- Traffic Prioritization
- Quality of Service
- IP Routing
- Address Resolution Protocol
- Multicast Filtering
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- System Defaults
- Introduction
- Web Configuration
- Using the Web Interface
- Basic Management Tasks
- Displaying System Information
- Displaying Hardware/Software Versions
- Configuring Support for Jumbo Frames
- Displaying Bridge Extension Capabilities
- Managing System Files
- Setting the System Clock
- Configuring the Console Port
- Configuring Telnet Settings
- Displaying CPU Utilization
- Configuring CPU Guard
- Displaying Memory Utilization
- Resetting the System
- Using Cloud Management
- Interface Configuration
- VLAN Configuration
- Address Table Settings
- Spanning Tree Algorithm
- Congestion Control
- Class of Service
- Quality of Service
- VoIP Traffic Configuration
- Security Measures
- AAA (Authentication, Authorization and Accounting)
- Configuring User Accounts
- Web Authentication
- Network Access (MAC Address Authentication)
- Configuring HTTPS
- Configuring the Secure Shell
- Access Control Lists
- Filtering IP Addresses for Management Access
- Configuring Port Security
- Configuring 802.1X Port Authentication
- DoS Protection
- DHCP Snooping
- IPv4 Source Guard
- ARP Inspection
- Basic Administration Protocols
- Configuring Event Logging
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol
- Power over Ethernet
- Simple Network Management Protocol
- Configuring Global Settings for SNMP
- Setting the Local Engine ID
- Specifying a Remote Engine ID
- Setting SNMPv3 Views
- Configuring SNMPv3 Groups
- Setting Community Access Strings
- Configuring Local SNMPv3 Users
- Configuring Remote SNMPv3 Users
- Specifying Trap Managers
- Creating SNMP Notification Logs
- Showing SNMP Statistics
- Remote Monitoring
- Switch Clustering
- Setting a Time Range
- LBD Configuration
- Smart Pair Configuration
- Multicast Filtering
- Overview
- Layer 2 IGMP (Snooping and Query for IPv4)
- Configuring IGMP Snooping and Query Parameters
- Specifying Static Interfaces for a Multicast Router
- Assigning Interfaces to Multicast Services
- Setting IGMP Snooping Status per Interface
- Filtering IGMP Query Packets and Multicast Data
- Displaying Multicast Groups Discovered by IGMP Snooping
- Displaying IGMP Snooping Statistics
- Filtering and Throttling IGMP Groups
- MLD Snooping (Snooping and Query for IPv6)
- Filtering and Throttling MLD Groups
- Filtering MLD Query Packets on an Interface
- IP Tools
- IP Configuration
- General IP Routing
- Unicast Routing
- Overview
- Configuring the Routing Information Protocol
- Configuring General Protocol Settings
- Clearing Entries from the Routing Table
- Specifying Network Interfaces
- Specifying Passive Interfaces
- Specifying Static Neighbors
- Configuring Route Redistribution
- Specifying an Administrative Distance
- Configuring Network Interfaces for RIP
- Displaying RIP Interface Settings
- Displaying Peer Router Information
- Resetting RIP Statistics
- IP Services
- Appendices
- Glossary
Chapter 13
| Basic Administration Protocols
Power over Ethernet
– 359 –
Power over Ethernet
The ECS2100-10PE/10P and ECS2100-28P/28PP switches can provide DC power to a
wide range of connected devices, eliminating the need for an additional power
source and cutting down on the amount of cables attached to each device. Once
configured to supply power, an automatic detection process is initialized by the
switch that is authenticated by a PoE signature from the connected device.
Detection and authentication prevent damage to non-compliant devices (prior to
IEEE 802.3af).
The switch’s power management enables individual port power to be controlled
within the switch’s power budget. Port power can be automatically turned on and
off for connected devices, and a per-port power priority can be set so that the
switch never exceeds its power budget. When a device is connected to a switch
port, its power requirements are detected by the switch before power is supplied. If
the power required by a device exceeds the power budget of the port or the whole
switch, power is not supplied.
Ports can be set to one of three power priority levels, critical, high, or low. To control
the power supply within the switch’s budget, ports set at critical to high priority
have power enabled in preference to those ports set at low priority. For example,
when a device connected to a port is set to critical priority, the switch supplies the
required power, if necessary by denying power to ports set for a lower priority
during bootup.
Note:
For more information on using the PoE provided by this switch refer to the
Installation Guide.
Setting the Switch’s
Overall PoE Power
Budget
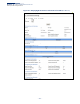
Use the Administration > PoE > PSE (Configure Global) page to set the maximum
PoE power budget for the switch (power available to all Gigabit Ethernet ports). If
the power demand from devices connected to the switch exceeds the power
budget, the switch uses port power priority settings to limit the supplied power.
Parameters
These parameters are displayed:
◆ PoE Maximum Available Power – The power budget for the switch (i.e., power
available to all switch ports). If devices connected to the switch require more
power than the switch budget, the port power priority settings are used to
control the supplied power.
◆ PoE Maximum Allocation Power – Sets a power budget for the switch.
(ECS2100-10PE: 50000-65000 milliwatts; Default: 65000 mW
ECS2100-10P: 50000-125000 milliwatts; Default: 125000 mW
ECS2100-28P: 50000-200000 milliwatts; Default: 200000 mW
ECS2100-28PP: 50000-370000 milliwatts without external power supply,