Firmware Manual
9000X AF Drives
MN04004001E
For more information visit: www.eaton.com
8-3
August 2010
Description of Parameters
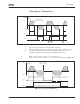
Figure 8-2: Programmable V/Hz Curve
Linear with flux optimization:
3 The frequency converter starts to search for the minimum motor current
in order to save energy, lower the disturbance level and the noise. This
function can be used in applications with constant motor load, such as
fans, pumps, etc.
109 V/Hz optimization (P1.13, P1.6.2)
Automatic
torque
boost
The voltage to the motor changes automatically which makes the motor
produce sufficient torque to start and run at low frequencies. The voltage
increase depends on the motor type and power. Automatic torque boost
can be used in applications where starting torque due to starting friction
is high, e.g. in conveyors.
Example:
What changes are required to start the load from 0 Hz?
● First set the motor nominal values (Parameter group 1.1).
Option 1: Activate the Automatic torque boost.
Option 2
: Programmable V/Hz curve
To obtain the required torque, the zero point voltage and midpoint voltage/frequency
(in parameter group 1.6) need to be set, so that the motor can draw enough current at
the low frequencies. First set parameter ID108 to Programmable V/Hz curve (value 2).
Increase the zero point voltage (ID606) to get enough current at zero speed. Then set
the midpoint voltage (ID605) to 1.4142*ID606 and the midpoint frequency (ID604) to
value ID606/100%*ID111.
Note: In high torque — low speed applications — it is likely that the motor will
overheat. If the motor has to run a prolonged time under these conditions,
special attention must be paid to cooling the motor. Use external cooling for
the motor if the temperature tends to rise too high.
ID605
(Default 10%)
ID606
(Default 1.3%)
ID604
(Default 5 Hz)
ID602
U[V]
f[Hz]
Un
ID603
Default: Nominal
Voltage of the Motor
Field Weakening
Point
Default: Nominal
Frequency of the
Motor