Technical data
CA08102001E For more information visit: www.eaton.com
40-281
Adjustable Frequency Drives
June 2008
40
SPA9000/SPI9000/SPN9000
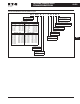
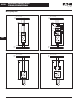
Figure 40-176. Combination Configuration
Common DC bus components are used in a multitude of combinations. Drives
which are braking can transfer the energy directly to the drives in motoring mode.
Advantages over Conventional Front Ends
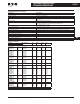
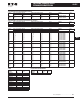
Table 40-393. Cutler-Hammer Front Ends vs. Conventional
Conventional regenerative front end (a.k.a. “anti-parallel thyristor bridge”) is not available from
Eaton.
Non-regenerative
Front End
Active
Front End
Conventional Regenerative
Front End
Input device Choke (L) Filter (LCL) Choke or auto-transformer (L)
Bridge type Diode/thyristor bridge IGBT bridge,
two-level type
Anti-parallel connected
thyristor bridge
Type of operation Controlled half-bridge High frequency
modulation
(1.5 to 3.6 kHz)
Firing angle controlled
Direction of power Motoring Motoring and
regenerating
Motoring and regenerating
Charging Constant current External required Usually internal
DC voltage Nominal (approx.
1.35 * U
N
)
Stable at +10% of
nominal (approx.
110% of 1.35 * U
N
)
Lowered DC voltage for
commutation margin
(e.g. 17% fi approx. 83% of
1.35 * U
N
) or autotransformer
on regenerative bridge
THD Similar to 6-pulse bridge
normal < 40%
Very low Similar to six-pulse bridge or
worse
2
3
Inverter
Common DC Bus
* Alternative
2
3
Inverter
Non-regenerative
Front End
(SPN) *
Active
Front End
(SPA) *
3
2
3
2