User manual
Table Of Contents
- 06230304_MA-PSI9000-2U-TFT-DE
- 1. Allgemeines
- 1.1 Zu diesem Dokument
- 1.2 Gewährleistung und Garantie
- 1.3 Haftungsbeschränkungen
- 1.4 Entsorgung des Gerätes
- 1.5 Produktschlüssel
- 1.6 Bestimmungsgemäße Verwendung
- 1.7 Sicherheit
- 1.8 Technische Daten
- 1.9 Aufbau und Funktion
- 1.9.1 Allgemeine Beschreibung
- 1.9.2 Blockdiagramm
- 1.9.3 Lieferumfang
- 1.9.4 Zubehör
- 1.9.5 Optionen
- 1.9.6 Die Bedieneinheit (HMI)
- 1.9.7 USB-Port (Rückseite)
- 1.9.8 Steckplatz für Schnittstellenmodule
- 1.9.9 Analogschnittstelle
- 1.9.10 Share-Bus-Anschluß
- 1.9.11 Sense-Anschluß (Fernfühlung)
- 1.9.12 Master-Slave-Bus
- 1.9.13 GPIB-Port (optional)
- 2. Installation & Inbetriebnahme
- 2.1 Transport und Lagerung
- 2.2 Auspacken und Sichtkontrolle
- 2.3 Installation
- 2.3.1 Sicherheitsmaßnahmen vor Installation und Gebrauch
- 2.3.2 Vorbereitung
- 2.3.3 Aufstellung des Gerätes
- 2.3.4 Anschließen an das Stromnetz (AC)
- 2.3.5 Anschließen von DC-Lasten
- 2.3.6 Erdung des DC-Ausgangs
- 2.3.7 Anschließen der Fernfühlung
- 2.3.8 Installation eines AnyBus-Schnittstellenmoduls
- 2.3.9 Anschließen der analogen Schnittstelle
- 2.3.10 Anschließen des „Share-Bus“
- 2.3.11 Anschließen des USB-Ports (Rückseite)
- 2.3.12 Erstinbetriebnahme
- 2.3.13 Erneute Inbetriebnahme nach Firmwareupdates bzw. längerer Nichtbenutzung
- 3. Bedienung und Verwendung
- 3.1 Personenschutz
- 3.2 Regelungsarten
- 3.3 Alarmzustände
- 3.4 Manuelle Bedienung
- 3.5 Fernsteuerung
- 3.6 Alarme und Überwachung
- 3.7 Bedieneinheit (HMI) sperren
- 3.8 Nutzerprofile laden und speichern
- 3.9 Der Funktionsgenerator
- 3.9.1 Einleitung
- 3.9.2 Allgemeines
- 3.9.3 Arbeitsweise
- 3.9.4 Manuelle Bedienung
- 3.9.5 Sinus-Funktion
- 3.9.6 Dreieck-Funktion
- 3.9.7 Rechteck-Funktion
- 3.9.8 Trapez-Funktion
- 3.9.9 DIN 40839-Funktion
- 3.9.10 Arbiträr-Funktion
- 3.9.11 Rampen-Funktion
- 3.9.12 UI- und IU-Tabellenfunktion (XY-Tabelle)
- 3.9.13 PV-Tabellenfunktion (Photovoltaik)
- 3.9.14 FC-Tabellenfunktion (Brennstoffzelle)
- 3.9.15 Fernsteuerung des Funktionsgenerators
- 3.10 Weitere Anwendungen
- 4. Instandhaltung & Wartung
- 5. Zubehör und Optionen
- 6. Service & Support
- 1. Allgemeines
- 06230304_MA-PSI9000-2U-TFT-EN
- 1. General
- 1.1 About this document
- 1.2 Warranty
- 1.3 Limitation of liability
- 1.4 Disposal of equipment
- 1.5 Product key
- 1.6 Intended usage
- 1.7 Safety
- 1.8 Technical Data
- 1.9 Construction and function
- 1.9.1 General description
- 1.9.2 Block diagram
- 1.9.3 Scope of delivery
- 1.9.4 Accessories
- 1.9.5 Options
- 1.9.6 The control panel (HMI)
- 1.9.7 USB port (rear side)
- 1.9.8 Interface module slot
- 1.9.9 Analog interface
- 1.9.10 Share Bus-Connection
- 1.9.11 Sense connector (remote sensing)
- 1.9.12 Master-Slave bus
- 1.9.13 GPIB port (optional)
- 2. Installation & commissioning
- 2.1 Transport and storage
- 2.2 Unpacking and visual check
- 2.3 Installation
- 2.3.1 Safety procedures before installation and use
- 2.3.2 Preparation
- 2.3.3 Installing the device
- 2.3.4 Connection to AC supply
- 2.3.5 Connection to DC loads
- 2.3.6 Grounding of the DC output
- 2.3.7 Connection of remote sensing
- 2.3.8 Installation of an AnyBus interface module
- 2.3.9 Connecting the analog interface
- 2.3.10 Connecting the “Share” bus
- 2.3.11 Connecting the USB port (rear side)
- 2.3.12 Initial commission
- 2.3.13 Commission after a firmware update or a long period of non-use
- 3. Operation and application
- 3.1 Personal safety
- 3.2 Operating modes
- 3.3 Alarm conditions
- 3.4 Manual operation
- 3.5 Remote control
- 3.6 Alarms and monitoring
- 3.7 Control panel (HMI) lock
- 3.8 Loading and saving a user profile
- 3.9 The function generator
- 3.9.1 Introduction
- 3.9.2 General
- 3.9.3 Method of operation
- 3.9.4 Manual operation
- 3.9.5 Sine wave function
- 3.9.6 Triangular function
- 3.9.7 Rectangular function
- 3.9.8 Trapezoidal function
- 3.9.9 DIN 40839 function
- 3.9.10 Arbitrary function
- 3.9.11 Ramp Function
- 3.9.12 UI and IU table functions (XY table)
- 3.9.13 PV table function (photovoltaics)
- 3.9.14 FC table function (fuel cell)
- 3.9.15 Remote control of the function generator
- 3.10 Other applications
- 4. Service and maintenance
- 5. Accessories and options
- 6. Service & Support
- 1. General
Page 41
EA Elektro-Automatik GmbH
Helmholtzstr. 31-33 • 41747 Viersen
Germany
Fon: +49 2162 / 3785-0
Fax: +49 2162 / 16230
www.elektroautomatik.de
ea1974@elektroautomatik.de
PSI 9000 2U Series
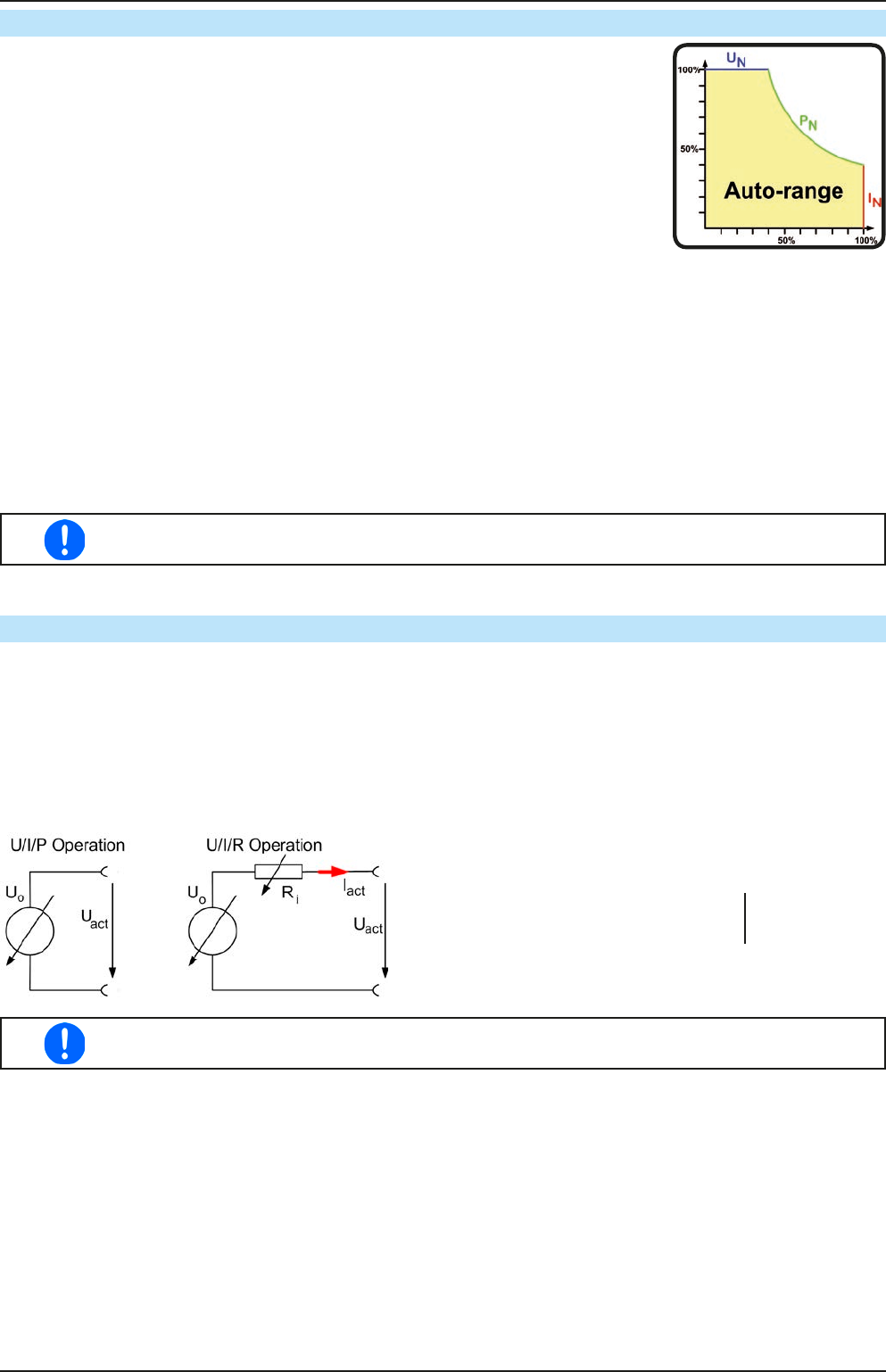
3.2.3 Power regulation / constant power / power limiting
Power regulation, also known as power limiting or constant power (CP), keeps the
DC output power of a power supply constant if the current owing to the load in
relation to the output voltage and the resistance of load reaches the adjusted value
according to P = U * I resp. P = U² / R. The power limiting then regulates the output
current according to I = sqr(P / R), where R is the load’s resistance.
Power limiting operates according to the auto-range principle such that at lower
output voltages higher current ows and vice versa in order to maintain constant
power within the range P
N
(see diagram to the right).
While the DC output is switched on and constant power mode is active, then the
condition “CP mode active” will be shown on the graphic display by the abbrevia-
tion CP, as well stored as status which can also be read as a status message via
digital interface.
3.2.3.1 Power derating
Due to fusing and cross sections of conductors and the extended input voltage range, power supply models as
from 1500 W have a xed derating, which becomes active below a certain input voltage level (for value see „1.8.3.
Specic technical data“). It then derates the maximum available output power for a 1500 W model down to 1000 W
and for a 3000 W model down to 2500 W. The derating only affects the power stages, so the full range for power
set value adjustment remains, though the device will switch earlier to constant power operation. In this situation,
constant power operation can not be indicated by status “CP”. Active derating can then only be detected by read-
ing the actual values of voltage and current and by calculating the power.
No status “CP” available if the adjusted power set value (Psel) is bigger than the derated actual
output power of the device.
3.2.4 Internal resistance regulation
Internal resistance control (abbr. CR) of power supplies is the simulation of a virtual internal resistor which is in
series to the voltage source and thus also in series to the load. According to Ohm’s law, this causes a voltage
drop, which will result in a difference between adjusted output voltage and actual output voltage. This will work in
constant current mode as well as in constant power mode, but here the output voltage will differ even more from
the adjusted voltage, because then constant voltage is not active.
The adjustable resistance range is generally dened between 0 and 30 * U
NOM
/ I
NOM
of the particular model. The
voltage setting in dependency of the resistance set value and the output current is done by calculation of the mi-
crocontroller and thus will be signicantly slower the other controllers inside the control circuit. Clarication:
U
Set
= U
0
- I
Act
* R
Set
P
Set
, I
Set
With resistance mode being active, i.e. mode R/I, the function generator will be ofine.
Resistance mode is not available during master-slave operation (MS).










