Specifications
Power Train Systems Operation 32
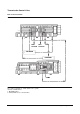
Modulating valve function
The modulating valve consists of 5 basic elements:
1. Orifice
2. Springs
3. Load piston
4. Modulating valve
5. Reaction slug
The function of the modulating valve is to control
clutch pressure during a shift. It allows the clutch
pressure to raise gently to the maximum transmission
pressure in order to provide a smooth clutch
engagement and a good shift feel for the vehicle
operator.
There are two forces acting on the modulation valve:
Force 1 = Pressure (load piston) / Area 1
Force 2 = Pressure (clutch) / Area 2
In order for the modulating valve to stay in a balance
position Force 1 must be equal to Force 2.
If for example Force 2 is too large (clutch pressure is
too large) then the valve will be forced to the left,
shutting off supply and opening the clutch and slug
pressure to drain, and reducing Force 2.
If Force 1 is too large then the valve would be forced
to the right, opening the clutch circuit to supply,
and increasing the value of Force 2 so it balances
Force 1. By regulating clutch pressures between
supply and drain, valve forces are balanced.
Figure 1
DR DR
DR
FLOW TO SELECTOR
SPOOLS
SPRING
LOAD PISTON
ORIFICE REACTION PLUG
PUMP
MODULATING VALVE