Service manual
Table Of Contents
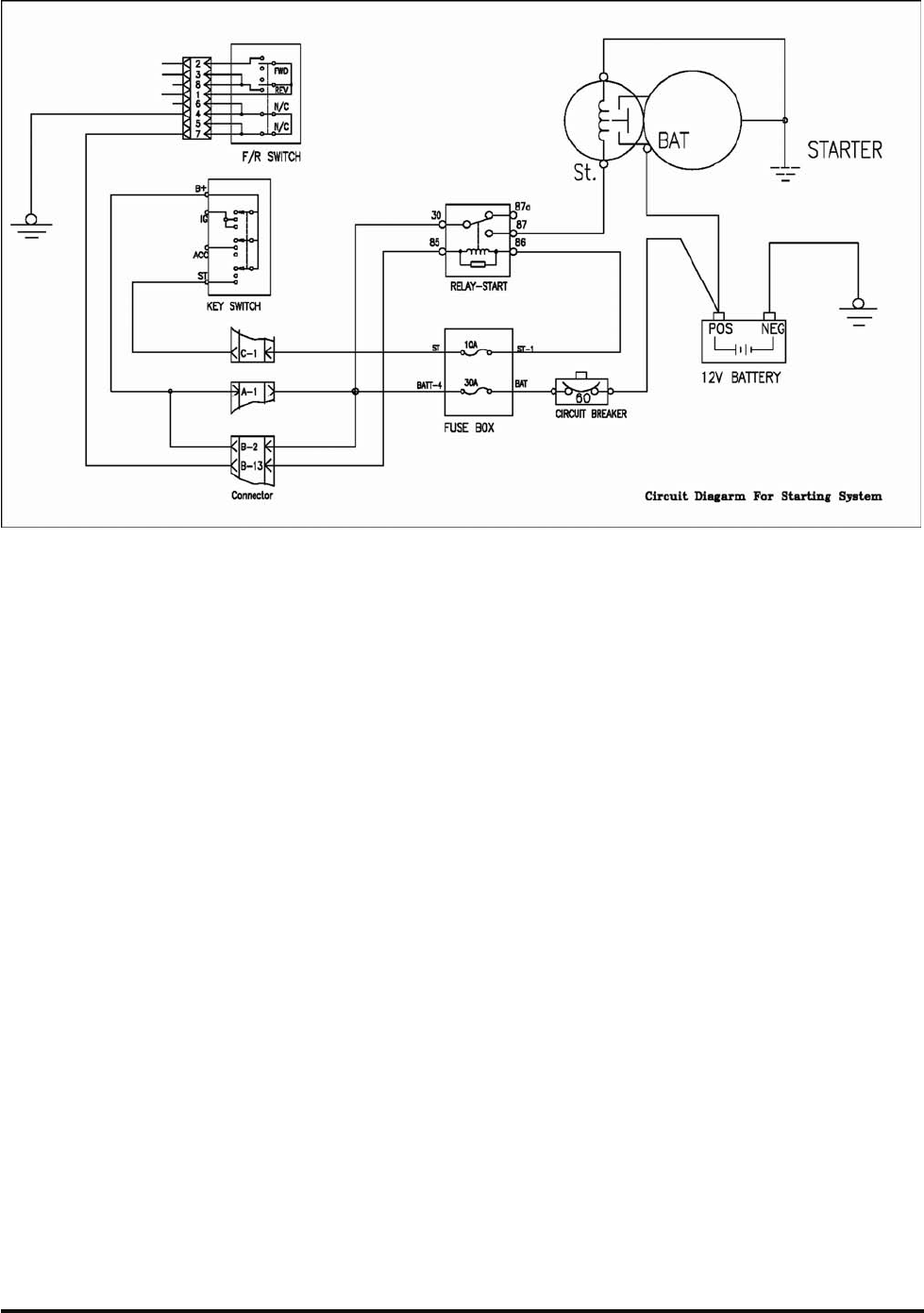
G420F(FE) Service Manual Chapter 4. Engine Electrical System 140
Diagnosis Procedure
The following simplified procedure is intended to
help the serviceman determine if a starting motor
needs to be removed and replaced or repaired. It is
not intended to cover all possible problems and
conditions, but to serve only as a guide. The most
common 12 volt circuit is shown and discussed.
General Information
All starting systems are made up of four elements.
They are the ignition switch, start relay, the starting
motor solenoid and starting motor.
Start switches are relatively low current devices.
They are rated to switch approximately 5 to 20 amps.
Because the coil of a start relay [between test point
(1)and (2)] draws about 1 amp, the start switch can
easily turn on the start relay and have long life.
The switch contacts of a typical start relay are rated
to switch 30 amps. Because the solenoid requires 5
to 20amps the start relay can easily switch this load.
The starting motor solenoid has two functions:
1. Engages the pinion with flywheel.
2. Is a high current switch rated about 1000 amps
that actually turns on the starting motor.
The starting motor solenoid has two coils. Pull-in
coil(W) draws about 40 amps and hold-in coil (X)
requires about 5 amps. The instant the start relay
closes, both coils (W) and (X) receive power. Battery
voltage is applied to the high end of both coils, at
test point (3)which is the start (S) terminal. The low
end of hold-in coil (X) is permanently grounded to
the ground post or motor housing of the starting
motor. Grounding for the low end, test point (4), of
pull-in coil (W) is momentary, and takes place
through the DC resistance of the starting motor. As
soon as magnetic force builds in both coils, the
pinion moves toward the flywheel ring gear. The
pinion will stop short of engagement of the flywheel
ring gear. Only then will the solenoid contacts close
to power the starting motor. This temporarily
removes the ground from pull-in coil (W), and puts
battery voltage on both ends of it while the starting
motor cranks. During this period, the pull-in coil is
out of the circuit. Cranking continues until power to
the solenoid is broken by releasing the ignition
switch.










