User Manual
Characteristic Min Typical Max
Input Voltage 2.5V
2.6V to 12V 14V
Output Voltage 2.5V 2.6V to 14V 15.5V
1
Continuous Input Current 0.5A
2
Continuous Output Current 0.5A
2
Output Ripple (Vp-p) 15mV 40mV 160mV
Quiescent current draw 6mA 15mA 32mA
3
Efficiency 75% 77%
Recommended ambient temperature range -20ºC
25ºC
55ºC
4
1
Max output
varies with manufacturing processes.
2
The 0.5A rating is for input and output voltages under 10V. For 10V and above, please see the
tables later on in the datasheet.
3
2.6V in, 14V out
4
Ambient temperatures higher than room temperature will decrease the amount of current AnyVolt
Micro can handle. For optimal performance, mount AnyVolt Micro in an open space with air
flowing across it.
Adjusting the output voltage
With the adjustment screw facing you, turning it clockwise increases the voltage, similar to the
volume control on a stereo system.
Current limits
Input and output current to/from the AnyVolt Micro should be kept track of with a multimeter if
you anticipate driving heavy loads.
Stepping up from a lower to a higher voltage means that there will be a higher current on the input
than the output. For this reason, it is important to make sure that both the input and output
current limits of 0.5A aren’t being exceeded. If for some reason you cannot use a multimeter to
monitor input current, you can also implicitly derive the input current using the input voltage,
output voltage, and output current.
Example:
The output of the AnyVolt Micro in a certain project is 12V, and it is supplying a constant 150mA.
What will the input current be if I am powering the AnyVolt Micro with a 5V supply?
“Power = Volts * Amps”
12V*0.15A = 1.8W
So the power output is 1.8W.
“Output power / efficiency = Input power”
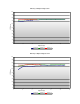
Looking at the efficiency curves of the AnyVolt Micro datasheet, efficiency is about 75% in this
situation.
1.8W / 0.75 = 2.4W
So the power going into the AnyVolt Micro is 2.4W
“Power / Volts = Amps”
2.4W / 5V = 0.48A
So the current at the AnyVolt Micro’s input is around 0.48A. This is within limits for now, but if
the input voltage supply were to drop significantly below 5V, the overcurrent condition would be
reached.