Specifications
Table Of Contents
- About This Manual
- 1.0 Introduction
- 2.0 Installation
- 3.0 Configuration Settings
- 4.0 Calibration
- 5.0 Scale Operations
- 5.1 Weight Unit Switching
- 5.2 Entering Tare Weights
- 5.2.1 One-Touch Tare, Tare Unknown
- 5.2.2 Digital Tare, Tare Weight Known
- 5.2.3 Tare Addition or Subtraction
- 5.2.4 Tare Exchange
- 5.3 Toggling Between Gross and Net
- 5.4 Entering Unit Weights
- 5.4.1 Unit Weight Operation by Sampling
- 5.4.2 Unit Weight Operation by Key Entry
- 5.5 Part Accumulation and Negative Counting - Without Recalling an Item Code
- 5.5.1 Part Accumulation
- 5.5.2 Negative Counting
- 5.5.3 Clearing Accumulated Data
- 5.6 Toggle Between Scales
- 5.7 Adding Parts To and Subtracting Parts From Inventory
- 5.7.1 Adding Parts to Inventory
- 5.7.2 Subtracting Parts From Inventory
- 5.7.3 Sample, Count and Print a Label
- 5.7.4 Scan ID Bar Code, Count and Print a Label
- 6.0 Scale Programming
- 6.1 Item Code Storage
- 6.1.1 Checking Memory Status
- 6.1.2 Program ID Code, Unit Weight, Tare Weight, Label Format, Part Name, Part Number, Lot Number, Location, Inventory Quantity, Threshold, and Setpoints
- 6.1.3 Delete Item Memory
- 6.2 Using Item Codes in Normal or Operation Mode
- 6.2.1 Recalling Numeric Item Codes using Item Code Number
- 6.2.2 Re-Computing Item Code Unit Weight
- 6.2.3 Quick Add Item to Memory
- 6.2.4 Tare Override
- 6.2.5 Inventory Operations Related to the Item Code Quantity
- 6.2.6 Delete Item Memory
- 6.3 Setting Tare in Operation Mode
- 6.3.1 One Touch Tare
- 6.3.2 Digital Tare (When Tare Weight is Known in Advance)
- 6.3.3 Tare Value Exchange (Tare Addition or Subtraction)
- 6.4 Setting a Lot Number
- 6.5 Setting a Sequence Number
- 7.0 External Printers, Barcode Scanners, Keyboards and Platforms
- 7.1 Connecting External Printers
- 7.1.1 SPEC Settings for External Printers
- 7.1.2 Connecting the Printer to the RS-232C Port
- 7.1.3 Eltron Printers
- 7.1.4 Epson Printers
- 7.2 Connecting a Barcode Scanner
- 7.2.1 Header Codes
- 7.2.2 Z Commands via Barcodes
- 7.2.3 Configuring the RS232C Port for a Scanner
- 7.2.4 Connecting the Scanner to the RS232C Port
- 7.2.5 Configuring the Keyboard Port for a Scanner
- 7.2.6 Programming the QSC-6000 Plus Quickscan RS232C Scanner
- 7.2.7 Programming the QuickScan Keyboard Wedge Scanner
- 7.3 Connecting the IBM Keyboard
- 7.4 Connecting an External Platform
- 8.0 Job Sequence Programming
- 9.0 Password Protecting the Programming Functions
- 10.0 DC-100 Error Message List
- 11.0 DC-100 Limited Warranty
48 DC-100 Operation Manual
7.2.2 Z Commands via Barcodes
You can also scan barcode representations of the scale’s Z commands. This allows the scale operator to use the
scanner to initiate certain scanner functions:
7.2.3 Configuring the RS232C Port for a Scanner
An RS232C scanner must be connected to the main port (next to the keyboard port). The spec settings should be
as follows:
Note: For instructions on how to set the DC-100’s customer specifications, refer to Section 3.1.
• SPEC 15: SIO Select job to 3:BARCODE SCANNER
• SPEC 16: Baud Rates (SIO) to the proper baud rate for your scanner
• SPEC 17: Data Length (SIO) to the proper length for your scanner
• SPEC 18: Parity Bit (SIO) to the proper setting for your scanner
• SPEC 19: Stop Bit (SIO) to the proper setting for your scanner
• SPEC 38: BAR CODE SCANNER (BCS) WITH HEADER to 0:Enable or 1:Disable depending on
whether the barcodes you are scanning have headers or not (see Header Codes above).
7.2.4 Connecting the Scanner to the RS232C Port
7.2.5 Configuring the Keyboard Port for a Scanner
A wedge scanner (a type of scanner which emulates a keyboard) can be connected to the IBM KEYBRD port. If
you choose this option, the spec settings should be as follows:
Note: For instructions on how to set the DC-100’s customer specifications, refer to Section 3.1.
• SPEC 37: IBM KEYBOARD PORT to 0:Barcode Scanner
• SPEC 38: BAR CODE SCANNER (BCS) WITH HEADER to 0:Enable or 1:Disable depending on
whether the barcodes you are scanning have headers or not (see Header Codes above).
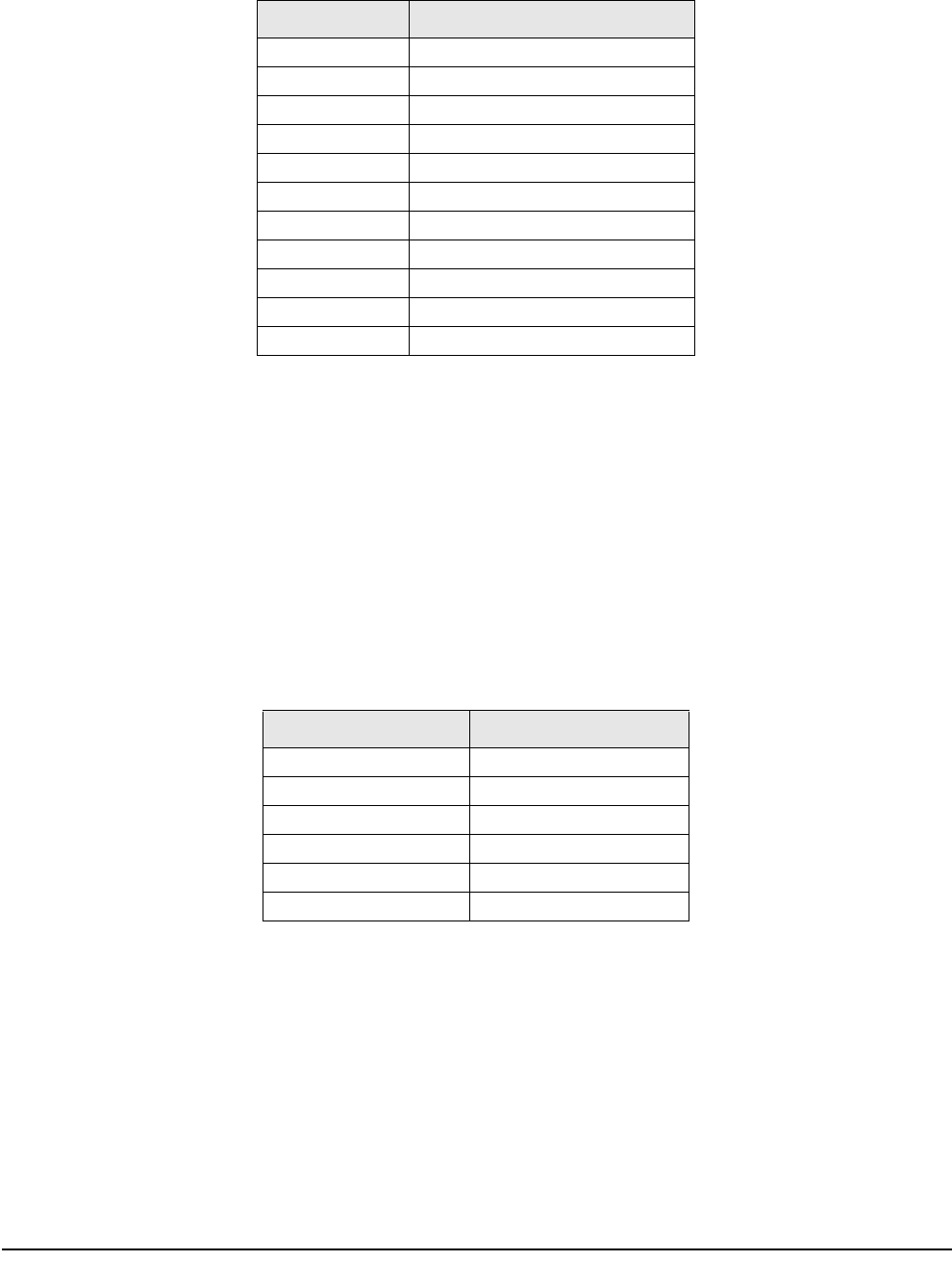
Z Command Function
Z0 Rezero
Z1 Print
Z2 Unit Weight Clear
Z3 Plus
Z4 Minus
Z5 Tare
Z6 Clear
ZS1 Scale 1
ZS2 Scale 2
ZS3 Scale 3
ZS4 Scale 4
Table 7-4. Z Command Functions
Pin Number Signal
2 GND
4 RXD
5 TXD
7 RTS
1 CTS
8 VCC
Table 7-5. Pin Configuration for Barcode Scanner RS232C Connection










