User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- S3C2450 User's Manual
- About this Document
- Table of Contents
- 01-Overview
- 02-SYSCON
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 FEATURE
- 3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 4 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
- 5 CLOCK MANAGEMENT
- 6 POWER MANAGEMENT
- 7 REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
- 8 INDIVIDUAL REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
- 8.1 CLOCK SOURCE CONTROL REGISTERS (LOCKCON0, LOCKCON1, OSCSET, MPLLCON, AND EPLLCON)
- 8.2 CLOCK CONTROL REGISTER (CLKSRC, CLKDIV, HCLKCON, PCLKCON, AND SCLKCON)
- 8.3 POWER MANAGEMENT REGISTERS (PWRMODE AND PWRCFG)
- 8.4 RESET CONTROL REGISTERS (SWRST AND RSTCON)
- 8.5 CONTROL OF RETENTION PAD(I/O) WHEN NORMAL MODE AND WAKE-UP FROM SLEEP MODE.
- 8.6 SYSTEM CONTROLLER STATUS REGISTERS (WKUPSTAT AND RSTSTAT)
- 8.7 BUS CONFIGURATION REGISTER (BUSPRI0, BUSPRI1, AND BUSMISC)
- 8.8 INFORMATION REGISTER 0,1,2,3
- 8.9 USB PHY CONTROL REGISTER (PHYCTRL)
- 8.10 USB PHY POWER CONTROL REGISTER (PHYPWR)
- 8.11 USB RESET CONTROL REGISTER (URSTCON)
- 8.12 USB CLOCK CONTROL REGISTER (UCLKCON)
- 03-MATRIX & EBI
- 04-Bus Priority
- 05-SMC
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 FEATURE
- 3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 4 SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 4.1 BANK IDLE CYCLE CONTROL REGISTERS 0-5
- 4.2 BANK READ WAIT STATE CONTROL REGISTERS 0-5
- 4.3 BANK WRITE WAIT STATE CONTROL REGISTERS 0-5
- 4.4 BANK OUTPUT ENABLE ASSERTION DELAY CONTROL REGISTERS 0-5
- 4.5 BANK WRITE ENABLE ASSERTION DELAY CONTROL REGISTERS 0-5
- 4.6 BANK CONTROL REGISTERS 0-5
- 4.7 BANK ONENAND TYPE SELECTION REGISTER
- 4.8 SMC STATUS REGISTER
- 4.9 SMC CONTROL REGISTER
- 06-DRAMC
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 3 MOBILE DRAM INITIALIZATION SEQUENCE
- 3.1 MOBILE DRAM(SDRAM OR MOBILE DDR) INITIALIZATION SEQUENCE
- 3.2 DDR2 INITIALIZATION SEQUENCE
- 3.3 MOBILE DRAM CONFIGURATION REGISTER
- 3.4 MOBILE DRAM CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.5 MOBILE DRAM TIMMING CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.6 MOBILE DRAM (EXTENDED ) MODE REGISTER SET REGISTER
- 3.7 MOBILE DRAM REFRESH CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.8 MOBILE DRAM WRITE BUFFER TIME OUT REGISTER
- 07-Nand Flash
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 FEATURES
- 3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 4 BOOT LOADER FUNCTION
- 5 GPC5/6/7 PIN CONFIGURATION TABLE IN IROM BOOT MODE
- 6 NAND FLASH MEMORY TIMING
- 7 NAND FLASH ACCESS
- 8 DATA REGISTER CONFIGURATION
- 9 STEPPINGSTONE (8KB IN 64KB SRAM)
- 10 1BIT / 4BIT / 8BIT ECC (ERROR CORRECTION CODE)
- 11 MEMORY MAPPING(NAND BOOT AND OTHER BOOT)
- 12 NAND FLASH MEMORY CONFIGURATION
- 13 NAND FLASH CONTROLLER SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 13.1 NAND FLASH CONTROLLER REGISTER MAP
- 13.2 NAND FLASH CONFIGURATION REGISTER
- 13.3 CONTROL REGISTER
- 13.4 COMMAND REGISTER
- 13.5 ADDRESS REGISTER
- 13.6 DATA REGISTER
- 13.7 MAIN DATA AREA ECC REGISTER
- 13.8 SPARE AREA ECC REGISTER
- 13.9 PROGRMMABLE BLOCK ADDRESS REGISTER
- 13.10 NFCON STATUS REGISTER
- 13.11 ECC0/1 ERROR STATUS REGISTER
- 13.12 MAIN DATA AREA ECC0 STATUS REGISTER
- 13.13 SPARE AREA ECC STATUS REGISTER
- 13.14 4-BIT ECC ERROR PATTEN REGISTER
- 13.15 ECC 0/1/2 FOR 8BIT ECC STATUS REGISTER
- 13.16 8BIT ECC MAIN DATA ECC 0/1/2/3 STATUS REGISTER
- 13.17 8BIT ECC ERROR PATTERN REGISTER
- 08-CF controller
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 INDIVIDUAL REGISTER DESCRIPTIONS
- 2.1 MUX_REG REGISTER
- 2.2 PCCARD CONFIGURATION & STATUS REGISTER
- 2.3 PCCARD INTERRUPT MASK & SOURCE REGISTER
- 2.4 PCCARD_ATTR REGISTER
- 2.5 PCCARD_I/O REGISTER
- 2.6 PCCARD_COMM REGISTER
- 2.7 ATA_CONTROL REGISTER
- 2.8 ATA_STATUS REGISTER
- 2.9 ATA_COMMAND REGISTER
- 2.10 ATA_SWRST REGISTER
- 2.11 ATA_IRQ REGISTER
- 2.12 ATA_IRQ_MASK REGISTER
- 2.13 ATA_CFG REGISTER
- 2.14 ATA_PIO_TIME REGISTER
- 2.15 ATA_XFR_NUM REGISTER
- 2.16 ATA_XFR_CNT REGISTER
- 2.17 ATA_TBUF_START REGISTER
- 2.18 ATA_TBUF_SIZE REGISTER
- 2.19 ATA_SBUF_START REGISTER
- 2.20 ATA_SBUF_SIZE REGISTER
- 2.21 ATA_CADDR_TBUF REGISTER
- 2.22 ATA_CADDR_SBUF REGISTER
- 2.23 ATA_PIO_DTR REGISTER
- 2.24 ATA_PIO_FED REGISTER
- 2.25 ATA_PIO_SCR REGISTER
- 2.26 ATA_PIO_LLR REGISTER
- 2.27 ATA_PIO_LMR REGISTER
- 2.28 ATA_PIO_LMR REGISTER
- 2.29 ATA_PIO_DVR REGISTER
- 2.30 ATA_PIO_CSD REGISTER
- 2.31 ATA_PIO_DAD REGISTER
- 2.32 ATA_PIO_RDATA REGISTER
- 2.33 BUS_FIFO_STATUS REGISTER
- 2.34 ATA_FIFO_STATUS REGISTER
- 09-DMA controller
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 DMA REQUEST SOURCES
- 3 DMA OPERATION
- 4 DMA SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 4.1 DMA INITIAL SOURCE REGISTER (DISRC)
- 4.2 DMA INITIAL SOURCE CONTROL REGISTER (DISRCC)
- 4.3 DMA INITIAL DESTINATION REGISTER (DIDST)
- 4.4 DMA INITIAL DESTINATION CONTROL REGISTER (DIDSTC)
- 4.5 DMA CONTROL REGISTER (DCON)
- 4.6 DMA STATUS REGISTER (DSTAT)
- 4.7 DMA CURRENT SOURCE REGISTER (DCSRC)
- 4.8 CURRENT DESTINATION REGISTER (DCDST)
- 4.9 DMA MASK TRIGGER REGISTER (DMASKTRIG)
- 4.10 DMA REQUESET SELECTION REGISTER (DMAREQSEL)
- 10-Interrupt controller
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 INTERRUPT CONTROLLER SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 2.1 SOURCE PENDING (SRCPND) REGISTER
- 2.2 INTERRUPT MODE (INTMOD) REGISTER
- 2.3 INTERRUPT MASK (INTMSK) REGISTER
- 2.4 INTERRUPT PENDING (INTPND) REGISTER
- 2.5 INTERRUPT OFFSET (INTOFFSET) REGISTER
- 2.6 SUB SOURCE PENDING (SUBSRCPND) REGISTER
- 2.7 INTERRUPT SUB MASK (INTSUBMSK) REGISTER
- 2.8 PRIORITY MODE REGISTER (PRIORITY_MODE)
- 2.9 PRIORITY UPDATE REGISTER (PRIORITY_UPDATE)
- 11-IOport
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 PORT CONTROL DESCRIPTIONS
- 3 I/O PORT CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.1 PORT A CONTROL REGISTERS (GPACON, GPADAT)
- 3.2 PORT B CONTROL REGISTERS (GPBCON, GPBDAT, GPBUDP, GPBSEL)
- 3.3 PORT C CONTROL REGISTERS (GPCCON, GPCDAT, GPCUDP)
- 3.4 PORT D CONTROL REGISTERS (GPDCON, GPDDAT, GPDUDP)
- 3.5 PORT E CONTROL REGISTERS (GPECON, GPEDAT, GPEUDP, GPESEL)
- 3.6 PORT F CONTROL REGISTERS (GPFCON, GPFDAT, GPFUDP)
- 3.7 PORT G CONTROL REGISTERS (GPGCON, GPGDAT, GPGUDP)
- 3.8 PORT H CONTROL REGISTERS (GPHCON, GPHDAT, GPHUDP)
- 3.9 PORT J CONTROL REGISTERS (GPJCON, GPJDAT, GPJUDP, GPJSEL)
- 3.10 PORT K CONTROL REGISTERS (GPKCON, GPKDAT, GPKUDP)
- 3.11 PORT L CONTROL REGISTERS (GPLCON, GPLDAT, GPLUDP, GPLSEL)
- 3.12 PORT M CONTROL REGISTERS (GPMCON, GPMDAT, GPMUDP)
- 3.13 MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL REGISTER (MISCCR)
- 3.14 DCLK CONTROL REGISTERS (DCLKCON)
- 3.15 EXTINTn (External Interrupt Control Register n)
- 3.16 EINTFLTn (External Interrupt Filter Register n)
- 3.17 EINTMASK (External Interrupt Mask Register)
- 3.18 EINTPEND (External Interrupt Pending Register)
- 3.19 GSTATUSn (General Status Registers)
- 3.20 DSCn (Drive Strength Control)
- 3.21 PDDMCON (Power Down SDRAM Control Register)
- 3.22 PDSMCON (Power Down SRAM Control Register)
- 4 GPIO ALIVE & SLEEP PART
- 12-Watchdog
- 13-PWM Timer
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 PWM TIMER OPERATION
- 3 PWM TIMER CONTROL REGISTERS
- 3.1 TIMER CONFIGURATION REGISTER0 (TCFG0)
- 3.2 TIMER CONFIGURATION REGISTER1 (TCFG1)
- 3.3 TIMER CONTROL (TCON) REGISTER
- 3.4 TIMER 0 COUNT BUFFER REGISTER & COMPARE BUFFER REGISTER (TCNTB0/TCMPB0)
- 3.5 TIMER 0 COUNT OBSERVATION REGISTER (TCNTO0)
- 3.6 TIMER 1 COUNT BUFFER REGISTER & COMPARE BUFFER REGISTER (TCNTB1/TCMPB1)
- 3.7 TIMER 1 COUNT OBSERVATION REGISTER (TCNTO1)
- 3.8 TIMER 2 COUNT BUFFER REGISTER & COMPARE BUFFER REGISTER (TCNTB2/TCMPB2)
- 3.9 TIMER 2 COUNT OBSERVATION REGISTER (TCNTO2)
- 3.10 TIMER 3 COUNT BUFFER REGISTER & COMPARE BUFFER REGISTER (TCNTB3/TCMPB3)
- 3.11 TIMER 3 COUNT OBSERVATION REGISTER (TCNTO3)
- 3.12 TIMER 4 COUNT BUFFER REGISTER (TCNTB4)
- 3.13 TIMER 4 COUNT OBSERVATION REGISTER (TCNTO4)
- 14-RTC
- 15-UART
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 3 UART SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 3.1 UART LINE CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.2 UART CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.3 UART FIFO CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.4 UART MODEM CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.5 UART TX/RX STATUS REGISTER
- 3.6 UART ERROR STATUS REGISTER
- 3.7 UART FIFO STATUS REGISTER
- 3.8 UART MODEM STATUS REGISTER
- 3.9 UART TRANSMIT BUFFER REGISTER (HOLDING REGISTER & FIFO REGISTER)
- 3.10 UART RECEIVE BUFFER REGISTER (HOLDING REGISTER & FIFO REGISTER)
- 3.11 UART BAUD RATE DIVISOR REGISTER
- 3.12 UART DIVIDING SLOT REGISTER
- 16-USB HOST Controller
- 17-USB 2.0 Device
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 3 TO ACTIVATE USB PORT1 FOR USB 2.0 FUNCTION
- 4 SIE (SERIAL INTERFACE ENGINE)
- 5 UPH (UNIVERSAL PROTOCOL HANDLER)
- 6 UTMI (USB 2.0 TRANSCEIVER MACROCELL INTERFACE)
- 7 USB 2.0 FUNCTION CONTROLLER SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 8 REGISTERS
- 8.1 INDEX REGISTER (IR)
- 8.2 ENDPOINT INTERRUPT REGISTER (EIR)
- 8.3 ENDPOINT INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER (EIER)
- 8.4 FUNCTION ADDRESS REGISTER (FAR)
- 8.5 ENDPOINT DIRECTION REGISTER (EDR)
- 8.6 TEST REGISTER (TR)
- 8.7 SYSTEM STATUS REGISTER (SSR)
- 8.8 SYSTEM CONTROL REGISTER (SCR)
- 8.9 EP0 STATUS REGISTER (EP0SR)
- 8.10 EP0 CONTROL REGISTER (EP0CR)
- 8.11 ENDPOINT# BUFFER REGISTER (EP#BR)
- 8.12 ENDPOINT STATUS REGISTER (ESR)
- 8.13 ENDPOINT CONTROL REGISTER (ECR)
- 8.14 BYTE READ COUNT REGISTER (BRCR)
- 8.15 BYTE WRITE COUNT REGISTER (BWCR)
- 8.16 MAX PACKET REGISTER (MPR)
- 8.17 DMA CONTROL REGISTER (DCR)
- 8.18 DMA TRANSFER COUNTER REGISTER (DTCR)
- 8.19 DMA FIFO COUNTER REGISTER (DFCR)
- 8.20 DMA TOTAL TRANSFER COUNTER REGISTER 1/2 (DTTCR 1/2)
- 8.21 DMA INTERFACE CONTROL REGISTER (DICR)
- 8.22 MEMORY BASE ADDRESS REGISTER (MBAR)
- 8.23 MEMORY CURRENT ADDRESS REGISTER (MCAR)
- 8.24 BURST FIFO CONTROL REGISTER(FCON)
- 8.25 BURST FIFO STATUS REGISTER(FSTAT)
- 8.26 AHB MASTER(DMA) OPERATION FLOW CHART
- 18-IIC bus interface
- 19-2D
- 20-HSSPI
- 21-HSMMC
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 FEATURES
- 3 BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 4 SEQUENCE
- 4.1 SD CARD DETECTION SEQUENCE
- 4.2 SD CLOCK SUPPLY SEQUENCE
- 4.3 SD CLOCK STOP SEQUENCE
- 4.4 SD CLOCK FREQUENCY CHANGE SEQUENCE
- 4.5 SD BUS POWER CONTROL SEQUENCE
- 4.6 CHANGE BUS WIDTH SEQUENCE
- 4.7 TIMEOUT SETTING FOR DAT LINE
- 4.8 SD TRANSACTION GENERATION
- 4.9 SD COMMAND ISSUE SEQUENCE
- 4.10 COMMAND COMPLETE SEQUENCE
- 4.11 TRANSACTION CONTROL WITH DATA TRANSFER USING DAT LINE
- 4.12 ABORT TRANSACTION
- 5 SDI SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 5.1 CONFIGURATION REGISTER TYPES
- 5.2 SDMA SYSTEM ADDRESS REGISTER
- 5.3 BLOCK SIZE REGISTER
- 5.4 BLOCK COUNT REGISTER
- 5.5 ARGUMENT REGISTER
- 5.6 TRANSFER MODE REGISTER
- 5.7 COMMAND REGISTER
- 5.8 RESPONSE REGISTER
- 5.9 BUFFER DATA PORT REGISTER
- 5.10 PRESENT STATE REGISTER
- 5.11 HOST CONTROL REGISTER
- 5.12 POWER CONTROL REGISTER
- 5.13 BLOCK GAP CONTROL REGISTER
- 5.14 WAKEUP CONTROL REGISTER
- 5.15 CLOCK CONTROL REGISTER
- 5.16 TIMEOUT CONTROL REGISTER
- 5.17 SOFTWARE RESET REGISTER
- 5.18 NORMAL INTERRUPT STATUS REGISTER
- 5.19 ERROR INTERRUPT STATUS REGISTER
- 5.20 NORMAL INTERRUPT STATUS ENABLE REGISTER
- 5.21 ERROR INTERRUPT STATUS ENABLE REGISTER
- 5.22 NORMAL INTERRUPT SIGNAL ENABLE REGISTER
- 5.23 ERROR INTERRUPT SIGNAL ENABLE REGISTER
- 5.24 AUTOCMD12 ERROR STATUS REGISTER
- 5.25 CAPABILITIES REGISTER
- 5.26 MAXIMUM CURRENT CAPABILITIES REGISTER
- 5.27 CONTROL REGISTER 2
- 5.28 CONTROL REGISTER 3
- 5.29 DEBUG REGISTER
- 5.30 CONTROL REGISTER 4
- 5.31 FORCE EVENT REGISTER FOR AUTO CMD12 ERROR STATUS
- 5.32 FORCE EVENT REGISTER FOR ERROR INTERRUPT STATUS
- 5.33 ADMA ERROR STATUS REGISTER
- 5.34 ADMA SYSTEM ADDRESS REGISTER
- 5.35 HOST CONTROLLER VERSION REGISTER
- 22-LCD controller
- 23-Camera Interface
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 EXTERNAL INTERFACE
- 3 EXTERNAL/INTERNAL CONNECTION GUIDE
- 4 CAMERA INTERFACE OPERATION
- 5 SOFTWARE INTERFACE
- 6 CAMERA INTERFACE SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 6.1 SOURCE FORMAT REGISTER
- 6.2 WINDOW OPTION REGISTER
- 6.3 GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTER
- 6.4 WINDOW OPTION REGISTER 2
- 6.5 Y1 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.6 Y2 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.7 Y3 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.8 Y4 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.9 CB1 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.10 CB2 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.11 CB3 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.12 CB4 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.13 CR1 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.14 CR2 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.15 CR3 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.16 CR4 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.17 CODEC TARGET FORMAT REGISTER
- 6.18 CODEC DMA CONTROL REGISTER
- 6.19 REGISTER SETTING GUIDE FOR CODEC SCALER AND PREVIEW SCALER
- 6.20 CODEC PRE-SCALER CONTROL REGISTER 1
- 6.21 CODEC PRE-SCALER CONTROL REGISTER 2
- 6.22 CODEC MAIN-SCALER CONTROL REGISTER
- 6.23 CODEC DMA TARGET AREA REGISTER
- 6.24 CODEC STATUS REGISTER
- 6.25 RGB1 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.26 RGB2 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.27 RGB3 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.28 RGB4 START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.29 PREVIEW TARGET FORMAT REGISTER
- 6.30 PREVIEW DMA CONTROL REGISTER
- 6.31 PREVIEW PRE-SCALER CONTROL REGISTER 1
- 6.32 PREVIEW PRE-SCALER CONTROL REGISTER 2
- 6.33 PREVIEW MAIN-SCALER CONTROL REGISTER
- 6.34 PREVIEW DMA TARGET AREA REGISTER
- 6.35 PREVIEW STATUS REGISTER
- 6.36 IMAGE CAPTURE ENABLE REGISTER
- 6.37 CODEC CAPTURE SEQUENCE REGISTER
- 6.38 CODEC SCAN LINE OFFSET REGISTER
- 6.39 PREVIEW SCAN LINE OFFSET REGISTER
- 6.40 IMAGE EFFECTS REGISTER
- 6.41 MSDMA Y START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.42 MSDMA CB START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.43 MSDMA CR START ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.44 MSDMA Y END ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.45 MSDMA CB END ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.46 MSDMA CR END ADDRESS REGISTER
- 6.47 MSDMA Y OFFSET REGISTER
- 6.48 MSDMA CB OFFSET REGISTER
- 6.49 MSDMA CR OFFSET REGISTER
- 6.50 MSDMA SOURCE IMAGE WIDTH REGISTER
- 6.51 MSDMA CONTROL REGISTER
- 24-TSADC
- 25-IIS Interface
- 26-IIS Multi Audio Interface
- 27-AC97 Controller
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 AC97 CONTROLLER OPERATION
- 3 OPERATION FLOW CHART
- 4 AC-LINK DIGITAL INTERFACE PROTOCOL
- 5 AC97 POWER-DOWN
- 6 CODEC RESET
- 7 AC97 CONTROLLER STATE DIAGRAM
- 8 AC97 CONTROLLER SPECIAL REGISTERS
- 8.1 AC97 SPECIAL FUNCION REGISTER SUMMARY
- 8.2 AC97 GLOBAL CONTROL REGISTER (AC_GLBCTRL)
- 8.3 AC97 GLOBAL STATUS REGISTER (AC_GLBSTAT)
- 8.4 AC97 CODEC COMMAND REGISTER (AC_CODEC_CMD)
- 8.5 AC97 CODEC STATUS REGISTER (AC_CODEC_STAT)
- 8.6 AC97 PCM OUT/IN CHANNEL FIFO ADDRESS REGISTER (AC_PCMADDR)
- 8.7 AC97 MIC IN CHANNEL FIFO ADDRESS REGISTER (AC_MICADDR)
- 8.8 AC97 PCM OUT/IN CHANNEL FIFO DATA REGISTER (AC_PCMDATA)
- 8.9 AC97 MIC IN CHANNEL FIFO DATA REGISTER (AC_MICDATA)
- 28-PCM Audio Interface
- 1 OVERVIEW
- 2 PCM AUDIO INTERFACE
- 3 PCM TIMING
- 3.1 PCM INPUT CLOCK DIAGRAM
- 3.2 PCM REGISTERS
- 3.3 PCM REGISTER SUMMARY
- 3.4 PCM CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.5 PCM CLK CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.6 THE PCM TX FIFO REGISTER
- 3.7 PCM RX FIFO REGISTER
- 3.8 PCM INTERRUPT CONTROL REGISTER
- 3.9 PCM INTERRUPT STATUS REGISTER
- 3.10 PCM FIFO STATUS REGISTER
- 3.11 PCM INTERRUPT CLEAR REGISTER
- 29-ELECTRICAL DATA
- 30-MECHANICAL DATA
S3C2450X RISC MICROPROCESSOR STATIC MEMORY CONTROLLER
5-7
3.3 SYNCHRONOUS READ/SYNCHRONOUS BURST READ
Single synchronous read operations have the same control signal timing as an asynchronous read operation, but
with different timing requirements for setup and hold relative to the clock. Because the output signals of the SMC
are generated internally from clocked logic, the timing for single synchronous reads is the same as for
asynchronous reads.
Synchronous burst read transfers are performed differently to asynchronous burst reads, because of the internal
address incrementing performed by synchronous burst devices. The PADDR outputs are held with the initial
address value, and the PSMAVD output is asserted during the transfer to indicate that the address is valid.
Four, eight, or continuous synchronous burst lengths are supported, and are controlled by the BurstLenRead bits
in the Bank Control Register SMBCRx when the SyncEnRead and BMRead bits indicate that the device supports
synchronous bursts.
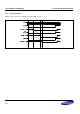
Figure 5-7 shows continuous burst read transfers, where WSTRD = 3 and WSTBRD = 0.
Synchronous Burst READ
SMCLK
ADDR
DATA(IN)
nCS
nOE
SMAVD
D(A)
D(A+4) D(A+8)
D(A+C)
A
WSTRD=3
Figure 5-7. External Synchronous Fixed Length Four Transfer Burst Read