Data Sheet
Table Of Contents
- 1.0 Device Overview
- 2.0 Can Message Frames
- 3.0 Message Transmission
- 4.0 Message Reception
- 5.0 Bit Timing
- 6.0 Error Detection
- 7.0 Interrupts
- 8.0 Oscillator
- 9.0 RESET
- 10.0 Modes of Operation
- 11.0 Register Map
- 12.0 SPI™ Interface
- 12.1 Overview
- 12.2 Reset Instruction
- 12.3 Read Instruction
- 12.4 Read RX Buffer Instruction
- 12.5 Write Instruction
- 12.6 Load TX Buffer Instruction
- 12.7 Request-To-Send (RTS) Instruction
- 12.8 Read Status Instruction
- 12.9 RX Status Instruction
- 12.10 Bit Modify Instruction
- Figure 12-1: Bit Modify
- Table 12-1: SPI™ Instruction Set
- Figure 12-2: Read instruction
- Figure 12-3: Read RX Buffer Instruction
- Figure 12-4: Byte Write instruction
- Figure 12-5: Load TX Buffer
- Figure 12-6: Request-to-send (RTS) instruction
- Figure 12-7: BIT Modify instruction
- Figure 12-8: Read Status instruction
- Figure 12-9: RX StatUs Instruction
- Figure 12-10: SPI™ Input Timing
- Figure 12-11: SPI™ Output TIming
- 13.0 Electrical Characteristics
- 14.0 PackAging Information
© 2005 Microchip Technology Inc. Preliminary DS21801D-page 55
MCP2515
9.0 RESET
The MCP2515 differentiates between two resets:
1. Hardware Reset – Low on RESET
pin.
2. SPI Reset – Reset via SPI command.
Both of these resets are functionally equivalent. It is
important to provide one of these two resets after
power-up to ensure that the logic and registers are in
their default state. A hardware reset can be achieved
automatically by placing an RC on the RESET
pin. (see
Figure 9-1). The values must be such that the device is
held in reset for a minimum of 2 µs after VDD reaches
operating voltage, as indicated in the electrical
specification (tRL).
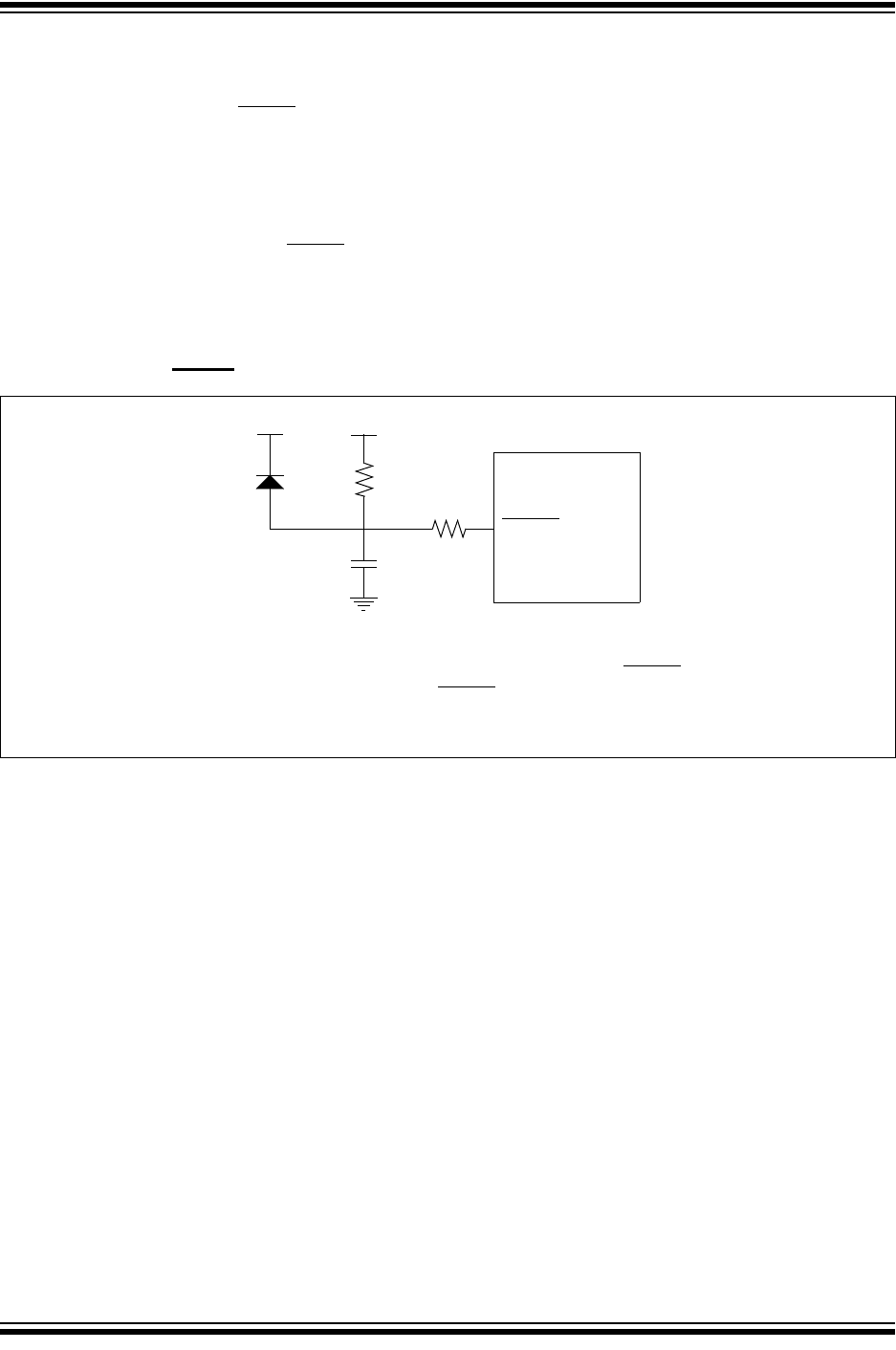
FIGURE 9-1: RESET PIN CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE
RESET
R1
(2)
VDD
VDD
R
C
D
(1)
Note 1: The diode D helps discharge the capacitor quickly when VDD powers down.
2: R1 = 1 kΩ to 10 kΩ will limit any current flowing into RESET
from external
capacitor C, in the event of RESET
pin breakdown due to Electrostatic
Discharge (ESD) or Electrical Overstress (EOS).










