Concept Guide
Table Of Contents
- About this Guide
- About Instant
- Setting up a W-IAP
- Automatic Retrieval of Configuration
- Instant User Interface
- Initial Configuration Tasks
- Customizing W-IAP Settings
- Modifying the W-IAP Host Name
- Configuring Zone Settings on a W-IAP
- Specifying a Method for Obtaining IP Address
- Configuring External Antenna
- Configuring Radio Profiles for a W-IAP
- Configuring Uplink VLAN for a W-IAP
- Changing the W-IAP Installation Mode
- Changing USB Port Status
- Master Election and Virtual Controller
- Adding a W-IAP to the Network
- Removing a W-IAP from the Network
- VLAN Configuration
- IPv6 Support
- Wireless Network Profiles
- Configuring Wireless Network Profiles
- Configuring Fast Roaming for Wireless Clients
- Configuring Modulation Rates on a WLAN SSID
- Multi-User-MIMO
- Management Frame Protection
- Disabling Short Preamble for Wireless Client
- Editing Status of a WLAN SSID Profile
- Editing a WLAN SSID Profile
- Deleting a WLAN SSID Profile
- Wired Profiles
- Captive Portal for Guest Access
- Understanding Captive Portal
- Configuring a WLAN SSID for Guest Access
- Configuring Wired Profile for Guest Access
- Configuring Internal Captive Portal for Guest Network
- Configuring External Captive Portal for a Guest Network
- Configuring Facebook Login
- Configuring Guest Logon Role and Access Rules for Guest Users
- Configuring Captive Portal Roles for an SSID
- Configuring Walled Garden Access
- Authentication and User Management
- Managing W-IAP Users
- Supported Authentication Methods
- Supported EAP Authentication Frameworks
- Configuring Authentication Servers
- Understanding Encryption Types
- Configuring Authentication Survivability
- Configuring 802.1X Authentication for a Network Profile
- Enabling 802.1X Supplicant Support
- Configuring MAC Authentication for a Network Profile
- Configuring MAC Authentication with 802.1X Authentication
- Configuring MAC Authentication with Captive Portal Authentication
- Configuring WISPr Authentication
- Blacklisting Clients
- Uploading Certificates
- Roles and Policies
- DHCP Configuration
- Configuring Time-Based Services
- Dynamic DNS Registration
- VPN Configuration
- IAP-VPN Deployment
- Adaptive Radio Management
- Deep Packet Inspection and Application Visibility
- Voice and Video
- Services
- Configuring AirGroup
- Configuring a W-IAP for RTLS Support
- Configuring a W-IAP for Analytics and Location Engine Support
- Managing BLE Beacons
- Clarity Live
- Configuring OpenDNS Credentials
- Integrating a W-IAP with Palo Alto Networks Firewall
- Integrating a W-IAP with an XML API Interface
- CALEA Integration and Lawful Intercept Compliance
- Cluster Security
- W-IAP Management and Monitoring
- Uplink Configuration
- Intrusion Detection
- Mesh W-IAP Configuration
- Mobility and Client Management
- Spectrum Monitor
- W-IAP Maintenance
- Monitoring Devices and Logs
- Hotspot Profiles
- ClearPass Guest Setup
- IAP-VPN Deployment Scenarios
- Acronyms and Abbreviations
399 | IAP-VPN Deployment Scenarios Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.5.1.0-4.3.1.0 | User Guide
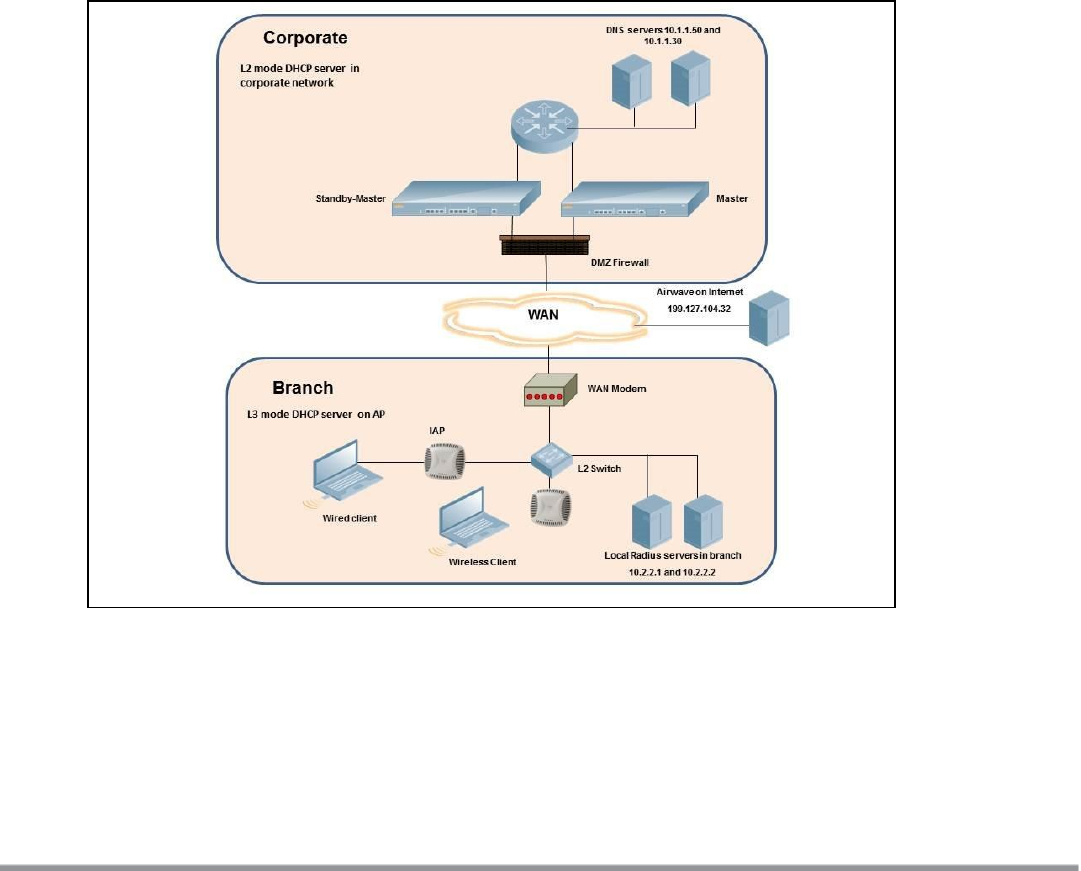
Scenario 2—IPsec: Single Datacenter with Multiple Controllers for
Redundancy
This scenario includes the following configuration elements:
l A VRRP instance between the master/standby-master pair, which is configured as the primary VPN IP
address.
l Tunneling of all traffic to datacenter.
l Exception route to bypass tunneling of RADIUS and W-AirWave traffic, which are locally reachable in the
branch and the Internet, respectively.
l All client DNS queries are tunneled to the controller.
l Distributed, L3 and Centralized, L2 mode DHCP on all branches. L3 is used by the employee network and L2
is used by the guest network with captive portal.
l Wired and wireless users in L2 and L3 modes.
l Access rules defined for wired and wireless networks.
Topology
Figure 121 shows the topology and the IP addressing scheme used in this scenario.
Figure 121 Scenario 2—IPsec: Single Datacenter with Multiple controllers for Redundancy
The following IP addresses are used in the examples for this scenario:
l 10.0.0.0/8 is the corporate network
l 10.20.0.0/16 subnet is reserved for L2 mode – used for guest network
l 10.30.0.0/16 subnet is reserved for L3 mode
l Client count in each branch is 200










