Concept Guide
Table Of Contents
- About this Guide
- About Instant
- Setting up a W-IAP
- Automatic Retrieval of Configuration
- Instant User Interface
- Initial Configuration Tasks
- Customizing W-IAP Settings
- Modifying the W-IAP Host Name
- Configuring Zone Settings on a W-IAP
- Specifying a Method for Obtaining IP Address
- Configuring External Antenna
- Configuring Radio Profiles for a W-IAP
- Configuring Uplink VLAN for a W-IAP
- Changing the W-IAP Installation Mode
- Changing USB Port Status
- Master Election and Virtual Controller
- Adding a W-IAP to the Network
- Removing a W-IAP from the Network
- VLAN Configuration
- IPv6 Support
- Wireless Network Profiles
- Configuring Wireless Network Profiles
- Configuring Fast Roaming for Wireless Clients
- Configuring Modulation Rates on a WLAN SSID
- Multi-User-MIMO
- Management Frame Protection
- Disabling Short Preamble for Wireless Client
- Editing Status of a WLAN SSID Profile
- Editing a WLAN SSID Profile
- Deleting a WLAN SSID Profile
- Wired Profiles
- Captive Portal for Guest Access
- Understanding Captive Portal
- Configuring a WLAN SSID for Guest Access
- Configuring Wired Profile for Guest Access
- Configuring Internal Captive Portal for Guest Network
- Configuring External Captive Portal for a Guest Network
- Configuring Facebook Login
- Configuring Guest Logon Role and Access Rules for Guest Users
- Configuring Captive Portal Roles for an SSID
- Configuring Walled Garden Access
- Authentication and User Management
- Managing W-IAP Users
- Supported Authentication Methods
- Supported EAP Authentication Frameworks
- Configuring Authentication Servers
- Understanding Encryption Types
- Configuring Authentication Survivability
- Configuring 802.1X Authentication for a Network Profile
- Enabling 802.1X Supplicant Support
- Configuring MAC Authentication for a Network Profile
- Configuring MAC Authentication with 802.1X Authentication
- Configuring MAC Authentication with Captive Portal Authentication
- Configuring WISPr Authentication
- Blacklisting Clients
- Uploading Certificates
- Roles and Policies
- DHCP Configuration
- Configuring Time-Based Services
- Dynamic DNS Registration
- VPN Configuration
- IAP-VPN Deployment
- Adaptive Radio Management
- Deep Packet Inspection and Application Visibility
- Voice and Video
- Services
- Configuring AirGroup
- Configuring a W-IAP for RTLS Support
- Configuring a W-IAP for Analytics and Location Engine Support
- Managing BLE Beacons
- Clarity Live
- Configuring OpenDNS Credentials
- Integrating a W-IAP with Palo Alto Networks Firewall
- Integrating a W-IAP with an XML API Interface
- CALEA Integration and Lawful Intercept Compliance
- Cluster Security
- W-IAP Management and Monitoring
- Uplink Configuration
- Intrusion Detection
- Mesh W-IAP Configuration
- Mobility and Client Management
- Spectrum Monitor
- W-IAP Maintenance
- Monitoring Devices and Logs
- Hotspot Profiles
- ClearPass Guest Setup
- IAP-VPN Deployment Scenarios
- Acronyms and Abbreviations
333 | Intrusion Detection Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.5.1.0-4.3.1.0 | User Guide
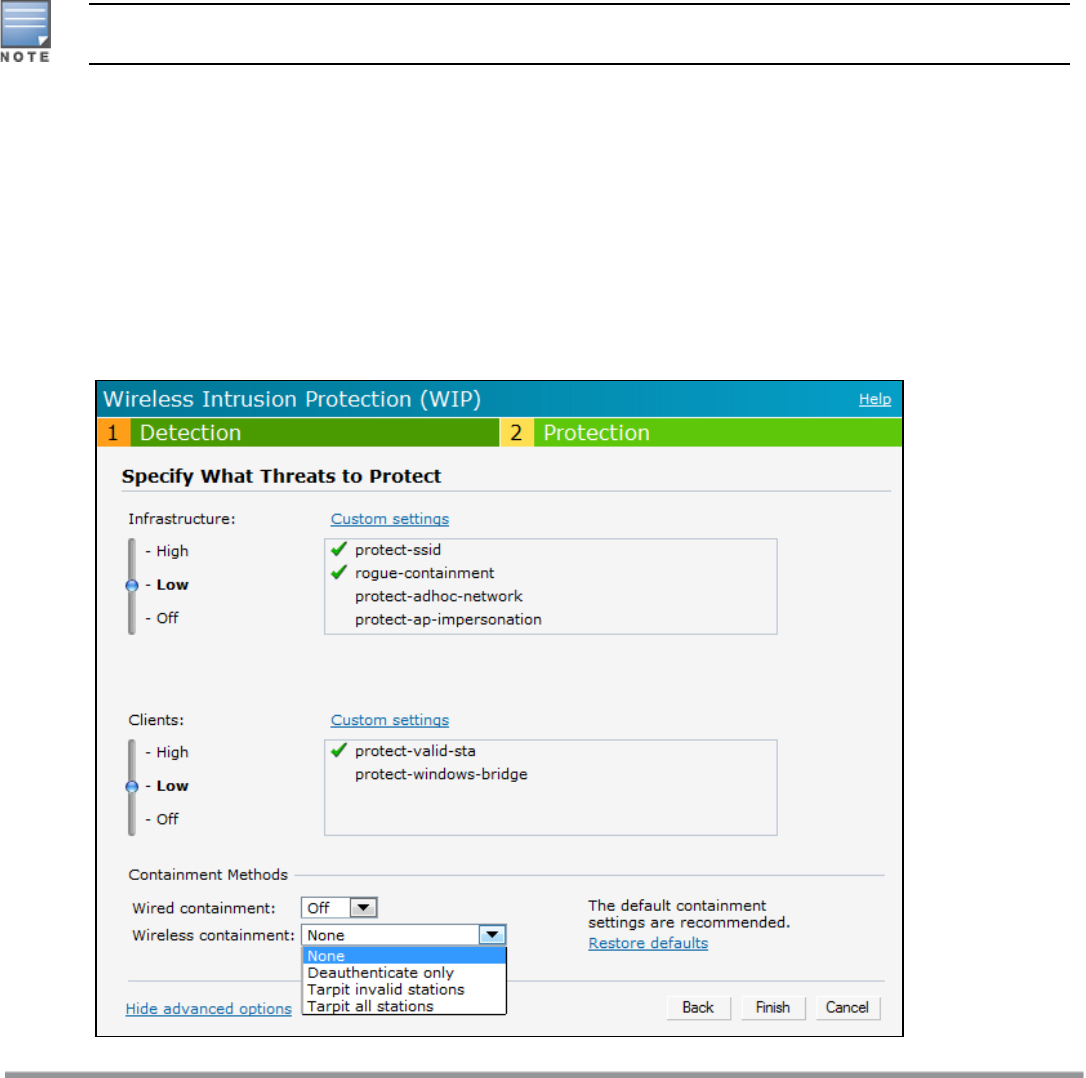
Containment Methods
You can enable wired and wireless containments to prevent unauthorized stations from connecting to your
Instant network.
Instant supports the following types of containment mechanisms:
l Wired containment—When enabled, W-IAPs generate ARP packets on the wired network to contain wireless
attacks.
n wired-containment-ap-adj-mac—Enables a wired containment to Rogue W-IAPs whose wired interface
MAC address is offset by one from its BSSID.
n wired-containment-susp-l3-rogue—Enables the users to identify and contain an W-IAP with a preset MAC
address that is different from the BSSID of the W-IAP, if the MAC address that the W-IAP provides is
offset by one character from its wired MAC address.
Enable the wired-containment-susp-l3-rogue parameter only when a specific containment is required, to
avoid a false alarm.
l Wireless containment—When enabled, the system attempts to disconnect all clients that are connected or
attempting to connect to the identified Access Point.
n None—Disables all the containment mechanisms.
n Deauthenticate only—With deauthentication containment, the Access Point or client is contained by
disrupting the client association on the wireless interface.
n Tarpit containment—With Tarpit containment, the Access Point is contained by luring clients that are
attempting to associate with it to a tarpit. The tarpit can be on the same channel or a different channel
as the Access Point being contained.
Figure 98 Containment Methods










