Concept Guide
Table Of Contents
- About this Guide
- About Instant
- Setting up a W-IAP
- Automatic Retrieval of Configuration
- Instant User Interface
- Initial Configuration Tasks
- Customizing W-IAP Settings
- Modifying the W-IAP Host Name
- Configuring Zone Settings on a W-IAP
- Specifying a Method for Obtaining IP Address
- Configuring External Antenna
- Configuring Radio Profiles for a W-IAP
- Configuring Uplink VLAN for a W-IAP
- Changing the W-IAP Installation Mode
- Changing USB Port Status
- Master Election and Virtual Controller
- Adding a W-IAP to the Network
- Removing a W-IAP from the Network
- VLAN Configuration
- IPv6 Support
- Wireless Network Profiles
- Configuring Wireless Network Profiles
- Configuring Fast Roaming for Wireless Clients
- Configuring Modulation Rates on a WLAN SSID
- Multi-User-MIMO
- Management Frame Protection
- Disabling Short Preamble for Wireless Client
- Editing Status of a WLAN SSID Profile
- Editing a WLAN SSID Profile
- Deleting a WLAN SSID Profile
- Wired Profiles
- Captive Portal for Guest Access
- Understanding Captive Portal
- Configuring a WLAN SSID for Guest Access
- Configuring Wired Profile for Guest Access
- Configuring Internal Captive Portal for Guest Network
- Configuring External Captive Portal for a Guest Network
- Configuring Facebook Login
- Configuring Guest Logon Role and Access Rules for Guest Users
- Configuring Captive Portal Roles for an SSID
- Configuring Walled Garden Access
- Authentication and User Management
- Managing W-IAP Users
- Supported Authentication Methods
- Supported EAP Authentication Frameworks
- Configuring Authentication Servers
- Understanding Encryption Types
- Configuring Authentication Survivability
- Configuring 802.1X Authentication for a Network Profile
- Enabling 802.1X Supplicant Support
- Configuring MAC Authentication for a Network Profile
- Configuring MAC Authentication with 802.1X Authentication
- Configuring MAC Authentication with Captive Portal Authentication
- Configuring WISPr Authentication
- Blacklisting Clients
- Uploading Certificates
- Roles and Policies
- DHCP Configuration
- Configuring Time-Based Services
- Dynamic DNS Registration
- VPN Configuration
- IAP-VPN Deployment
- Adaptive Radio Management
- Deep Packet Inspection and Application Visibility
- Voice and Video
- Services
- Configuring AirGroup
- Configuring a W-IAP for RTLS Support
- Configuring a W-IAP for Analytics and Location Engine Support
- Managing BLE Beacons
- Clarity Live
- Configuring OpenDNS Credentials
- Integrating a W-IAP with Palo Alto Networks Firewall
- Integrating a W-IAP with an XML API Interface
- CALEA Integration and Lawful Intercept Compliance
- Cluster Security
- W-IAP Management and Monitoring
- Uplink Configuration
- Intrusion Detection
- Mesh W-IAP Configuration
- Mobility and Client Management
- Spectrum Monitor
- W-IAP Maintenance
- Monitoring Devices and Logs
- Hotspot Profiles
- ClearPass Guest Setup
- IAP-VPN Deployment Scenarios
- Acronyms and Abbreviations
Airtime Fairness Mode
The airtime fairness feature provides equal access to all clients on the wireless medium, regardless of client
type, capability, or operating system, thus delivering uniform performance to all clients. This feature prevents
the clients from monopolizing resources. You can configure airtime fairness mode parameters through the
Instant UI or the CLI.
In the Instant UI
1. For Airtime fairness mode configuration, specify any of the following values under the RF>ARM >
Show advanced options tab:
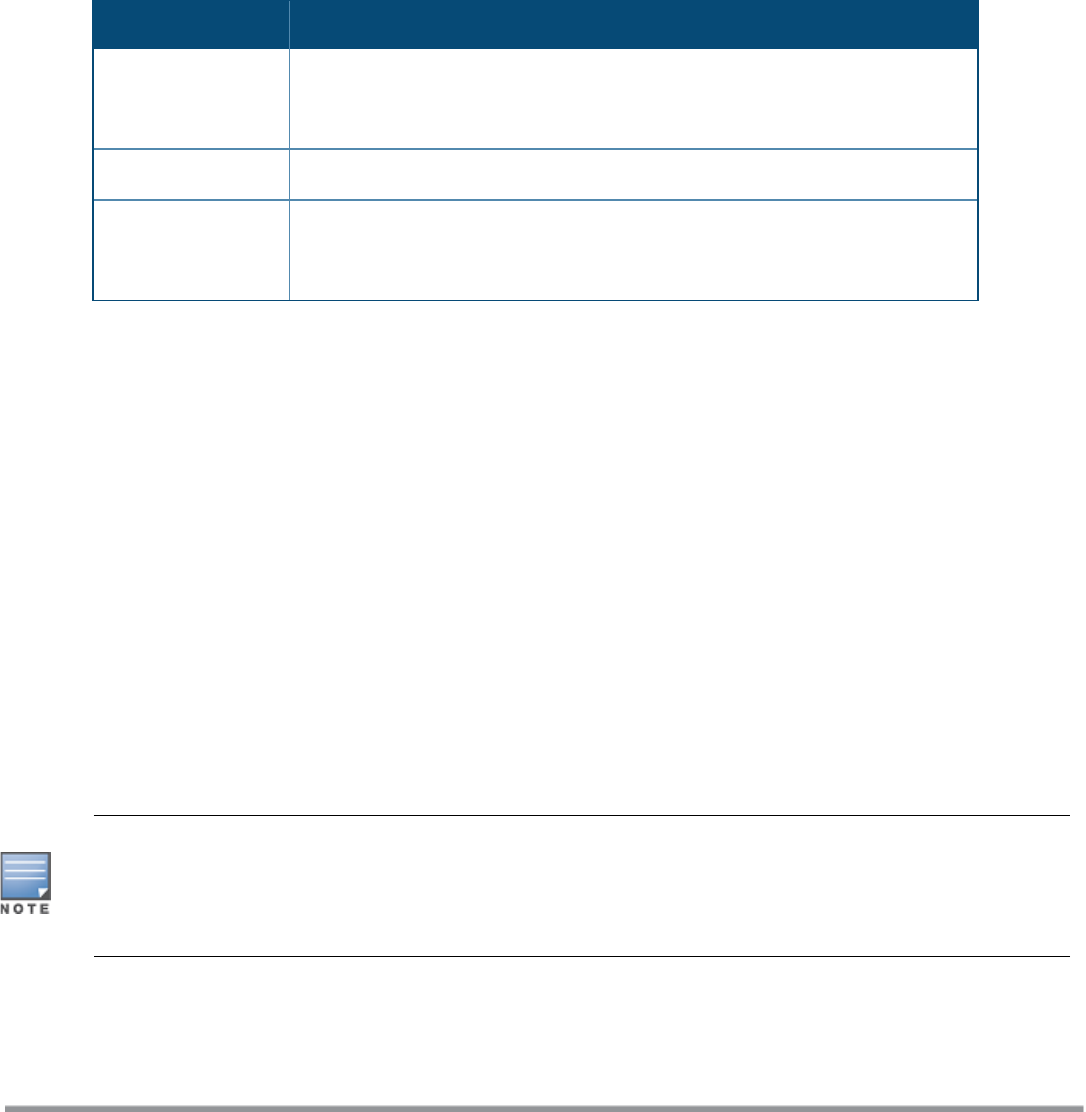
Parameter Description
Default Access
Select this option to provide access based on client requests. When Air Time
Fairness is set to default access, per-user and per-SSID bandwidth limits are
not enforced.
Fair Access
Select this option to allocate Airtime evenly across all the clients.
Preferred Access
Select this option to set a preference where 802.11n clients are assigned more
airtime than 802.11a/11g. The 802.11a/11g clients get more airtime than
802.11b. The ratio is 16:4:1.
Table 54: Airtime Fairness Mode—Configuration Parameters
2. Click OK.
In the CLI
(Instant AP)(config)# arm
(Instant AP)(ARM)# air-time-fairness-mode {<Default Access>| <Fair Access> | <Preferred
Access>
(Instant AP)(ARM)# end
(Instant AP)# commit apply
Client Match
The ARM client match feature continually monitors a client's RF neighborhood to provide ongoing client band
steering and load balancing, and enhanced W-IAP reassignment for roaming mobile clients. This feature
supersedes the legacy band steering and spectrum load balancing features, which unlike client match, do not
trigger W-IAP changes for clients already associated to a W-IAP. In addition to this, the Client Match feature
provides the smartphone handoff assist function which helps smartphones to switch between 3G and 4G
networks when the Wi-Fi connectivity is poor. The W-IAP monitors the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI)
of the smartphone and checks if it remains under the threshold connectivity strength for a certain duration
and deauthenticates the client.
Legacy 802.11a/b/g access points do not support the client match feature. When client match is enabled on
802.11n-capable access points, the client match feature overrides any settings configured for the legacy
band steering, station handoff assist, or load balancing feature. 802.11ac-capable access points do not
support the legacy band steering, station handoff assist, or load balancing settings; so these access points
must be managed using client match.
Dell Networking W-Series Instant 6.5.1.0-4.3.1.0 | User Guide Adaptive Radio Management | 251










