Developers Guide
23 Understanding RAID with Dell SC Series Storage | 3104-CD-DS
6 RAID management
SC Series arrays are designed to manage RAID levels automatically, however the following operations may
be performed if the need arises;
Rebalancing RAID: Redistributes data and typically occurs after changing the number of disks or
changing the redundancy of the tier
Modify tier redundancy: Increases or decreases the number of disks for parity or mirror
Creating storage types: Associates disks to a redundancy level
Create a storage profile: Allows for RAID level and tier binding at the volume level
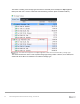
6.1 RAID rebalancing considerations
When disks are added or removed or tier redundancy is modified, a RAID rebalance is needed to redistribute
the data across all disks in a disk folder.
The RAID rebalance process follows these guidelines:
RAID rebalancing begins with the smallest RAID sets (RAID 5-5).
RAID rebalancing has the potential to fail or deadlock when moving data on some RAID sets. If this
occurs, it may be necessary to add disk space to the array for RAID rebalancing to complete.
Depending on the total capacity used, a considerable amount of time may be needed to completely
redistribute the data pages. In addition, ample space needs to be available before this operation can occur.
Space available, amount of data to rebalance, the requirement for new RAID sets and load on the system all
impact the time for the rebalance to complete.
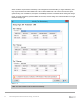
6.2 Modifying tier redundancy
Each disk folder has a corresponding storage type. Tier redundancy may be changed from single parity or
mirror to dual parity or mirror.
Before modifying tier redundancy, be sure there is sufficient space in the tier for a raid rebalance,
and consider any impact a RAID rebalance may have on the system.