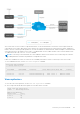
API Guide
Table Of Contents
- VXLAN and BGP EVPN Configuration Guide for Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 Release 10.5.1
- VXLAN
- VXLAN concepts
- VXLAN as NVO solution
- Configure VXLAN
- L3 VXLAN route scaling
- DHCP relay on VTEPs
- View VXLAN configuration
- VXLAN MAC addresses
- VXLAN commands
- hardware overlay-routing-profile
- interface virtual-network
- ip virtual-router address
- ip virtual-router mac-address
- member-interface
- nve
- remote-vtep
- show hardware overlay-routing-profile mode
- show interface virtual-network
- show nve remote-vtep
- show nve remote-vtep counters
- show nve vxlan-vni
- show virtual-network
- show virtual-network counters
- show virtual-network interface counters
- show virtual-network interface
- show virtual-network vlan
- show vlan (virtual network)
- source-interface loopback
- virtual-network
- virtual-network untagged-vlan
- vxlan-vni
- VXLAN MAC commands
- clear mac address-table dynamic nve remote-vtep
- clear mac address-table dynamic virtual-network
- show mac address-table count extended
- show mac address-table count nve
- show mac address-table count virtual-network
- show mac address-table extended
- show mac address-table nve
- show mac address-table virtual-network
- Example: VXLAN with static VTEP
- BGP EVPN for VXLAN
- BGP EVPN compared to static VXLAN
- VXLAN BGP EVPN operation
- Configure BGP EVPN for VXLAN
- VXLAN BGP EVPN routing
- BGP EVPN with VLT
- VXLAN BGP commands
- VXLAN EVPN commands
- Example: VXLAN with BGP EVPN
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN — Multiple AS topology
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN — Centralized L3 gateway
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN — Border leaf gateway with asymmetric IRB
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN—Symmetric IRB
- Example - VXLAN BGP EVPN symmetric IRB with unnumbered BGP peering
- Example: Migrating from Asymmetric IRB to Symmetric IRB
- Controller-provisioned VXLAN
- Support resources
- Index
Topics:
• Configure controller-provisioned VXLAN
• Configure and control VXLAN from VMware vCenter
• Example: VXLAN with a controller configuration
• VXLAN Controller commands
Configure controller-provisioned VXLAN
To configure the NSX controller, follow these steps on each OS10 VTEP:
1. Configure the source interface used for controller-based VXLAN provisioning. Assign an IPv4 address to a loopback
interface. Assign the loopback interface to an NVE instance. The loopback interface must belong to the default VRF. For
detailed information, see the Configure source IP address on VTEP.
2. Configure NSX controller reachability.
3. Assign local access interfaces to be managed by the controller. The VLAN IDs of member access interfaces created using
the OS10 CLI must be different from the VLAN IDs of port-scoped VLANs created by the NSX controller for virtual
networks.
4. (Optional) Enable BFD in the NSX and the VTEP. OS10 complies with RFC5880 for Bidirectional Forwarding Detection.
Configuration notes
● NSX controller-provisioned VXLAN is not supported if an OS10 switch operates in OpenFlow-only mode.
●
Only one mode of VxLAN provisioning is supported at a time: NSX controller-based, static VXLAN, or BGP EVPN.
● An OS10 switch does not send VXLAN access port statistics to the NSX controller.
● Controller-provisioned VXLAN is not supported on VTEPs configured as peers in a VLT domain. Only VTEPs in standalone
mode are supported.
Specify the controller reachability information
In OS10 VTEP, the controller configuration command initializes a connection to an OVSDB-based controller.
OS10 supports only one controller connection at a time.
NOTE: Currently, the only supported OVSDB-based controller is NSX.
To configure an OVSDB controller on the OS10 VTEP:
1. Enable VXLAN in CONFIGURATION mode.
OS10(config)# nve
2. Changes the mode to CONFIGURATION-NVE-OVSDB from where you can configure the controller parameters.
OS10(config-nve)# controller ovsdb
3. Specify the IP address, OVSDB controller port, and SSL as a secure connection protocol between the OS10 VTEP and the
controller in CONFIGURATION-NVE-OVSDB mode.
OS10(config-nve-ovsdb)# ip ip-address port port-number ssl
The range of port-numberis from 0 to 65535. Configure the port-number as 6640 and the connection type as SSL.
4. (Optional) Specify a time interval, in milliseconds (ms). This is the duration the switch waits between the connection
attempts to the controller.
OS10(config-nve-ovsdb)# max-backoff interval
The range is from 1000 to 180,000 ms. The default is 8000 ms.
OS10# configure terminal
OS10(config)# nve
OS10(config-nve)# controller ovsdb
OS10(config-nve-ovsdb)# ip 10.11.66.110 port 6640 ssl
Controller-provisioned VXLAN
165