Deployment Guide
Table Of Contents
- VXLAN and BGP EVPN Configuration Guide for Dell EMC SmartFabric OS10 Release 10.5.0
- VXLAN
- VXLAN concepts
- VXLAN as NVO solution
- Configure VXLAN
- L3 VXLAN route scaling
- Overlay ECMP for L3 prefix routes
- DHCP relay on VTEPs
- View VXLAN configuration
- VXLAN MAC addresses
- VXLAN commands
- hardware overlay-ecmp-profile mode
- hardware overlay-routing-profile
- interface virtual-network
- ip virtual-router address
- ip virtual-router mac-address
- member-interface
- nve
- remote-vtep
- show hardware overlay-ecmp-profile mode
- show hardware overlay-routing-profile mode
- show interface virtual-network
- show nve remote-vtep
- show nve remote-vtep counters
- show nve vxlan-vni
- show virtual-network
- show virtual-network counters
- show virtual-network interface counters
- show virtual-network interface
- show virtual-network vlan
- show vlan (virtual network)
- source-interface loopback
- virtual-network
- virtual-network untagged-vlan
- vxlan-vni
- VXLAN MAC commands
- clear mac address-table dynamic nve remote-vtep
- clear mac address-table dynamic virtual-network
- show mac address-table count extended
- show mac address-table count nve
- show mac address-table count virtual-network
- show mac address-table extended
- show mac address-table nve
- show mac address-table virtual-network
- Example: VXLAN with static VTEP
- BGP EVPN for VXLAN
- BGP EVPN compared to static VXLAN
- VXLAN BGP EVPN operation
- Disable RT ASN in BGP EVPN
- Configure BGP EVPN for VXLAN
- VXLAN BGP EVPN routing
- BGP EVPN with VLT
- VXLAN BGP commands
- VXLAN EVPN commands
- Example: VXLAN with BGP EVPN
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN — Multiple AS topology
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN — Centralized L3 gateway
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN — Border leaf gateway with asymmetric IRB
- Example: VXLAN BGP EVPN—Symmetric IRB
- Controller-provisioned VXLAN
- Support resources
Configure VLT
(Optional) To use VXLAN in a VLT domain, configure the VLT domain — including the VLT Interconnect (VLTi) interfaces,
backup heartbeat, and VLT MAC address — as described in the OS10 Enterprise Edition User Guide in the Virtual link trunking
section.
Required VLT VXLAN configuration:
● The IP address of the VTEP source Loopback interface must be same on the VLT peers.
● If you use a port-scoped VLAN to assign tagged access interfaces to a virtual network, to identify traffic belonging to each
virtual network, you must configure a unique VLAN ID for the VLT Interconnect (VLTi) link.
● Configure a VLAN to transmit VXLAN traffic over the VLTi link in VIRTUAL-NETWORK mode. All traffic sent and received
from a virtual network on the VLTi carries the VLTi VLAN ID tag.
Configure the same VLTi VLAN ID on both VLT peers. You cannot use the ID of an existing VLAN on a VLT peer or the
reserved untagged VLAN ID. You can use the VLTi VLAN ID to assign tagged or untagged access interfaces to a virtual
network.
virtual-network vn-id
vlti-vlan vlan-id
● Although a VXLAN virtual network has no access port members that connect to downstream servers, you must configure
a switch-scoped VLAN or VLTi VLAN. The presence of this VLAN ensures that the VLTi link is added as a member of the
virtual network so that mis-hashed ARP packets received from the VXLAN tunnel reach the intended VLT node.
Best practices:
● If a VLT peer loses connectivity to the underlay L3 network, it continues to transmit routing traffic to the network through
the VLTi link on a dedicated L3 VLAN to the other VLT peer. Configure a L3 VLAN between VLT peers in the underlay
network and enable routing on the VLAN; for example:
OS10(config)# interface vlan4000
OS10(config-if-vl-4000)# no shutdown
OS10(config-if-vl-4000)# ip address 41.1.1.1/24
OS10(config-if-vl-4000)# ip ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0
● To reduce traffic loss when a VLT peer boots up and joins an existing VLT domain, or when the VLTi links fails and the VLT
peer is still up as detected by the VLT heartbeat, create an uplink state group. Configure all access VLT port channels on the
peer as upstream links. Configure all network-facing links as downstream link. For example:
OS10(config)# uplink-state-group 1
OS10(conf-uplink-state-group-1)# enable
OS10(conf-uplink-state-group-1)# downstream ethernet1/1/1-1/1/2
OS10(conf-uplink-state-group-1)# upstream port-channel 10
L3 VXLAN route scaling
The S4100-ON series, S5200-ON series, S4048T-ON, S4248-ON series, and S6010-ON switches support native VxLAN routing
— routing in and out of tunnels (RIOT). RIOT requires dedicated hardware resources reserved for overlay routing. You cannot
use these dedicated resources for underlay routing.
Each overlay ARP entry requires a routing next-hop in the hardware to bind a destination tenant VM IP address to the
corresponding tenant VM MAC address and VNI. Each virtual-network interface assigned to an IP subnet requires a routing
interface in the hardware.
OS10 supports preset profiles to re-allocate the number of resources reserved for overlay ARP entries. The number of entries
reserved for each preset mode differs according to OS10 switch.
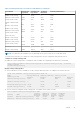
Table 3. Routing next-hops reserved on OS10 switches
OS10 Switch Overlay next-
hop entries
Underlay next-
hop entries
Overlay L3
RIF entries
Underlay L3 RIF entries
S41xx-ON series:
default-overlay-routing
—
4096
—
28672
—
2048
—
10240
14 VXLAN