Users Guide
Table Of Contents
- Dell EMC Configuration Guide for the S3048–ON System 9.14.0.0
- About this Guide
- Configuration Fundamentals
- Getting Started
- Console Access
- Accessing the CLI Interface and Running Scripts Using SSH
- Default Configuration
- Configuring a Host Name
- Accessing the System Remotely
- Configuring the Enable Password
- Configuration File Management
- Managing the File System
- Enabling Software Features on Devices Using a Command Option
- View Command History
- Upgrading Dell EMC Networking OS
- Verify Software Images Before Installation
- Using HTTP for File Transfers
- Management
- Configuring Privilege Levels
- Configuring Logging
- Track Login Activity
- Limit Concurrent Login Sessions
- Enabling Secured CLI Mode
- Log Messages in the Internal Buffer
- Disabling System Logging
- Sending System Messages to a Syslog Server
- Changing System Logging Settings
- Display the Logging Buffer and the Logging Configuration
- Configuring a UNIX Logging Facility Level
- Synchronizing Log Messages
- Enabling Timestamp on Syslog Messages
- File Transfer Services
- Terminal Lines
- Setting Timeout for EXEC Privilege Mode
- Using Telnet to get to Another Network Device
- Lock CONFIGURATION Mode
- LPC Bus Quality Degradation
- Reloading the system
- Viewing the Reason for Last System Reboot
- 802.1X
- Port-Authentication Process
- Configuring 802.1X
- Important Points to Remember
- Configuring dot1x Profile
- Configuring MAC addresses for a do1x Profile
- Configuring the Static MAB and MAB Profile
- Configuring Critical VLAN
- Enabling 802.1X
- Configuring Request Identity Re-Transmissions
- Forcibly Authorizing or Unauthorizing a Port
- Re-Authenticating a Port
- Configuring Timeouts
- Configuring Dynamic VLAN Assignment with Port Authentication
- Guest and Authentication-Fail VLANs
- Access Control List (ACL) VLAN Groups and Content Addressable Memory (CAM)
- Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- IP Access Control Lists (ACLs)
- Important Points to Remember
- IP Fragment Handling
- Configure a Standard IP ACL
- Configure an Extended IP ACL
- Configure Layer 2 and Layer 3 ACLs
- Assign an IP ACL to an Interface
- Applying an IP ACL
- Configure Ingress ACLs
- Configure Egress ACLs
- IP Prefix Lists
- ACL Remarks
- ACL Resequencing
- Route Maps
- Logging of ACL Processes
- Flow-Based Monitoring
- Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD)
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- Border Gateway Protocol version 4 (BGPv4)
- Autonomous Systems (AS)
- Multiprotocol BGP
- Sessions and Peers
- Implementing BGP global and address family
- BGP Attributes for selecting Best Path
- Implement BGP with Dell EMC Networking OS
- Configuration Information
- Configuring a basic BGP network
- Enabling BGP
- Configuring a BGP peer
- Configuring AS4 Number Representations
- Configuring a BGP VRF address family
- Route-refresh and Soft-reconfiguration
- Aggregating Routes
- Filtering BGP Routes
- Filtering BGP Routes Using Route Maps
- Filtering BGP Routes Using AS-PATH Information
- Configuring Peer Groups
- Configuring BGP Fast Fall-Over
- Configuring Passive Peering
- Maintaining Existing AS Numbers During an AS Migration
- Allowing an AS Number to Appear in its Own AS Path
- Enabling Graceful Restart
- Filtering on an AS-Path Attribute
- Regular Expressions as Filters
- Redistributing Routes
- Enabling Additional Paths
- Configuring IP Community Lists
- Configuring an IP Extended Community List
- Filtering Routes with Community Lists
- Manipulating the COMMUNITY Attribute
- Changing MED Attributes
- Changing the LOCAL_PREFERENCE Attribute
- Configuring the local System or a Different System to be the Next Hop for BGP-Learned Routes
- Changing the WEIGHT Attribute
- Enabling Multipath
- Route Reflectors
- Configuring BGP Confederations
- Enabling Route Flap Dampening
- Changing BGP Timers
- Setting the extended timer
- Enabling or disabling BGP neighbors
- Route Map Continue
- Enabling MBGP Configurations
- MBGP support for IPv6
- Configuring IPv6 MBGP between peers
- Example-Configuring IPv4 and IPv6 neighbors
- Configure IPv6 NH Automatically for IPv6 Prefix Advertised over IPv4 Neighbor
- BGP Regular Expression Optimization
- Debugging BGP
- Content Addressable Memory (CAM)
- Control Plane Policing (CoPP)
- Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- DHCP Packet Format and Options
- Assign an IP Address using DHCP
- Implementation Information
- Configure the System to be a DHCP Server
- Configure the System to be a Relay Agent
- Configure the System to be a DHCP Client
- DHCP Relay When DHCP Server and Client are in Different VRFs
- Configure the System for User Port Stacking (Option 230)
- Configure Secure DHCP
- Source Address Validation
- Equal Cost Multi-Path (ECMP)
- FIPS Cryptography
- Force10 Resilient Ring Protocol (FRRP)
- GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP)
- High Availability (HA)
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
- IGMP Implementation Information
- IGMP Protocol Overview
- Configure IGMP
- Viewing IGMP Enabled Interfaces
- Selecting an IGMP Version
- Viewing IGMP Groups
- Adjusting Timers
- Preventing a Host from Joining a Group
- Enabling IGMP Immediate-Leave
- IGMP Snooping
- Fast Convergence after MSTP Topology Changes
- Egress Interface Selection (EIS) for HTTP and IGMP Applications
- Protocol Separation
- Enabling and Disabling Management Egress Interface Selection
- Handling of Management Route Configuration
- Handling of Switch-Initiated Traffic
- Handling of Switch-Destined Traffic
- Handling of Transit Traffic (Traffic Separation)
- Mapping of Management Applications and Traffic Type
- Behavior of Various Applications for Switch-Initiated Traffic
- Behavior of Various Applications for Switch-Destined Traffic
- Interworking of EIS With Various Applications
- Designating a Multicast Router Interface
- Interfaces
- Basic Interface Configuration
- Advanced Interface Configuration
- Interface Types
- View Basic Interface Information
- Resetting an Interface to its Factory Default State
- Enabling a Physical Interface
- Enabling Energy Efficient Ethernet
- View EEE Information
- Clear EEE Counters
- Physical Interfaces
- Automatic recovery of an Err-disabled interface
- Egress Interface Selection (EIS)
- Management Interfaces
- VLAN Interfaces
- Loopback Interfaces
- Null Interfaces
- Port Channel Interfaces
- Port Channel Definition and Standards
- Port Channel Benefits
- Port Channel Implementation
- Interfaces in Port Channels
- Configuration Tasks for Port Channel Interfaces
- Creating a Port Channel
- Adding a Physical Interface to a Port Channel
- Reassigning an Interface to a New Port Channel
- Configuring the Minimum Oper Up Links in a Port Channel
- Adding or Removing a Port Channel from a VLAN
- Assigning an IP Address to a Port Channel
- Deleting or Disabling a Port Channel
- Load Balancing Through Port Channels
- Changing the Hash Algorithm
- Bulk Configuration
- Defining Interface Range Macros
- Monitoring and Maintaining Interfaces
- Configuring wavelength for 10–Gigabit SFP+ optics
- Link Dampening
- Link Bundle Monitoring
- Using Ethernet Pause Frames for Flow Control
- Configure the MTU Size on an Interface
- Port-Pipes
- Auto-Negotiation on Ethernet Interfaces
- View Advanced Interface Information
- Configuring the Traffic Sampling Size Globally
- Dynamic Counters
- Discard Counters
- Internet Protocol Security (IPSec)
- IPv4 Routing
- IP Addresses
- Configuration Tasks for IP Addresses
- Assigning IP Addresses to an Interface
- Configuring Static Routes
- Configure Static Routes for the Management Interface
- IPv4 Path MTU Discovery Overview
- Using the Configured Source IP Address in ICMP Messages
- Configuring the Duration to Establish a TCP Connection
- Enabling Directed Broadcast
- Resolution of Host Names
- Enabling Dynamic Resolution of Host Names
- Specifying the Local System Domain and a List of Domains
- Configuring DNS with Traceroute
- ARP
- Configuration Tasks for ARP
- Configuring Static ARP Entries
- Enabling Proxy ARP
- Clearing ARP Cache
- ARP Learning via Gratuitous ARP
- Enabling ARP Learning via Gratuitous ARP
- ARP Learning via ARP Request
- Configuring ARP Retries
- ICMP
- Configuration Tasks for ICMP
- Enabling ICMP Unreachable Messages
- UDP Helper
- Enabling UDP Helper
- Configurations Using UDP Helper
- UDP Helper with Broadcast-All Addresses
- UDP Helper with Subnet Broadcast Addresses
- UDP Helper with Configured Broadcast Addresses
- UDP Helper with No Configured Broadcast Addresses
- Troubleshooting UDP Helper
- IPv6 Routing
- Protocol Overview
- Implementing IPv6 with Dell EMC Networking OS
- ICMPv6
- Path MTU discovery
- IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
- Configuration Task List for IPv6 RDNSS
- Secure Shell (SSH) Over an IPv6 Transport
- Configuration Tasks for IPv6
- Adjusting Your CAM-Profile
- Assigning an IPv6 Address to an Interface
- Assigning a Static IPv6 Route
- Configuring Telnet with IPv6
- SNMP over IPv6
- Displaying IPv6 Information
- Displaying an IPv6 Interface Information
- Showing IPv6 Routes
- Showing the Running-Configuration for an Interface
- Clearing IPv6 Routes
- Disabling ND Entry Timeout
- Configuring IPv6 RA Guard
- Intermediate System to Intermediate System
- Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
- Layer 2
- Manage the MAC Address Table
- MAC Learning Limit
- Setting the MAC Learning Limit
- mac learning-limit Dynamic
- mac learning-limit mac-address-sticky
- mac learning-limit station-move
- mac learning-limit no-station-move
- Learning Limit Violation Actions
- Setting Station Move Violation Actions
- Recovering from Learning Limit and Station Move Violations
- Disabling MAC Address Learning on the System
- NIC Teaming
- Configure Redundant Pairs
- Far-End Failure Detection
- Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
- 802.1AB (LLDP) Overview
- Optional TLVs
- TIA-1057 (LLDP-MED) Overview
- Configure LLDP
- CONFIGURATION versus INTERFACE Configurations
- Enabling LLDP
- Enabling LLDP on Management Ports
- Advertising TLVs
- Storing and Viewing Unrecognized LLDP TLVs
- Viewing the LLDP Configuration
- Viewing Information Advertised by Adjacent LLDP Neighbors
- Configuring LLDPDU Intervals
- Configuring LLDP Notification Interval
- Configuring LLDP Notification Interval
- Configuring Transmit and Receive Mode
- Configuring the Time to Live Value
- Debugging LLDP
- Relevant Management Objects
- Microsoft Network Load Balancing
- Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP)
- Protocol Overview
- Anycast RP
- Implementation Information
- Configure Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
- Enable MSDP
- Manage the Source-Active Cache
- Accept Source-Active Messages that Fail the RFP Check
- Specifying Source-Active Messages
- Limiting the Source-Active Messages from a Peer
- Preventing MSDP from Caching a Local Source
- Preventing MSDP from Caching a Remote Source
- Preventing MSDP from Advertising a Local Source
- Logging Changes in Peership States
- Terminating a Peership
- Clearing Peer Statistics
- Debugging MSDP
- MSDP with Anycast RP
- Configuring Anycast RP
- MSDP Sample Configurations
- Multicast Listener Discovery Protocol
- Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP)
- Protocol Overview
- Spanning Tree Variations
- Configure Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol
- Enable Multiple Spanning Tree Globally
- Adding and Removing Interfaces
- Creating Multiple Spanning Tree Instances
- Influencing MSTP Root Selection
- Interoperate with Non-Dell Bridges
- Changing the Region Name or Revision
- Modifying Global Parameters
- Modifying the Interface Parameters
- Configuring an EdgePort
- Flush MAC Addresses after a Topology Change
- MSTP Sample Configurations
- Debugging and Verifying MSTP Configurations
- Multicast Features
- Object Tracking
- Open Shortest Path First (OSPFv2 and OSPFv3)
- Protocol Overview
- OSPF with Dell EMC Networking OS
- Configuration Information
- OSPFv3 NSSA
- Configuration Task List for OSPFv3 (OSPF for IPv6)
- Enabling IPv6 Unicast Routing
- Applying cost for OSPFv3
- Assigning IPv6 Addresses on an Interface
- Assigning Area ID on an Interface
- Assigning OSPFv3 Process ID and Router ID Globally
- Assigning OSPFv3 Process ID and Router ID to a VRF
- Configuring Stub Areas
- Configuring Passive-Interface
- Redistributing Routes
- Configuring a Default Route
- Enabling OSPFv3 Graceful Restart
- OSPFv3 Authentication Using IPsec
- Troubleshooting OSPFv3
- Policy-based Routing (PBR)
- PIM Sparse-Mode (PIM-SM)
- PIM Source-Specific Mode (PIM-SSM)
- Port Monitoring
- Private VLANs (PVLAN)
- Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus (PVST+)
- Protocol Overview
- Implementation Information
- Configure Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus
- Enabling PVST+
- Disabling PVST+
- Influencing PVST+ Root Selection
- Modifying Global PVST+ Parameters
- Modifying Interface PVST+ Parameters
- Configuring an EdgePort
- PVST+ in Multi-Vendor Networks
- Enabling PVST+ Extend System ID
- PVST+ Sample Configurations
- Quality of Service (QoS)
- Implementation Information
- Port-Based QoS Configurations
- Policy-Based QoS Configurations
- DSCP Color Maps
- Enabling QoS Rate Adjustment
- Enabling Strict-Priority Queueing
- Weighted Random Early Detection
- Pre-Calculating Available QoS CAM Space
- Configuring Weights and ECN for WRED
- Configuring WRED and ECN Attributes
- Guidelines for Configuring ECN for Classifying and Color-Marking Packets
- Applying Layer 2 Match Criteria on a Layer 3 Interface
- Applying DSCP and VLAN Match Criteria on a Service Queue
- Classifying Incoming Packets Using ECN and Color-Marking
- Guidelines for Configuring ECN for Classifying and Color-Marking Packets
- Sample configuration to mark non-ecn packets as “yellow” with Multiple traffic class
- Sample configuration to mark non-ecn packets as “yellow” with single traffic class
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Remote Monitoring (RMON)
- Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP)
- Protocol Overview
- Configuring Rapid Spanning Tree
- Important Points to Remember
- Configuring Interfaces for Layer 2 Mode
- Enabling Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Globally
- Adding and Removing Interfaces
- Modifying Global Parameters
- Modifying Interface Parameters
- Enabling SNMP Traps for Root Elections and Topology Changes
- Influencing RSTP Root Selection
- Configuring an EdgePort
- Configuring Fast Hellos for Link State Detection
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
- Security
- AAA Accounting
- AAA Authentication
- Obscuring Passwords and Keys
- AAA Authorization
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- Protection from TCP Tiny and Overlapping Fragment Attacks
- Enabling SCP and SSH
- Using SCP with SSH to Copy a Software Image
- Removing the RSA Host Keys and Zeroizing Storage
- Configuring When to Re-generate an SSH Key
- Configuring the SSH Server Key Exchange Algorithm
- Configuring the HMAC Algorithm for the SSH Server
- Configuring the HMAC Algorithm for the SSH Client
- Configuring the SSH Server Cipher List
- Configuring the SSH Client Cipher List
- Configuring DNS in the SSH Server
- Secure Shell Authentication
- Troubleshooting SSH
- Telnet
- VTY Line and Access-Class Configuration
- Role-Based Access Control
- Two Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Configuring the System to Drop Certain ICMP Reply Messages
- Dell EMC Networking OS Security Hardening
- Service Provider Bridging
- sFlow
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Protocol Overview
- Implementation Information
- SNMPv3 Compliance With FIPS
- Configuration Task List for SNMP
- Important Points to Remember
- Set up SNMP
- Reading Managed Object Values
- Writing Managed Object Values
- Configuring Contact and Location Information using SNMP
- Subscribing to Managed Object Value Updates using SNMP
- Enabling a Subset of SNMP Traps
- Enabling an SNMP Agent to Notify Syslog Server Failure
- Copy Configuration Files Using SNMP
- Copying a Configuration File
- Copying Configuration Files via SNMP
- Copying the Startup-Config Files to the Running-Config
- Copying the Startup-Config Files to the Server via FTP
- Copying the Startup-Config Files to the Server via TFTP
- Copy a Binary File to the Startup-Configuration
- Additional MIB Objects to View Copy Statistics
- Obtaining a Value for MIB Objects
- MIB Support to Display Reason for Last System Reboot
- MIB Support for Power Monitoring
- MIB Support to Display the Available Memory Size on Flash
- MIB Support to Display the Software Core Files Generated by the System
- SNMP Support for WRED Green/Yellow/Red Drop Counters
- MIB Support to Display the Available Partitions on Flash
- MIB Support to Display Egress Queue Statistics
- MIB Support to ECMP Group Count
- MIB Support for entAliasMappingTable
- MIB Support for LAG
- MIB Support to Display Unrecognized LLDP TLVs
- MIB Support for LLDP Notification Interval
- Manage VLANs using SNMP
- Managing Overload on Startup
- Enabling and Disabling a Port using SNMP
- Fetch Dynamic MAC Entries using SNMP
- Example of Deriving the Interface Index Number
- Monitoring BGP sessions via SNMP
- Monitor Port-Channels
- Enabling an SNMP Agent to Notify Syslog Server Failure
- Troubleshooting SNMP Operation
- Transceiver Monitoring
- Stacking
- Storm Control
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- Protocol Overview
- Configure Spanning Tree
- Important Points to Remember
- Configuring Interfaces for Layer 2 Mode
- Enabling Spanning Tree Protocol Globally
- Adding an Interface to the Spanning Tree Group
- Modifying Global Parameters
- Modifying Interface STP Parameters
- Enabling PortFast
- Selecting STP Root
- STP Root Guard
- Enabling SNMP Traps for Root Elections and Topology Changes
- Configuring Spanning Trees as Hitless
- STP Loop Guard
- Displaying STP Guard Configuration
- SupportAssist
- System Time and Date
- Tunneling
- Uplink Failure Detection (UFD)
- Upgrade Procedures
- Virtual LANs (VLANs)
- Virtual Link Trunking (VLT)
- Overview
- Configure Virtual Link Trunking
- RSTP Configuration
- PVST+ Configuration
- Peer Routing Configuration Example
- eVLT Configuration Example
- PIM-Sparse Mode Configuration Example
- Verifying a VLT Configuration
- Additional VLT Sample Configurations
- Troubleshooting VLT
- Reconfiguring Stacked Switches as VLT
- Specifying VLT Nodes in a PVLAN
- Association of VLTi as a Member of a PVLAN
- MAC Synchronization for VLT Nodes in a PVLAN
- PVLAN Operations When One VLT Peer is Down
- PVLAN Operations When a VLT Peer is Restarted
- Interoperation of VLT Nodes in a PVLAN with ARP Requests
- Scenarios for VLAN Membership and MAC Synchronization With VLT Nodes in PVLAN
- Configuring a VLT VLAN or LAG in a PVLAN
- Proxy ARP Capability on VLT Peer Nodes
- VLT Nodes as Rendezvous Points for Multicast Resiliency
- Configuring VLAN-Stack over VLT
- IPv6 Peer Routing in VLT Domains Overview
- VLT Proxy Gateway
- Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)
- Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
- Debugging and Diagnostics
- Standards Compliance
- X.509v3
- Introduction to X.509v3 certification
- X.509v3 support in
- Information about installing CA certificates
- Information about Creating Certificate Signing Requests (CSR)
- Information about installing trusted certificates
- Transport layer security (TLS)
- Online Certificate Status Protocol (OSCP)
- Verifying certificates
- Event logging
Important Points about Shared LAG State Tracking
The following is more information about shared LAG state tracking.
• This feature is available for static and dynamic LAGs.
• Only a LAG can be a member of a failover group.
• You can congure shared LAG state tracking on one side of a link or on both sides.
• If a LAG that is part of a failover group is deleted, the failover group is deleted.
• If a LAG moves to the Down state due to this feature, its members may still be in the Up state.
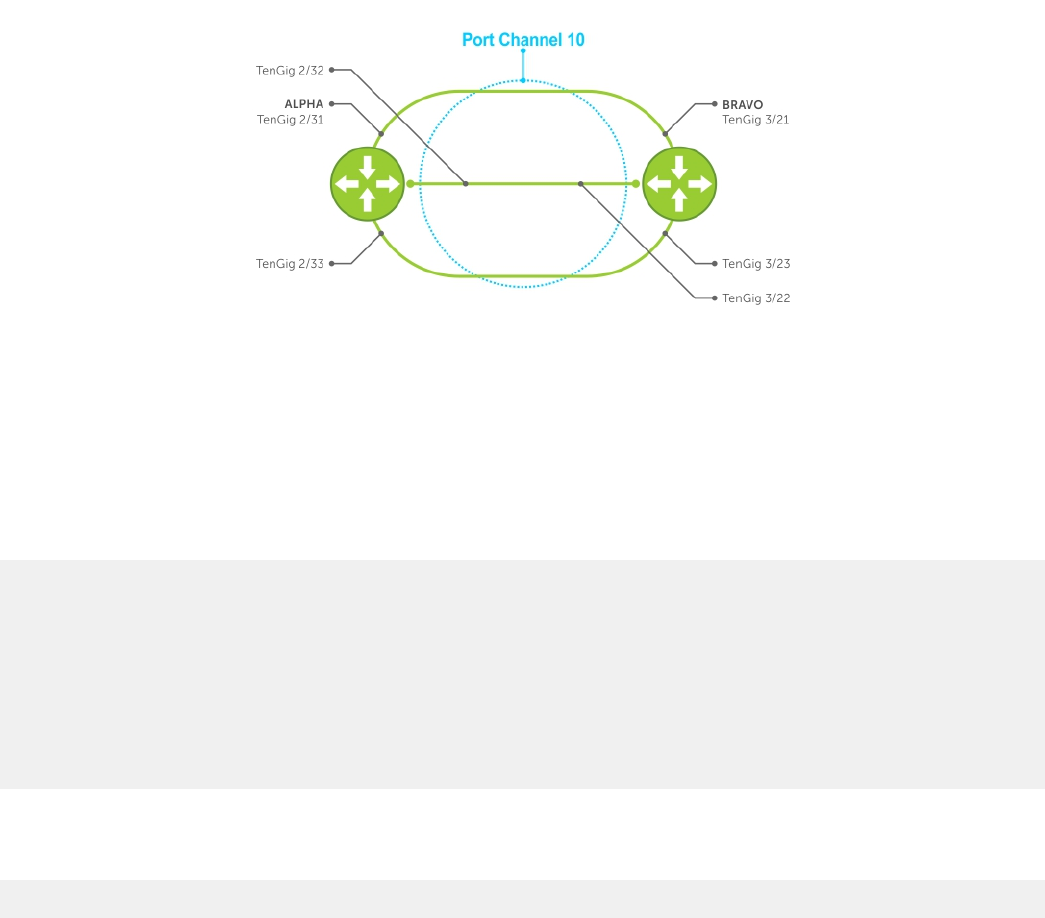
LACP Basic Conguration Example
The screenshots in this section are based on the following example topology. Two routers are named ALPHA and BRAVO, and their
hostname prompts reect those names.
Figure 54. LACP Basic Conguration Example
Congure a LAG on ALPHA
The following example creates a LAG on ALPHA.
Example of Conguring a LAG
Alpha(conf)#interface port-channel 10
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#no ip address
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#switchport
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#no shutdown
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#show config
!
interface Port-channel 10
no ip address
switchport
no shutdown
!
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#
Example of Viewing a LAG Port Conguration
The following example inspects a LAG port conguration on ALPHA.
Alpha#sh int GigabitEthernet 2/31
GigabitEthernet 2/31 is up, line protocol is up
450
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)










