Users Guide
FIP Snooping on Ethernet Bridges
In a converged Ethernet network, intermediate Ethernet bridges can snoop on FIP packets during the login process on an FCF. Then, using
ACLs, a transit bridge can permit only authorized FCoE trac to be transmitted between an FCoE end-device and an FCF. An Ethernet
bridge that provides these functions is called a FIP snooping bridge (FSB).
On a FIP snooping bridge, ACLs are created dynamically as FIP login frames are processed. The ACLs are installed on switch ports
congured for the following port modes:
• ENode mode for server-facing ports
• FCF mode for a trusted port directly connected to an FCF
You must enable FIP snooping on an Aggregator and congure the FIP snooping parameters. When you enable FIP snooping, all ports on
the switch by default become ENode ports.
Dynamic ACL generation on an Aggregator operating as a FIP snooping bridge functions as follows:
• Global ACLs are applied on server-facing ENode ports.
• Port-based ACLs are applied on ports directly connected to an FCF and on server-facing ENode ports.
• Port-based ACLs take precedence over global ACLs.
• FCoE-generated ACLs take precedence over user-congured ACLs. A user-congured ACL entry cannot deny FCoE and FIP snooping
frames.
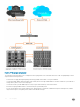
The below illustration depicts an Aggregator used as a FIP snooping bridge in a converged Ethernet network. The ToR switch operates as
an FCF for FCoE trac. Converged LAN and SAN trac is transmitted between the ToR switch and an Aggregator. The Aggregator
operates as a lossless FIP snooping bridge to transparently forward FCoE frames between the ENode servers and the FCF switch.
FIP Snooping
77