CLI Guide
Revised command
omconfig chassis volts index=3
minwarnthresh=3.300
When you type the revised command with three decimal points, you receive another error message:
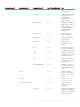
Table 3. Error messages for commands with three decimals
Message
Error! This voltage probe min warning
threshold must be between 11.400 and 12.480.
Revised command
omconfig chassis volts index=3
minwarnthresh=11.500
Message
Voltage probe warning threshold(s) set
successfully.
Scripting And Comparing Using CLI
The Server Administrator CLI allows administrators to write batch programs for the operating system. For an enterprise with many systems,
an administrator could write a conguration script that species the warning thresholds for each major component of a system and also
species a set of actions that the administrator wants each system to take in case of a warning or failure event. In most critical cases, the
administrator could write a script so that the system shuts down to prevent damage. The administrator could then distribute and execute
the script to many managed systems at the same time. Such a scenario facilitates conguring any number of new systems acquired by a
company and makes implementation of new system administration policies easier across many existing systems that require re-
conguration.
A similar scenario is used to populate a large number of newly acquired systems with detailed asset information. Much of the information
are the same, such as the manufacturer or lessor of the system, whether support for the system is outsourced, name of the company
providing insurance for the system, method of depreciation, and so on. Any variable that is common to all systems is scripted, sent to all
managed systems, and executed. Asset information that is unique to a system is scripted as a group and sent to that managed node for
execution. For example, a script could specify values for all unique variables such as the owner, primary user phone number, asset tag, and
so on. Scripts to populate unique values would set all unique variables at once rather than one by one through the system's command line.
In many cases, the CLI allows a user with a very well-dened task in mind to retrieve information about the system rapidly. If a user wants
to review a comprehensive summary of all system components and save that summary information to a le for comparison with later
system states, the CLI is ideal.
Using CLI commands, administrators can write batch programs or scripts to execute at specic times. When these programs are executed,
they can capture reports on components of interest, such as fan RPMs during periods of highest system usage compared with the same
measurements at times of lowest system usage. Command results are routed to a le for later analysis. Reports can help administrators
gain information that are used to adjust usage patterns, to justify purchasing new system resources, or to focus on the health of a problem
component.
Command syntax overview
Commands vary in complexity. The simplest command has only command level 1. The omhelp command is a simple command. When you
type omhelp, a list of the main CLI commands is displayed.
The next level of complexity includes commands that contain command levels 1 and 2. All of the about commands are examples of
command level 2 complexity. The omcong about and omreport about commands display a very brief summary. The summary shows
version information for the systems management software installed on the system; for example, Server Administrator 1.x.
Some commands have command level 1 and command level 2 and one name=value pair. Consider the following example command that
instructs Server Administrator for more details about the environment for Server Administrator:
omreport about details=true
12
Introduction