Deployment Guide
Table Of Contents
- Dell OpenManage Deployment Toolkit Version 5.5 Command Line Interface Reference Guide
- Introduction
- Command Syntax Overview
- DTK Seamless package
- SYSCFG
- Features
- SYSCFG General Options
- SYSCFG For BIOS Configuration
- SYSCFG BIOS commands
- BIOS Option Settings
- Boot Settings
- Integrated Devices
- Network Settings
- Memory Settings
- Miscellaneous Settings
- One-Time Boot
- Processor Settings
- SATA Settings
- Serial Communication
- Slot Disablement
- System Information
- System Profile Settings
- System Security
- UEFI Boot Settings
- DTKTORACADM
- SYSCFG Options On PowerEdge Systems Prior To PowerEdge 12G Systems
- Sub Options And Arguments For power Option
- Sub Options And Arguments For tcm Option
- Sub Options And Arguments For tpm Option
- SYSCFG For BMC And Remote Access Controller Configuration
- bmcversion
- chassistype*
- clearsel*
- controlpanelaccess
- deviceguid*
- encryptkey
- fiberchannel
- floppy
- formfactor
- hddfailover
- hpcmode
- htassist
- idecdrom
- idracgui
- lpt
- memdynamicpower
- memintleave
- memremap
- mouse
- noraidprompt*
- oldsetuppwd
- oldsyspwd
- opticaldrivectrl
- remflashmedia
- serial1
- serial2
- slotname
- sma
- sysrev*
- usb
- usbflash
- vflash
- identify
- idracversion
- kvmstatusonlcd
- lancfgparams
- lanchannelaccess
- lanchannelinfo
- lanuseraccess
- lcd1
- lcd2
- loaddefaults*
- nextboot
- nmibutton
- passwordaction
- pefcfgparams
- powerbutton
- powerctl
- racreset*
- serialcfgparams
- serialchannelaccess
- serialchannelinfo
- serialuseraccess
- solaction
- solcfgparams
- ssninfo
- useraction
- username
- version*
- virutualmedia
- SYSCFG For State Configuration
- SYSCFG for System Configuration
- SYSCFG For IPv6 Configuration
- PCI Reporting
- RAIDCFG
- Features
- Supported RAID Controllers
- RAIDCFG Options And Arguments
- RAID Configuration Utility Options And Arguments
- General Help
- Enumerating RAID Controllers
- Creating Virtual Disks
- Enumerating Array Disks
- Blinking And Unblinking Array Disks
- Enumerating Virtual Disks
- Deleting Virtual Disks
- Increasing Virtual Disk Size
- Setting A Virtual Disk As Bootable Virtual Disk
- Blinking And Unblinking Virtual Disks
- Setting Virtual Disk Name
- Setting Environment Variables
- RAID Replication Options
- Assigning, Unassigning, And Listing Global Hot Spares
- Importing And Clearing Foreign Configurations
- Importing Secured Foreign Configuration
- Displaying Foreign Key Ids
- Creating Encryption Key
- Changing Encryption Key
- Deleting Encryption Key
- Configuring Physical Disk Rebuild
- Configuring Array Disk As RAID
- Configuring Physical Disk State
- Replacing Physical Disk Of A Virtual Disk
- Consistency check for virtual disk
- Erasing Encrypted Physical Disk
- Discarding Preserved Cache
- Initializing Virtual Disks
- Resetting The Controller
- Enabling And Disabling Persistent Dedicated Hot Spares
- Setting And Displaying The PCIe Link Speed
- Setting Boot Mode
- Configuring Auto Import
- Miscellaneous Options
- Quick Reference To RAIDCFG Commands
- UPINIT
- Messages And Codes
- BMC Platform Events Filter Alert Messages
- Sample File Formats
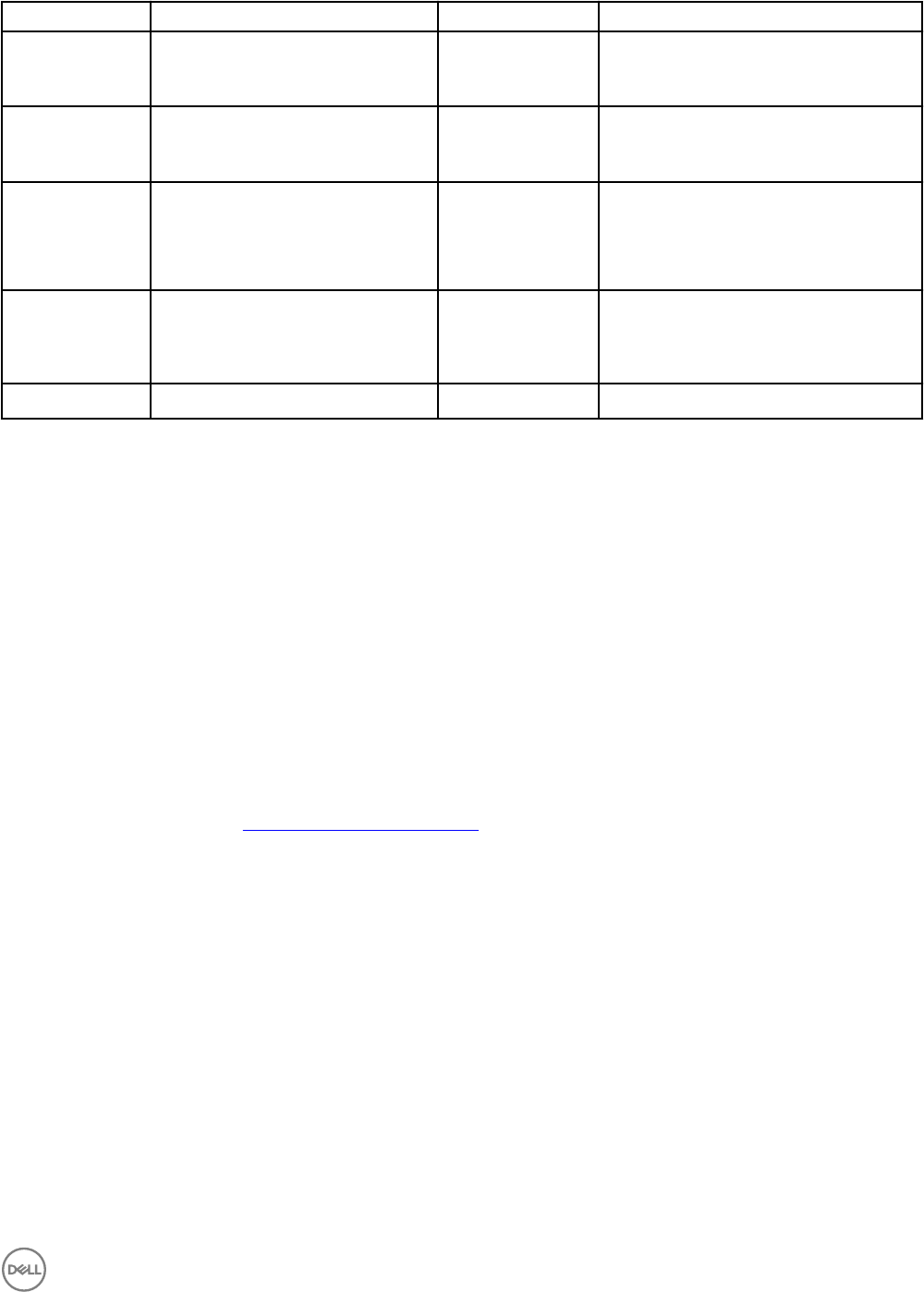
Option Sub-option Valid Arguments Description
--ipsrcv6=auto
NA
Automatically congures the IPv6 addresses.
A:>syscfg lcpv6 --ipsrcv6=auto
--dnssrcv6=auto
NA
Automatically congures the DNS address.
A:>syscfg lcpv6 --dnssrcv6=auto
--dnssrcv6=static
--
dnsserver1v6=<ipv6dnsserver
1address>
NA
Allows you to manually set the DNS address.
--
linklocaladdripv6=<linkloca
laddripv6>
Allows you to view IPv6 addresses.
A:>syscfg lcpv6 --
linklocaladdripv6=134.56.45.233
--gatewayv6=<gatewayv6>
Allows you to view IP gatewayv6 address.
PCI Reporting
The scan of the PCI bus uses a le to resolve PCI vendor and device codes to vendor information strings. The format of the PCI
output is as follows:
PCI Bus: 2, Device: 4, Function: 0
Vendor: 8086 - Intel Corp.
Device: 1229 - 82557/8/9 [Ethernet Pro 100]
Sub Vendor:8086 - Intel Corp.
Sub Device:1017 - EtherExpress PRO/100+ Dual Port Server Adapter
Slot: 01
Class: 02 - Network
SubClass: 00 - Ethernet
If the le for vendor resolution is not present, the utility prints Unknown next to a vendor name. If the le for environment variable
names is not present, the utility fails the environment variable operation.
The pci.ids le is located at \DELL\TOOLKIT\TOOLS on Windows systems and /opt/dell/toolkit/bin on Linux systems. For more
information and examples, see the Options For System Conguration.
Environment Variable File
The environment variable le can be used for discovering and recording system information to environment variables. The le
consists of several sections with .ini format that map PCI vendor/device numbers to environment variable values. The environment
variable le is sys.ini in \DELL\TOOLKIT\TOOLS on Windows systems and on Linux systems, you can nd it in /opt/dell/toolkit/bin .
For example, the [DELLNIC] section header designates that an environment variable named dellnic1 should be set to the
value of the name or value pair whose name matches the NIC's vendor or device number. If multiple NICs are present on a system,
the environment variables are numbered sequentially: dellnic1, dellnic2 , and so on
Environmental Variable File Excerpt (sys.ini)
145










