Deployment Guide
17 Leaf-Spine Deployment and Best Practices Guide | Version 1.0
6 Layer 3 configuration planning
6.1 BGP ASN configuration
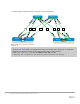
When EBGP is used, an autonomous system number (ASN) is assigned to each switch. Valid private, 2-byte
ASNs range from 64512 through 65534. Figure 11 shows the ASN assignments used for leaf and spine
switches in the BGP examples in this guide.
Rack 2Rack 1
64601 64602
VLT i
VLT i
64702
64701
64703
64704
BGP ASN assignments
ASNs should follow a logical pattern for ease of administration and allow for growth as additional leaf and
spine switches are added. In this example, an ASN with a "6" in the hundreds place represents a spine switch
(e.g. 64601) and an ASN with a "7" in the hundreds place represents a leaf switch (e.g. 64701).
6.2 IP addressing
Establishing a logical, scalable IP address scheme is important before deploying a leaf-spine topology. This
section covers the IP addressing used in the layer 3 examples in this guide.
6.2.1 Loopback addresses
Loopback addresses may be used as router IDs when configuring routing protocols. As with ASNs, loopback
addresses should follow a logical pattern that will make it easier for administrators to manage the network and
allow for growth. Figure 12 shows the loopback addresses used as router IDs in the BGP and OSPF
examples in this guide.