White Papers
Table Of Contents
- Executive Summary (updated May 2011)
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Dell NFS Storage Solution Technical Overview
- 3. NFS Storage Solution with High Availability
- 4. Evaluation
- 5. Performance Benchmark Results (updated May 2011)
- 6. Comparison of the NSS Solution Offerings
- 7. Conclusion
- 8. References
- Appendix A: NSS-HA Recipe (updated May 2011)
- A.1. Pre-install preparation
- A.2. Server side hardware set-up
- A.3. Initial software configuration on each PowerEdge R710
- A.4. Performance tuning on the server
- A.5. Storage hardware set-up
- A.6. Storage Configuration
- A.7. NSS HA Cluster setup
- A.8. Quick test of HA set-up
- A.9. Useful commands and references
- A.10. Performance tuning on clients (updated May 2011)
- A.11. Example scripts and configuration files
- Appendix B: Medium to Large Configuration Upgrade
- Appendix C: Benchmarks and Test Tools
Dell HPC NFS Storage Solution - High Availability Configurations
Page 22
As mentioned before, all performance benchmarking was done in a failure-free situation to understand
the maximum capability of the solution.
5.1. InfiniBand Sequential Reads and Writes
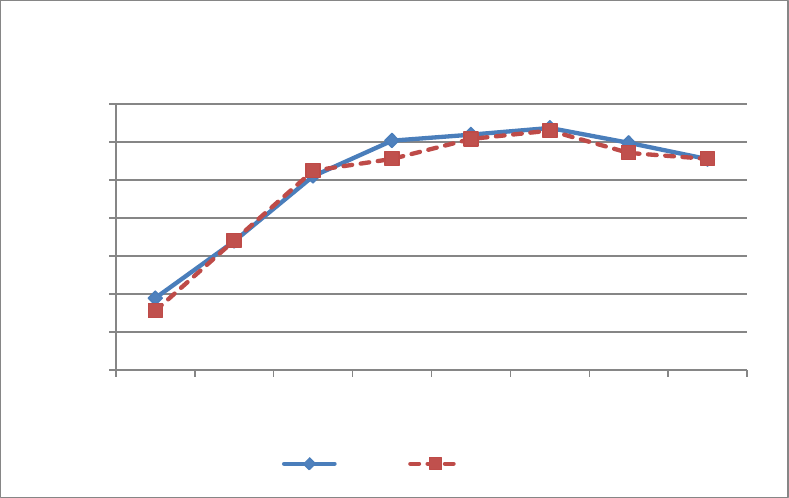
The results of the IPoIB sequential write tests are shown in 8. The figure shows the aggregate
throughput that can be achieved when a number of clients are simultaneously writing to the
storage over the InfiniBand fabric. Results are presented for the NSS-HA Medium and Large
configurations. The results show that the peak performance of the solution is about 1260 MB/s.
Both the Medium and the Large configuration provide similar bandwidth. In the Medium
configuration, the storage controller cache is used by two virtual disks, while in Large configuration
the cache is shared across four virtual disks. The disadvantage of the smaller cache per virtual
disks balances out the advantage of the additional disk spindles in the Large configuration,
resulting in similar performance across the two configurations. Additionally, the NFS sync export
option and cache mirroring between the RAID controllers on the MD3200 limit the write
performance of the solution. The data shows that in both configurations, there is a drop in
performance after a certain number of clients. This is due to the fact that the storage arrays are
populated with NearLine SAS drives and NFS concurrent write traffic causes the disks to become
seek bound causing the decline in performance.
Figure 8 - IPoIB Large Sequential Write Performance
IPoIB sequential read results are shown in Figure 9. The figure shows the aggregate throughput that
can be achieved when a number of clients are simultaneously reading from the storage over the
InfiniBand fabric. The results show that the peak read performance of the NSS-HA Large solution is
about 2430 MB/s. The Medium configuration peaks at 1510 MB/second. The Large configuration has
double the number of disks than the Medium configuration and the additional disk spindles help the
read performance. The solution scales well and the saturation point is not observed with even 64
clients.
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1 2 4 8 16 32 48 64
Througput: MB/sec
Number of clients
IPoIB Large sequential writes
Large Medium










