Reference Guide
Technical support and resources
19 Reference Architecture of Dell EMC Ready Solution for HPC Life Sciences | Document 309
3.2.1 SOAPdenovo2
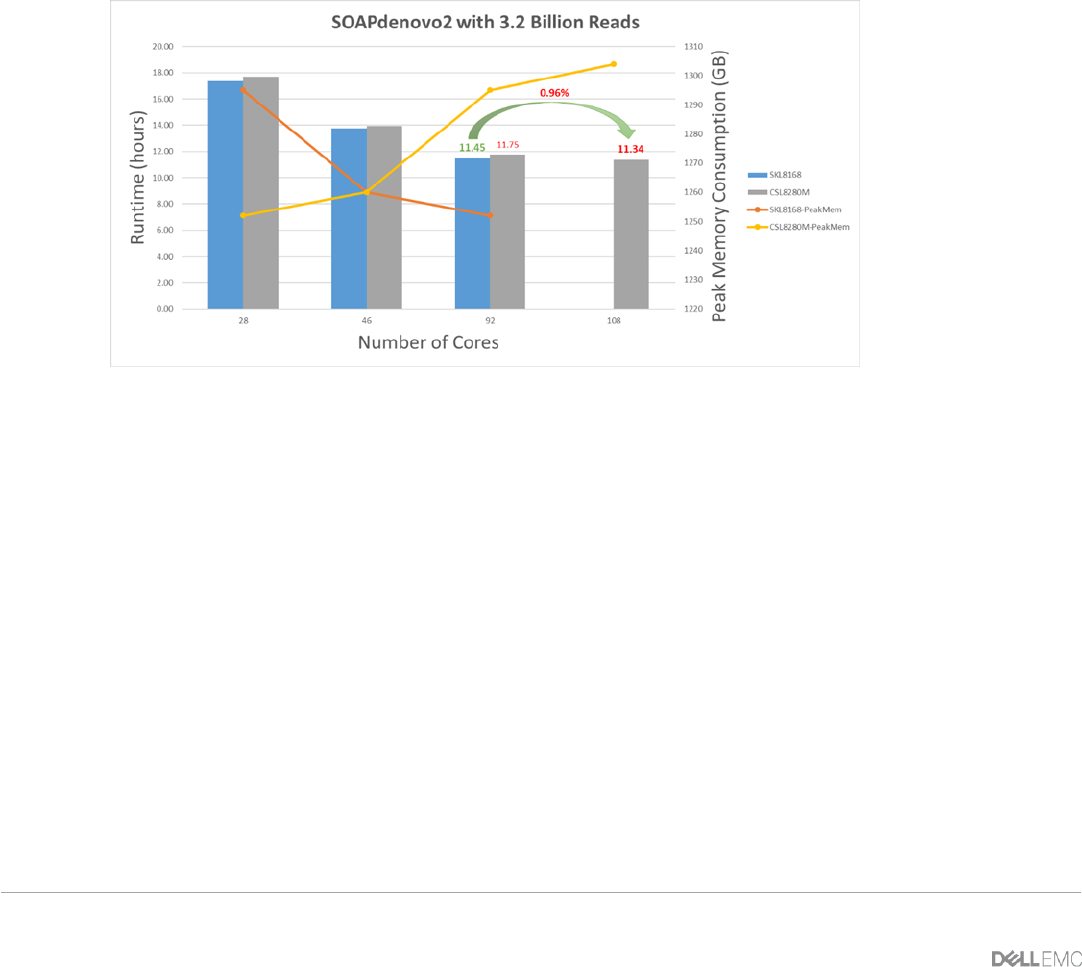
The maximum performance gain by upgrading from 8168 to 8280M is roughly 1% as shown in 92 cores of
8168 versus 108 cores of 8280M comparisons from Figure 9. For the test, one core per CPU was unused and
allocated for the operating system and other housekeeping operations. Although the results show that
Cascade Lake 8280M is slower by 2% on average with various number of cores used, the comparisons
between 92 cores of 8168 and 108 cores of 8280M confirmed that Cascade Lake 8280M performs slightly
better than Skylake 8168.
SOAPdenovo2 seems to be memory bandwidth bounded. The peak memory consumption is constantly rising
as more cores are used for a process with the 1 DPC configuration on 2nd Gen CPU, while the peak memory
consumption is declining with 2 DPC configuration on 1st Gen CPU. As shown Figure 9 in our previously
published blog, memory bandwidth can differ by 11% between 1 DPC and 2 DPC configurations with the
same type of dual ranked DIMMs. To come to a more definitive conclusion, further tests are required with the
2 DPC configuration (DDR4-2666) on 2nd Gen 8280M CPU.
Figure 9 Runtime and peak memory consumption plots for SOAPdenovo2 with various number of cores
3.2.2 SPAdes
Cascade 8280M performs better across the tests with various number of cores, and 5% better performance is
achievable in a comparison between 92-core 8168 and 108-core 8280M as shown in Figure 10. The patterns
of peak memory consumption are nearly similar between the two CPUs; however, 8280M with the 1 DPC
configuration shows higher memory consumptions than 8168 with the 2 DPC configuration. Although memory
bandwidth does not seem to be critical as we can see from SOAPdenovo2 tests, the 2 DPC configuration with
DDR4-2666 MHz can be a better configuration for de novo assembly.










