Reference Guide
Performance evaluation and analysis
16 Reference Architecture of Dell EMC Ready Solution for HPC Life Sciences | Document 309
3.1.1 Single sample test
Three 2nd generation CPUs are picked to compare with four 1st generation CPUs, listed in Table 1. The
purpose of this single sample test is to determine suitable CPUs for next generation sequencing (NGS) data
analysis. All steps described in Figure 10 are tested on the Dell PowerEdge R640 with 50x whole human
genome listed in Table 1 below.
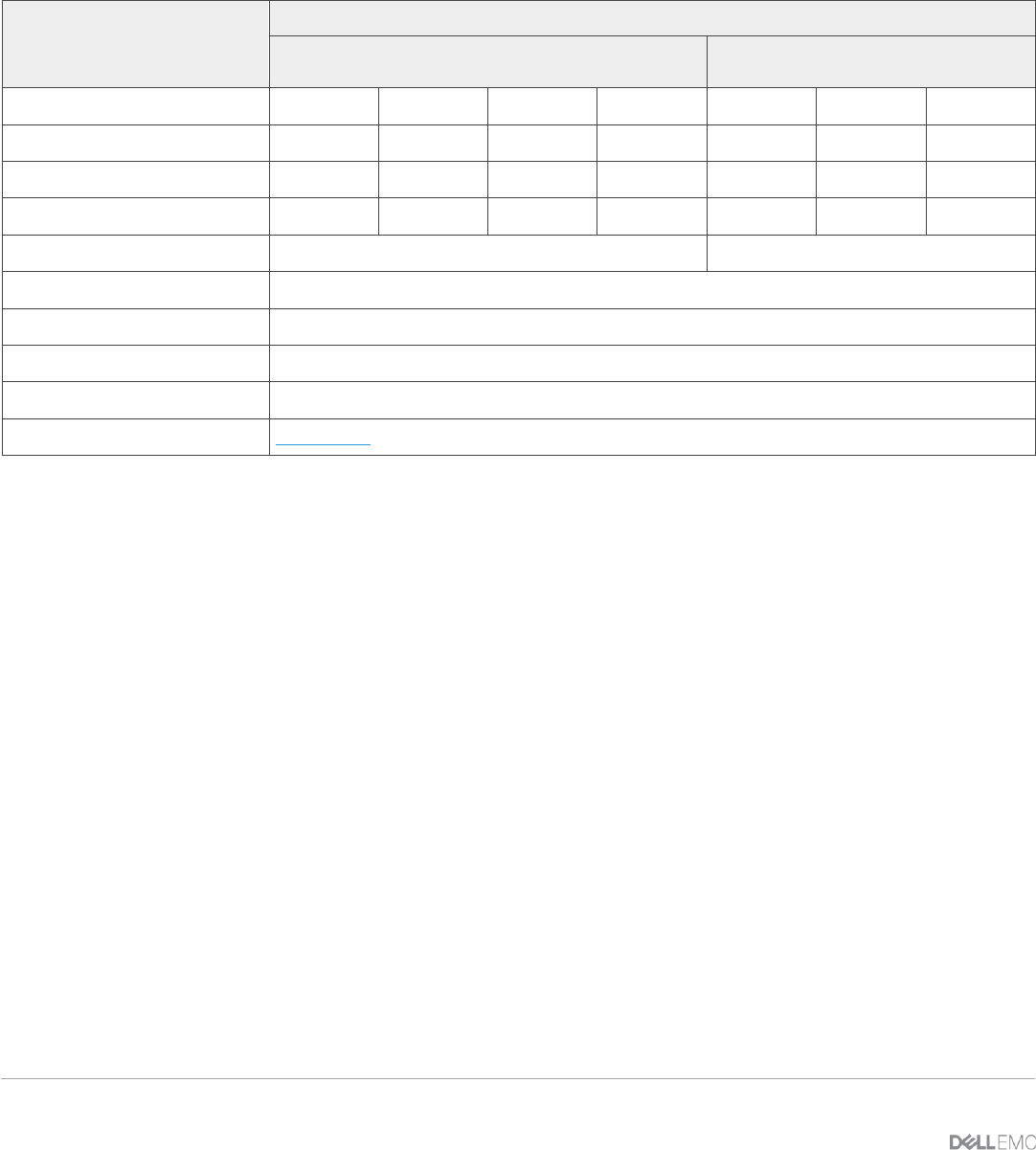
Table 1 Test configuration for single sample variant calling
Dell PowerEdge R640
Intel 1
st
Gen Xeon Scalable Processors
Intel 2
nd
Gen Xeon Scalable
Processors
CPU
2x 6154
2x 6148
2x 6152
2x 6138
2x 6248
2x 6252
2x 6230
Base Frequency (GHz)
3.0
2.4
2.1
2.0
2.5
2.1
2.1
Number of Cores
18
20
22
20
20
24
20
TDP (W)
200
150
140
140
150
125
125
Memory
24x 16GB DDR4-2666MHz, 2 DPC
12x 32GB DDR4-2933MHz, 1 DPC
Storage
10x 1.2TB SAS 12 Gbps, 10K in RAID 0
System Bios
2.1.3
Kernel
3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64
OS
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.6
Sequence Reads
ERR194161, 50x Whole Human Genome for variant calling
As shown in Figure 7, each step behaves quite differently on each CPU that was tested, and the performance
differences among different steps with the tested CPUs ranges from 0.61% to 46.34%. All three 2
nd
Gen
CPUs tested show slightly better performance for most steps in the pipeline. Although 6154 is fastest among
tested CPUs, 6154 was not recommended for customers who want to achieve the highest throughput. The
fourth step, realigning insertion and deletion step runs on a single core as GATK was not written to utilize
multiple cores, and 6248 and 6230 outperformed. Surprisingly, 6230 performs better than 6248 in the fourth
step.










