Reference Guide
34 Management Networks for Dell EMC Networking
B Connecting to upstream management
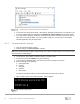
Uplink ports on the management switch are used for connecting to the upstream management network. This
network can consist of one or more NMS, management stations, and traffic between them and the managed
devices. Uplink ports are identified as any Ethernet port that is not the lowest bandwidth on the switch (not
including any OOB port). A 10GbE port on a switch which primarily has 1GbE ports is considered an uplink
port, and a 100GbE port on a switch which primarily has 10GbE ports is considered an uplink port. Uplink
ports are usually the highest bandwidth ports on a switch.
Configuring these uplinks to connect to upstream management is the same whether the management network
is in-band or OOB. With OOB management, the OOB port on each managed device is attached to one of the
lower bandwidth ports on the OOB management switch. The management switch itself becomes in-band as
far as the management network is concerned. Provide an IP address to the management VLAN on any
switch, dedicated OOB or not, to allow for routing and troubleshooting.
Optionally, the OOB port on each management switch may be used to allow for a second tier OOB network.
The management traffic is routed between the first and second tiers as required.
Note: If using an OOB port, it must be on a different IP subnet than the in-band ports of the same switch.
OOB
iDRAC
iDRAC
OOB
Server
Server
Chassis
(MX, FX2, etc.)
Other device
Leaf Switch
Leaf Switch
OOB
OOB
Upstream
Management Network
Upstream
Production Network
Server
Server
Chassis
(MX, FX2, etc.)
Other device
Leaf Switch
Leaf Switch
Production VLANs
Management VLANs
Upstream
Networks
OOB management
In-band management
Topologies showing separation of management and production networks