Users Guide
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 SmartFabric Services for PowerEdge MX: An overview
- 3 SmartFabric mode requirements, guidelines, and restrictions
- 3.1 Create multi-chassis management group
- 3.2 Upstream network requirements
- 3.3 VLAN scaling guidelines
- 3.4 Configuring port speed and breakout
- 3.5 Switch slot placement for SmartFabric mode
- 3.6 Switch-to-Switch cabling
- 3.7 NIC teaming guidelines
- 3.8 Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) behavior
- 3.9 Other restrictions and guidelines
- 4 Creating a SmartFabric
- 4.1 Physically cable MX chassis and upstream switches
- 4.2 Define VLANs
- 4.3 Create the SmartFabric
- 4.4 Configure uplink port speed or breakout, if needed
- 4.5 Create Ethernet uplink
- 4.6 Configure Fibre Channel universal ports
- 4.7 Create Fibre Channel uplinks
- 4.8 Configuring the upstream switch and connect uplink cables
- 5 Deploying a server
- 6 SmartFabric operations
- 7 Switch operations
- 8 Validating the SmartFabric deployment
- 9 SmartFabric troubleshooting
- 9.1 Troubleshooting errors encountered for port group breakout
- 9.2 Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- 9.3 Verify VLT/vPC configuration on upstream switches
- 9.4 Discovery of FEM and compute sleds
- 9.5 Troubleshooting uplink errors
- 9.6 Troubleshooting FC/FCoE
- 9.7 SmartFabric Services – Troubleshooting commands
- 10 Uplink configuration scenarios
- 10.1 Scenario 1 - SmartFabric deployment with Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON upstream switches
- 10.2 Scenario 2 - SmartFabric connected to Cisco Nexus 3232C switches
- 10.3 Scenario 3: Connect MX9116n FSE to Fibre Channel storage - NPIV Proxy Gateway mode
- 10.4 Scenario 4: Connect MX9116n FSE to Fibre Channel storage - FC Direct Attach
- 10.5 Scenario 5: Connect MX5108n to Fibre Channel storage - FSB
- 10.6 Scenario 6: Configure Boot from SAN
- A Hardware used in this document
- B Dell EMC Unity information
- C Additional information
- D Validated components
- E Technical resources
- F Support and feedback
42 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
5.3 Create identity pools
Dell EMC recommends the use of identity pools. Virtual identity pools are used in conjunction with server
templates to automate network onboarding of compute sleds. Follow these steps to create an ID pool:
1. Open the OME-M console.
2. From the navigation menu, click Configure, then click Identity Pools.
3. In the Network panel, click Create. The Create Identity Pool window displays.
4. Type Ethernet CNA into the Pool Name box.
5. Optionally, enter a description in the Description box.
6. Click Next.
7. Click to select the Include Ethernet Virtual MAC Addresses option.
8. In the Starting MAC Address box, type a unique MAC address (e.g.
06:3C:F9:A4:CC:00).
9. Type 255 in the Number of Virtual MAC Identities box, click Next, then click Next
again.
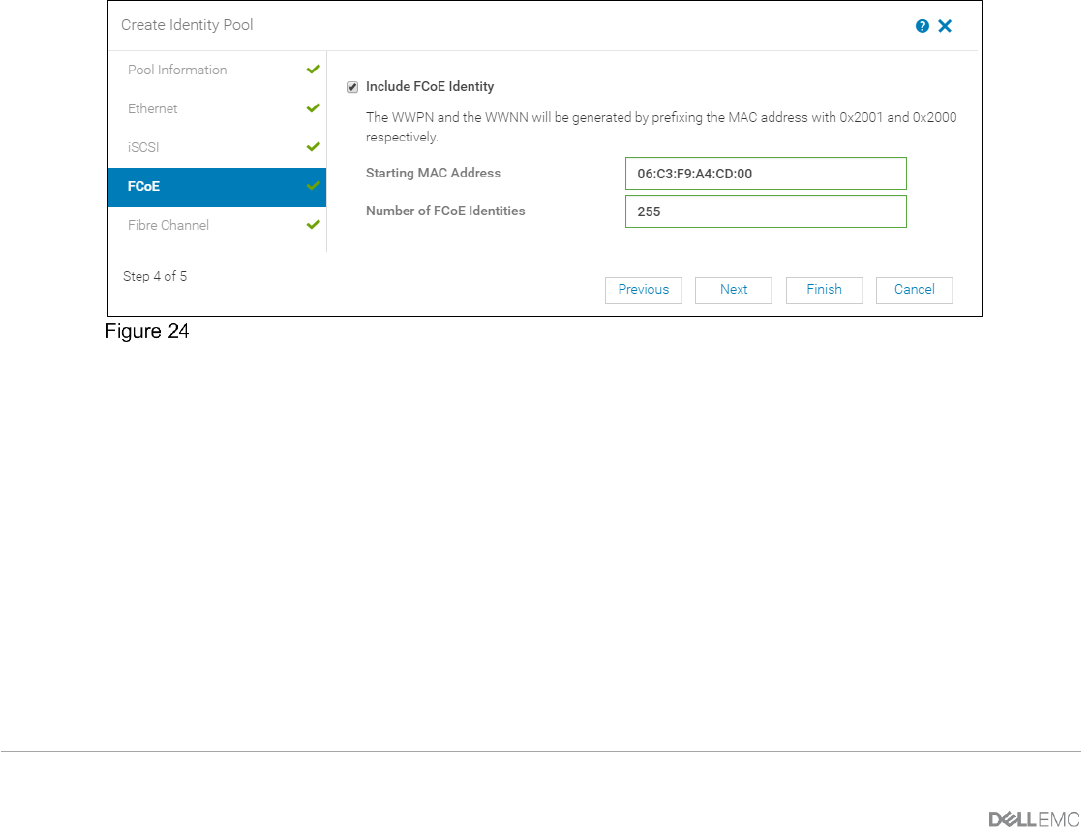
10. Select the Include FCoE Identity option if using FCoE
11. In the Starting MAC Address box, type a unique MAC address (e.g.
06:3C:F9:A4:CD:00).
12. Type 255 in the Number of FCoE identities box for FCoE scenarios.
Include FCoE Identity
13. Click Finish, then click Finish again.
5.4 Associate server template with networks – no FCoE
After successfully creating a new template, associate the template with a network:
1. From the Deploy pane, select the template to be associated with VLANs. In this example, MX740c
with Intel mezzanine server template is selected.
2. Click Edit Network.
3. In the Edit Network window, complete the following:
• Optionally, from the Identity Pool list, choose the desired identity pool. In this example,
Ethernet ID Pool is selected
• Optionally, from the NIC Teaming option, choose the desired NIC Teaming option.