Users Guide
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 SmartFabric Services for PowerEdge MX: An overview
- 3 SmartFabric mode requirements, guidelines, and restrictions
- 3.1 Create multi-chassis management group
- 3.2 Upstream network requirements
- 3.3 VLAN scaling guidelines
- 3.4 Configuring port speed and breakout
- 3.5 Switch slot placement for SmartFabric mode
- 3.6 Switch-to-Switch cabling
- 3.7 NIC teaming guidelines
- 3.8 Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) behavior
- 3.9 Other restrictions and guidelines
- 4 Creating a SmartFabric
- 4.1 Physically cable MX chassis and upstream switches
- 4.2 Define VLANs
- 4.3 Create the SmartFabric
- 4.4 Configure uplink port speed or breakout, if needed
- 4.5 Create Ethernet uplink
- 4.6 Configure Fibre Channel universal ports
- 4.7 Create Fibre Channel uplinks
- 4.8 Configuring the upstream switch and connect uplink cables
- 5 Deploying a server
- 6 SmartFabric operations
- 7 Switch operations
- 8 Validating the SmartFabric deployment
- 9 SmartFabric troubleshooting
- 9.1 Troubleshooting errors encountered for port group breakout
- 9.2 Troubleshooting Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
- 9.3 Verify VLT/vPC configuration on upstream switches
- 9.4 Discovery of FEM and compute sleds
- 9.5 Troubleshooting uplink errors
- 9.6 Troubleshooting FC/FCoE
- 9.7 SmartFabric Services – Troubleshooting commands
- 10 Uplink configuration scenarios
- 10.1 Scenario 1 - SmartFabric deployment with Dell EMC PowerSwitch Z9100-ON upstream switches
- 10.2 Scenario 2 - SmartFabric connected to Cisco Nexus 3232C switches
- 10.3 Scenario 3: Connect MX9116n FSE to Fibre Channel storage - NPIV Proxy Gateway mode
- 10.4 Scenario 4: Connect MX9116n FSE to Fibre Channel storage - FC Direct Attach
- 10.5 Scenario 5: Connect MX5108n to Fibre Channel storage - FSB
- 10.6 Scenario 6: Configure Boot from SAN
- A Hardware used in this document
- B Dell EMC Unity information
- C Additional information
- D Validated components
- E Technical resources
- F Support and feedback
18 Dell EMC PowerEdge MX SmartFabric Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
For more information on configuration and deployment, see Section 10.3.
2.6.2 Direct Attached (F_port)
Direct Attached mode, or F_port, is used when FC storage needs to be directly connected to the switch. The
switch supports the required services such as name server and zoning that are typical of FC switches.
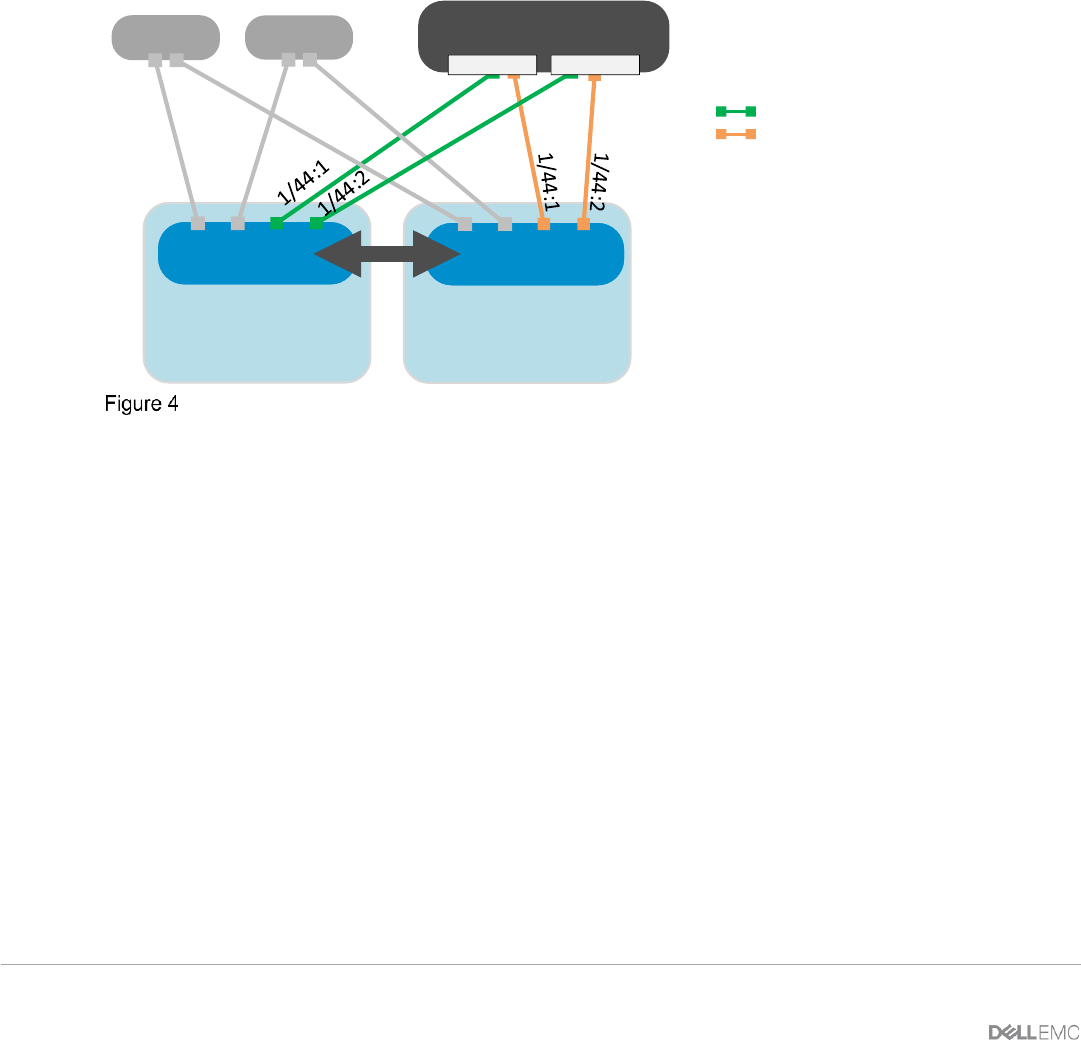
This example demonstrates Fibre Channel directly attaching to the Dell EMC Unity 500F storage array.
MX9116n FSE universal ports 44:1 and 44:2 are required for FC connections and operate in F_port mode,
which allows for an FC storage array to be connected directly to the MX9116n FSE. The uplink type enables
F_port functionality on the MX9116n unified ports, converting FCoE traffic to native FC traffic and passing that
traffic to a directly attached FC storage array.
This mode is supported only on the MX9116n FSE.
Unity 500F
MX9116n
(Leaf 2)
MX9116n
(Leaf 1)
VLT
MX7000
Spine 2
Spine 1
FC SAN B
Unity 500F
Controller A Controller B
chassis 1
MX7000
chassis 2
FC SAN A
Fibre Channel (F_Port) direct connect network to Dell EMC Unity
For more information on configuration and deployment, see Section 10.4.
2.6.3 FCoE (FSB)
FCoE Transit, or FSB mode is used when connecting PowerEdge MX to an upstream switch that accepts
FCoE and converts it to native FC, such as the Dell EMC PowerSwitch S4148U. This mode is typically used
when an existing FCoE infrastructure is in place that PowerEdge MX must connect to. In Figure 5, uplink type
enables NPG FC Gateway functionality on the MX9116n FSE unified ports, converting FCoE traffic to native
FC traffic on PowerSwitch S4148U-ON and passing that traffic to an external FC switch.
When operating in FSB mode, the switch snoops FIP packets on FCoE-enabled VLANs and discovers the
following information:
• End nodes (ENodes)
• Fibre Channel forwarders (FCFs)
• Connections between ENodes and FCFs
• Sessions between ENodes and FCFs
Using the discovered information, the switch installs ACL entries that provide security and point-to-point link
emulation.










