Users Guide
Table Of Contents
- Dell Migrate User's Guide
- Contents
- Introduction
- Data Migration
- Migrate and erase data from old PC
- Check the network settings
- Change the system locale
- Device discovery and prechecks
- Unsupported Windows version
- Applications to close before migrating
- Start Migrate
- Launch Data Assistant on your old PC
- Launch Migrate through SupportAssist on your new Dell PC
- Code verification
- Migrate multiple accounts
- Searching for files and settings
- Troubleshooting network disconnect issues during migration
- Create Data Assistant shortcut
- Select files to migrate
- Migration of file attributes
- Mapping the drives
- Migration progress
- Migration summary
- Migration completion
- Retry or finish the migration process after it was canceled
- Troubleshooting migration failure
- Troubleshooting when migration is completed with warnings
- Issues while launching Data Assistant on old PC
- Data Erase
- Perform erase without migration
- Prechecks for erase
- Disabling BitLocker
- Troubleshooting hard disk failure issues
- Troubleshooting when external storage is found
- Set reminder
- Levels of erase
- Reset SupportAssist OS Recovery
- Windows reset Windows 10
- Prerequisites for resetting Windows 8.1
- Troubleshooting Windows reset
- Manual Reboot
- Running Dell Migrate on desktop PCs
- Tips for faster data migration
- Migration of OneDrive files
all your files from the old PC to the new PC, the file attributes are also migrated along with the files which ensures that the
same sort order is maintained for all the files based on criteria such as creation time, modification time, and so on.
The file attributes which are migrated along with a file are:
● Timestamp
○ Created time—the time at which the file was created on the old PC is applied to the file after it is copied to the new PC.
○ Modified time—the time at which the file was updated, or some content of the file was changed on the old PC. The
same timestamp is applied to the file after it is copied to the new PC.
The file timestamp is helpful when you want to sort the files by the date of creation and date of modification.
NOTE: The last access time of the file is not updated because it is dynamic and it gets updated when a file is accessed.
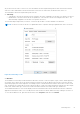
Figure 80. Timestamp of a file
● Metadata
The metadata of a file usually contains information about the contents of a file. Description, origin, content, and file properties
are common across all the files. A file can have properties that are more specific based on the file type. Some files can have
a particular property that others might lack. For example, a photo contains information related to the location of where it was
shot, the aperture set, and the device used to capture the photo. A video file contains information related to the video length,
frame rates, and the audio type. A music file contains information related to the media, audio type, and bit rates.
The metadata information is often used to display extra useful information about the file and annotate the files on different
applications that may be used to view or modify the files such as Microsoft Word, Adobe Photoshop, editing tools, and so on.
To view the metadata of a file, right-click the file name, select Properties, and then select Details.
Data Migration
51