Users Guide
Table Of Contents
- Table of Contents
- 1 Regulatory and Safety Approvals
- 2 Functional Description
- 3 Network Link and Activity Indication
- 4 Features
- 4.1 Software and Hardware Features
- 4.2 Virtualization Features
- 4.3 VXLAN
- 4.4 NVGRE/GRE/IP-in-IP/Geneve
- 4.5 Stateless Offloads
- 4.6 Priority Flow Control
- 4.7 Virtualization Offload
- 4.8 SR-IOV
- 4.9 Network Partitioning (NPAR)
- 4.10 Security
- 4.11 RDMA over Converged Ethernet – RoCE
- 4.12 VMWare Enhanced Networking Stack (ENS)
- 4.13 Supported Combinations
- 4.14 Unsupported Combinations
- 5 Installing the Hardware
- 6 Software Packages and Installation
- 7 Updating the Firmware
- 8 Link Aggregation
- 9 System-Level Configuration
- 10 PXE Boot
- 11 SR-IOV – Configuration and Use Case Examples
- 12 NPAR – Configuration and Use Case Example
- 13 Tunneling Configuration Examples
- 14 RoCE – Configuration and Use Case Examples
- 15 DCBX – Data Center Bridging
- 16 DPDK – Configuration and Use Case Examples
- Revision History
Broadcom NetXtreme-E-UG304-2CS
125
NetXtreme-E User Guide User Guide for Dell Platforms
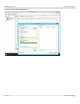
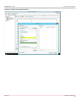
Figure 43: Drive Mapping
Each of the network drives generate 16 RDMA connections for a total of 112 with seven drives.
14.3.1.6 Traffic Generation
To exercise all 16 RDMA connections simultaneously using a different traffic generation tool:
If MLTT (License Software) is being used:
– Change the number of thread counts from 1 to 16. This ensures that all 16 channels have traffic running.
If Diskspd (freeware and successor to SQLIO) is being used:
– Use a combination of the following two parameters which produce a product of 16, for example:
-o2 -t8, -o4 -t4, or -o1 -t16
-o: Outstanding I/O request. This is your queue depth.
-t: Number of threads per file.
14.3.1.7 Verifying RDMA
To verify RDMA:
Create a file share on the remote system and open that share using Windows Explorer. To avoid a hard disk read/write speed
bottleneck, a RAM disk is recommended as the network share under test.
1. From PowerShell, run the following commands:
Get-SmbMultichannelConnection | fl *RDMA*
ClientRdmaCapable : True
ServerRdmaCapable : True
2. If both client and server show True, then any file transfers over this SMB connection use SMB.
3. The following commands can be used to enable/disable SMB Multichannel:
Server Side:
– Enable – Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableMultiChannel $true
– Disable – Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableMultiChannel $false
Client Side:
– Enable – Set-SmbClientConfiguration -EnableMultiChannel $true
– Disable – Set-SmbClientConfiguration -EnableMultiChannel $false